* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Critical angle - Kelso High School
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Phase-contrast X-ray imaging wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Smart glass wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
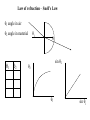
Revision 1. Sketch a wave and mark on it the wavelength and amplitude. 2. What is meant by the frequency of a wave and give its unit? 3. Define the period of a wave? 4. Give two equations to calculate the velocity of a wave. 5. What is refraction? 6. Draw a diagram of a light wave being refracted, going from air into glass. Mark on the normal, the incident and refracted angles. 7. Draw a diagram showing reflection. Mark the normal and the angles of incidence and reflection. 8. What is total internal reflection? Draw an optical fibre showing this. 6. Draw a diagram of a light wave being refracted, going from air into glass. Mark on the normal, the incident and refracted angles. 7. Draw a diagram showing reflection. Mark the normal and the angles of incidence and reflection. 8. What is total internal reflection? Draw an optical fibre showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out about interference in this unit. Tutorial questions p61 Qu 1 to 4 SAQs page 1 to 6 Law of refraction – Snell’s Law 1 angle in air 2 angle in material 1 2 1 2 sin 2 2 1 sin 1 sin 1 sin 2 sin 1 = n sin 2 n = sin 1 sin 2 n – refractive index of a material The refractive index of a vacuum is 1, for gasses it is almost 1. n has no units. n is always greater than 1 Always take 1 to be the angle in vacuum (or air) Find the refractive index of plastic and if you have time repeat the experiment to get the refractive index of glass. Critical angle NB: The angle in air, 1, is always bigger than in the other material. For the critical angle 1 = 90o Sin 90o = 1 n= 1 2 1 sin c Expt Find the critical angle of plastic and glass and use this to calculate their refractive indices. Tutorial questions 18 and 19 NB. The frequency of the light is unchanged when it is refracted. ( i.e. it stays the same colour). A higher frequency of light has a higher refractive index. i.e. blue light bends more than red. White light prism n = sin 1 = v1 = 1 sin 2 v2 vacuum (air) is 1 2 Tutorial questions 20 to 28 Revision Ex 8.4, 8.5