* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viola systems building blocks
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
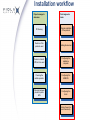
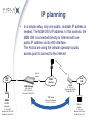
Viola Systems M2M solution installation Technical Support Installation Wireless Industry Solutions Which VPN to use? L2TP-VPN The L2TP (layer 2 tunneling protocol) commonly tunnels PPP (pointto-point protocol) and other upper layer protocols over IP (Internet protocol). L2TP packets are sent within UDP datagrams. SSH-VPN The SSH-VPN within Viola M2M solution is implemented with Open SSH. It uses cryptographic keys for authentication and encrypted transport layer. SSH packets are encapsulated inside TCP packets, which increases the protocol overhead. OpenVPN With Arctic 3G Gateway, the OpenVPN can be used. It is recommended for high security and small protocol overhead. Which VPN to use? The decision between the three VPN technologies would be made on basis of the following arguments: • • • L2TP-VPN provides faster round-trip times and less overhead but no data encryption SSH-VPN is safer with data encryption, but is also slower with more protocol overhead OpenVPN is generally recommended if available in the product. Installation workflow Project manager’s decisions Field engineer’s tasks IP Planning Physical installation of the products Decision of the products used Cabling the devices Decision of which VPN is to be used Configuring the installation computer Choosing the cellular operator Configuring the M2M GW Choosing between private or public APN Configuring the Arctic Testing the end-toend connectivity Installation checklist SIM cards for Arctics (with GPRS service enabled) PIN codes Access point name, username and password Private access point, if needed IP plan Passwords IT department for assistance, if present Manuals for every device related to the installation Cables; network, power, serial, etc. Antennas for Arctics, external antennas, if needed Power supplies and cables for each device Grounding, especially with shielded Ethernet and serial cables DIN rail mounting kits, if needed A computer for installation, e.g. laptop with Windows Installation procedure 1) Make sure that the previous checklist is checked through. 2) Gather the arrived equipment into one central place 3) Connect the cables 4) Configure the M2M GW and Arctic 5) Test the end-to-end connection locally (LAN connection) 6) Test the connection with GPRS/EDGE via M2M GW’s VPN tunnel locally 7) Place the Arctics to remote locations 8) Test the end-to-end connection IP planning • The IP networking plan plays very important role when setting up the Viola Systems M2M solution. It is a good practice to have a ready-made IP plan before continuing setting up the devices. • How many private and public IP addresses are needed depends on the number of M2M GWs and Arctics and the number of TCP/IP connected devices behind the Arctics, if any. • The private IP addresses are typically used in M2M GW's LAN, in VPN peer IPs and in Arctic's LAN. To avoid overlapping the network address space (thus causing possible routing problems), it is a good practice to use different class of private IP addresses for each set of addresses. IP planning • In a simple setup, only one public, routable IP address is needed; The M2M GW's IP address. In this scenario, the M2M GW is connected directly to Internet with one public IP address via its eth0 interface. The Arctics are using the cellular operator’s public access point to connect to the internet. Public IP address M2M LAN Eth1 Eth0 Arctic LAN GPRS Internet Arctic M2M Gateway IP: 10.10.10.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: VPN Eth0: Public IP Eth1: 192.168.0.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 VPN tunnel SCADA computer IP: 192.168.0.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 192.168.0.1 VPN peer IP addresses: 172.16.0.1:172.16.0.2 Ethernet device IP: 10.10.10.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 10.10.10.1 IP planning - II • The M2M GW is behind the firewall in a de-militarized zone (DMZ). Since the M2M GW has now a private IP address, there must be a way for connecting to it from Internet. • The connection from Internet to M2M GW is implemented with D-NAT and port forwarding. Also here the Arctics are using the cellular operator’s public access point for connecting to the Internet. DMZ IP: 192.168.1.1/24 M2M LAN Eth1 Eth0 M2M Gateway Eth0: 192.168.1.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 192.168.1.1 Public IP address GPRS Internet DMZ Arctic LAN Arctic Firewall IP: 10.10.11.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: VPN DNAT + port forwarding Eth1: 192.168.0.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 SCADA computer IP: 192.168.0.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 192.168.0.1 VPN tunnel VPN peer IP addresses: 172.16.0.3:172.16.0.4 Ethernet device IP: 10.10.11.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 10.10.10.1 IP planning - III • In some solutions it is decided to use the operator’s private access point in cellular network. This will always need a special contract with cellular operator. Using the private access point has a benefit in form of fixed IP addresses for each SIM card, but they’re also more expensive solution. Cellular operator’s VPN tunnel Static IP address associated to the SIM card 192.168.1.1 M2M LAN Eth1 Eth0 M2M Gateway DMZ network 192.168.1.0/24 Arctic LAN GPRS Private APN DMZ Arctic VPN Router IP: 10.10.10.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: VPN Eth0: 192.168.1.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 192.168.1.1 Eth1: 192.168.0.1 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 SCADA computer IP: 192.168.0.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 192.168.0.1 VPN tunnel VPN peer IP addresses: 172.16.0.1:172.16.0.2 Ethernet device IP: 10.10.10.2 Netmask: 255.255.255.0 Default GW: 10.10.10.1 Arctic’s connectors Arctic’s cables • Power supply cable The Arctic is shipped without a power supply. Viola Systems stocks suitable power supply with cable. • Ethernet cable If Arctic is connected to a computer, a cross-connect cable may be needed. A connection to a switch is done with direct cable. There’s also an Arctic Accessory Kit, (power supply, null modem cable, cross connected Ethernet cable). • Serial cable for console port When connecting a computer to Arctic’s console port, a crossconnected (i.e. null modem) cable is used. • Serial cable for RS1 application port (Gateways) The RS1 application port is always RS-232 and switchable between the console and application (plain data) port. • Serial cable for RS2 application port (Gateways) The RS2 port is configurable between RS-232 and RS-485/422 (full and half duplex are supported). • Antenna cable If the Arctic is located inside a cabinet, the signal level of cellular network may not be sufficient for operation when using the standard antenna. An external antenna with FME (female) Cabling the Arctic • The needed cables are depending on the application and the type of Arctic used • The Arctic Router products have only console serial port, where as the Gateway products have one serial port that can be switched between console or application port and one serial application port • Measured power consumptions (note: add a safety coefficient for power supply, recommended power supply’s output power is 5 Watts or more at 12 VDC) Vcc/V Inom/A Imax/A Pmax/W 6 0.40 0.48 2.88 12 0.20 0.25 2.00 24 0.10 0.13 3.12 Cabling the Arctic - II • Arctic’s Ethernet specifications: - 10 Base-T or 100 Base-T - Supports auto negotiation - Supports half duplex and full duplex • Commonly, the unshielded twisted pair CAT5e (UTP) cable is the best solution • If using shielded Ethernet connection, shield is connected to power supply ground (consider possible voltage potential differences) • Max cable length 100 meters (328 feet) between two active devices M2M GW’s connectors • M2M GW’s back panel Power supply connector Keyboard connector PS/2 VGA Connector 15-pin Port 1: eth0 WAN port Port 2: eth1 LAN port Cabling the M2M GW • • • • There are two Ethernet connectors at the back side of M2M GW. The left one (seen from the back side), marked with number "1" stamped to the right side of the connector, is the WAN port of M2M GW. It is the eth0 interface in M2M's graphical user interface. The second Ethernet connector, marked with number "2" is the LAN port of the M2M GW. It is the eth1 interface in M2M GW's GUI. There are also connectors for local console with analog VGA connector for monitor and USB port for local keyboard (do not use PS/2 connector for keyboard). The local console is helpful in some situations (e.g. if one has locked him/herself out from the Ethernet ports by firewall), but it is not usually needed, while initially configuring the M2M GW. The power supply of M2M GW is rated for input voltages between 100-240 Volts AC. The connector in M2M GW is standard IEC 60320, type C14 that accepts the C13 plug, the wall or rack socket connector type varies country by country.