* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antihelmintic drugs
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
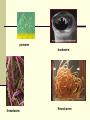
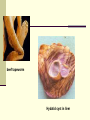
Antihelmintic drugs By Dr.Mohamed Abd AlMoneim Attia Antihelmintic drugs Drugs active against nematodes Diethylcarbamazine (systemic) Albendazole Mebendazole Pyrantel pamoate Ivermectin Drugs active against trematodes Drugs active against cestodes Niclosamide Praziquantel Praziquantel Metrifonate Albendazole oxamnquine mebendazole Drugs active against nematodes Intestinal nematodes includes: 1-enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) 2-ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm) 3-ancyclostoma & necator species (hookworm) 4-strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm) Tissue nematodes: onchocerca,filariasis pinworm hookworm threadworm Round worm Albendazole Mechanism of action: block glucose uptake by the parasite leading to decrease production of energy and subsequent parasite immobilization Uses: 1-treatment of roundworm,pinworm,hookworm infection 2-alternative treatment of threadworm,filariasis 3-hydatid disease & cysticercosis Side effects: 1- short course treatment :has few side effects 2-long course treatments: leucopenia, alopecia & elevation of liver enzymes Diethylcarbamazine Mechanism of action: Immobilizes microfilaria by unknown mechanism increase host susceptibility to attack it. Uses: 1. Drug of choice in filarial infection of the eye (loa loa) 1. Alternate drug in elephantiasis. Side effects: 1-headache,malasie,weakness,nausea 2-reaction to dying filaria includes: fever, rash,ocular damage, joint pain and lymphangitis Ivermectin Mechanism of action: facilitates GABA mediated neurotransmission in nematodes causing immobilization of the parasite, facilitating its removal by reticuloendothelial system. Uses: Drug of choice in treatment of onchocercosis, and threadworm infection Side effects: Mazzotti reactions(due to killing of microfilaria) and includes,fever, joint pain, rash hypotension,tachycardia Mebendazole Mechanism of action: Inhibit glucose uptake and microtubule synthesis in nematodes. Uses: Primary drug in roundworm and pinworm infection Side effects: GIT upsets, alopecia and agranulocytosis in high dose Piperazine Mechanism of action: Act as GABA receptor agonist causing paralysis of the parasite and expelled live by normal intestinal peristalsis Uses: alternate drug in treatment of roundworm infection. Side effects: GIT upsets, teratogenic Pyrantel pamoate Mechanism of action: Stimulate nicotinic receptor present at the NMJ of nematode.contraction of the muscle occurs followed by depolarization induced paralysis. Uses: 1- drug of choice for hookworm & roundworm infection 2-alternate drug in pinworm infection Side effects: mild GIT upsets Thiabendazole Mechanism of action: like mebendazole Uses: alternate drug in threadworm infection Side effects: unsafe drug 1-GIT irritation,headache,drowsiness 2-leukopenia,haematuria 3-allergic reaction Drugs active against trematodes Medically important trematodes are: 1-schistosoma species (blood fluke) 2-clonorchis sinesis (liver flukes in southeast Asia) 3-paragonimus westermani ( lung fluke in Asia,India) Praziquantel Mechanism of action: Increase membrane permeability to calcium causing muscle contraction followed by paralysis leading to vacuolization and death of the parasite. Uses: 1- drug of choice of all trematodes infection 2-one of 2 drugs of choice in cestodes infection Side effects: 1-common adverse effects: GIT upset,headach,malaise,skin rash 2-intracranial hypertension and convulsion if used in ttt of neurocysticercosis Contraindication: ocularcysticercosis Bithionol Uses: Drug of choice in ttt of fascioliasis ( sheep liver fluke) Side effects: 1-common: N/V,headache,phototoxcity 2-less common: protenuria,leucopenia Drugs active against cestodes The 4 important cestodes are: 1-taenia saginata ( beef tapeworm) 2-taenia solium ( pork tapeworm that causes cysticerci in brain and eye) 3-diphyllobothrium latum ( fish tapeworm) 4-echinococcus granulosus (dog tapeworm that cause hydatid cysts in lung,liver,and brain) beef tapeworm Hydatid cyst in liver Niclosamide Mechanism of action: Act by activating ATPases Uses: 1- 1 of 2 drugs of choice ( with praziquantel) in ttt of fish,pork,and beef tapeworms infection 2-not effective in cycticercosis (albendazole or praziquantel is used) 3- not effective in hydatid disease ( albendazole is used). Side effects: Mild GIT upset, rash headache Drug for treatment of nematodes Infecting organism Ascaris(roundworm) Drug of choice Alternative drug Albendazole,mebendazole,py rantel pamoate piperazine Ancylostoma(hookworm) Albendazole,mebendazole, pyrantel pamoate Strongyloids stercoralis(threadworm ivermectin Albendazole,mebendaz ole, Enterobius vermicularis(pinworm) filariasis Mebendazole,pyrantel albendazole pamoate diethylcarbamazine ivermectin onchocericasis ivermectin -------- Drug for treatment of trematodes Infecting organism Drug of choice Alternative drug s,.haematobium praziquantel metrifonate s.mansoni praziquantel oxamniquine s.japonicum praziquantel Fasciola hepatica bithional Fasciolopsis buski Praziquantel or niclosamide Drug for treatment of cestodes Infecting organism Drug of choice t.Saginata (beef tapeworm) Praziquantel or niclosamide t.Solium(pork tapeworm) Praziquantel or niclosamide albendazole Cysticercosis(pork tapeworm larval stage) Diphyllobothrium latium(fish tapeworm) Hydatid disease Praziquantel or niclosamide albendazole Alternative drug mebendazole praziquantel Drugs for leishmaniasis Sodium stibogluconate: for all types of leishmania ( must be given by injection and cardiotoxic) Alternate drugs: 1-Pentamidine for visceral leishmaniasis 2-Fluconazole or metronidazole for cutaneous lesions 3-Amphotricin B for mucocutaneous lesions ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS Therapeutic Strategies Inhibit muscle contraction Inhibit energy metabolism Limit distribution of generally toxic drugs Thank you