* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.1 Angles of Triangles
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
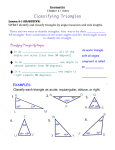
5.1 Angles of Triangles Classifying Triangles by Sides and by Angles Classifying Triangles by Sides Scalene Triangle- Isosceles TriangleNo congruent At least 2 congruent sides sides Equilateral Triangle3 congruent sides Classifying Triangles by Angles Acute Triangle3 acute angles Right Triangle1 right angle Obtuse Triangle1 obtuse angle Equiangular Triangle3 congruent angles Example 1: Classifying Triangles by Sides and Angles Classify the triangular shape of the support beams in the diagram by its sides and angles measures. The triangle has 2 congruent sides, so it isosceles. 70° The triangle has 3 acute angles. 55° It is an acute is an acute isosceles triangle. 55° Example 2: Classifying a Triangle in the Coordinate Plane Classify ∆𝑂𝑃𝑄 by its sides. Then determine if it is a right triangle. Step 1: Use the distance formula to find the side lengths. Distance = (𝒙𝟐 − 𝒙𝟏 )𝟐 +(𝒚𝟐 − 𝒚𝟏 )𝟐 𝑶𝑷 = 𝑶𝑸 = 𝑷𝑸 = (−𝟏 − 𝟎)𝟐 +(𝟐 − 𝟎)𝟐 = 𝟓 ≈ 𝟐. 𝟐 (𝟔 − 𝟎)𝟐 +(𝟑 − 𝟎)𝟐 = 𝟒𝟓 ≈ 𝟔. 𝟕 𝟔 − (−𝟏) 𝟐 + (𝟑 − 𝟐)𝟐 = 𝟓𝟎 ≈ 𝟕. 𝟏 Because no sides are congruent ∆𝑂𝑃𝑄 is scalene. Example 2: Classifying a Triangle in the Coordinate Plane Classify ∆𝑂𝑃𝑄 by its sides. Then determine if it is a right triangle. Step 2: Check for right angles by finding the slope of each line. 𝚫𝒚 𝒚 −𝒚 slope = = 𝟐 𝟏 𝚫𝒙 𝒙𝟐 −𝒙𝟏 𝟐−𝟏 𝑶𝑷 = = −𝟐 −𝟏 − 𝟎 𝑷𝑸 = 𝟑−𝟐 1 = 𝟔 − (−𝟏) 7 𝟑−𝟎 𝟏 𝑶𝑸 = = 𝟔−𝟎 𝟐 Since OP and OQ are opposite reciprocals they are perpendicular. This means that angle O is 90°. ∆𝑶𝑷𝑸 is a right scalene triangle. Finding Angle Measure of Triangles When the sides of a polygon are extended, other angles are formed. The original angles are the interior angles. The angles that form linear pairs with the interior angles are the exterior angles. Triangle Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Exterior Angle Theorem The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles. Example 3: Finding an Angle Measure Find m< JKM. Using the exterior angle theorem m<J + m<L = m<JKM. x + 70 = 2x – 5 -x -x 70 = x – 5 +5 +5 75 = x m<JKM = 2(75) – 5 = 145° Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary. Example 4: Modeling with Mathematics In the painting, the red triangle is a right triangle. The measure of one acute angle in the triangle is twice the measure of the other. Find the measure of each acute angle. <1 = (2x)° <2 = x° The corollary to the triangle sum theorem says that the acute angles in a right triangle are complementary. 2x + x = 90 3x = 90 x = 30 1 2 m<1 = 60° m<2 = 30° You Try! 1)Find the measure of <1. 5(25) – 10 115° 2) Find the measure of each acute angle. =64° =26° Use Exterior Angle Theorem: 3x + 40 = 5x – 10 50 = 2x 25 = x <1 + 115 = 180 m<1 = 65° Use the Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem: 2x + (x – 6) = 90 3x – 6 = 90 3x = 96 x = 32