* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circuit Delay Performance Estimation
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
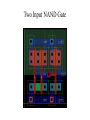
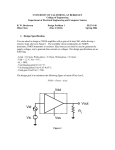
Circuit Delay Performance Estimation • Most digital designs have multiple signal paths and the slowest one of these paths is called the critical path • Timing analyzers can be used to determine this path. • The critical path needs to be optimized and this can be done at any of the following levels: – – – – Architectural or micro-architectural level Logic level Circuit level and Layout level. Delay Estimation • It is ideal to have the ability to estimate circuit delays without going through extensive simulations. • Some definitions of importance in delay estimation: – Rise time is the time the wave-form takes to rise from 10% to 90% of its steady state value – Fall time is the time the wave-form takes to fall from 90% of its steady state value to 10% – The average delay or edge rate is (tr + tf)/2 – Propagation delay is the maximum time from the input crossing the 50% to the output crossing the 50%. RC Delay Model • Our model will assume minimum device sizes for delay estimation – A minimum sized nMOS has resistance R – Recall that in general the mobility of electrons is twice that of holes. – We have thus designed pMOS devices to have twice the widths of nMOS devices to attain symmetric rise and fall times. – This fact allows us to estimate the resistance of a pMOS to be 2R. Delay Estimation (RC Models) • Transistors with increased widths have reduced resistance i.e. increase a minimum width transistor by k the resistance reduces to R/k. • A pMOS device of double width therefore has a resistance value of 2R/2 = R. • Parallel and series transistors combine just like resistors in parallel and resistors in series. RC Delay Models • Multiple transistors in series and all conducting have a higher resistance. • Capacitance to be considered is intrinsic i.e. it is internal to the transistor. • We assume that the gate capacitance Cg is equivalent to the diffusion capacitance Cdiff of the source or drain. • Contacts increase both resistance and capacitance, thus un-contacted nodes have less capacitance. The Elmore Delay Model • Transistors that are conducting must be reviewed as resistors. VDD Vin R1 R2 C1 R3 C2 RN C3 CN • The Elmore delay estimates the delay of an RC ladder as the sum over each node in the ladder resistance Rn-i between that node and the source multiplied by C on the node. AND Gate Intrinsic Capacitance Two Input NAND Gate