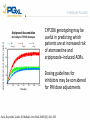
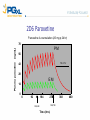
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CYP2D6 - PGXL Laboratories
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Dextropropoxyphene wikipedia , lookup