* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STA220 – Guided Notes 6.3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
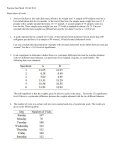
STA220 – Guided Notes 6.3 To test hypotheses regarding the population mean assuming the population standard deviation is known, two requirements must be satisfied: 1. A simple random sample is obtained. 2. The population from which the sample is drawn is normally distributed or the sample size is large (n≥30). Example 1: A trucking company claims that the average weight of a fully loaded moving van is 12,000 lb. The highway patrol decides to check this claim. A random sample of 30 moving vans shows that the average weight is 12,100 lb. with a standard deviation of 800 lb. Construct a hypothesis test to determine whether the average weight of a moving van is more than 12,000 lb. Use a 5% level of significance. Example 2: Jerry is doing a project for his sociology class in which he tests the claim that the Pleasant View housing project contains family units of average size 3.3 people (the national average). A random sample of 64 families from Pleasant View project shows a sample mean of 3.8 people per family unit with sample standard deviation 1.3. Construct a hypothesis test to determine whether the average size of a family unit in Pleasant View is different from the national average of 3.3. Use a 2% level of significance. The observed significance level, or p-value, for a test is the probability of observing the results actually observed (z*) assuming the null hypothesis is true. 𝑃(𝑧 ≥ 𝑧 ∗ |𝐻𝑜 ) The lower this probability, the less likely H0 is true. Procedure Example 3 In a test 𝐻0 : 𝜇 = 100 against 𝐻𝑎 : 𝜇 ≠ 100, the sample data yielded the test statistic z = 2.32. Find the p-value for the test. Example 4: The amount of time to finish the US census is of interest to the federal government. A member of the Census bureau claims it takes no more than ten minutes to fill out the census. A sample of 52 randomly chosen citizens were timed while completing the census. They had a mean of 10.6 minutes and a standard deviation of 2.25 minutes. Use a 5% significance level and the p-value method to test the claim from the member of the census bureau. Example 5: Historically, the average height for males was believed to be 68 inches. A doctor believes the average height has increased over the last 100 years. He claims the average male is now 70 inches tall. A random sample of 50 men had an average height of 68.9 inches and a standard deviation of 2.8 inches. Use a 10% significance level and the pvalue method to test the doctor’s claim. Test Hypothesis about a Population Mean: t-Statistic Procedure Definition Example 6: The lifespan for the general population of males born in 1980 is 77 years old. A worker for the Census Bureau claims that the average lifespan for college professors is greater than 77. A random sample of 17 deceased college professors had a mean lifespan of 89 and a standard deviation of 9.5 years. Use a significance level of 10% to test the CB worker’s claim. Example 7: The Natural Foods Diet claims that people lose an average of ten pounds in two months on the plan. A random sample of 26 people lost an average 8.9 pounds on the diet in two months. The standard deviation was 3.25 pounds. Use a 2% significance level to test the claim that the diet helps people lose an average of 10 pounds in two months.