* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5. Biodiversity
Conservation movement wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
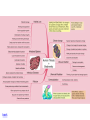
5. Biodiversity International Environmental Law Professor Dr. Christina Voigt 1. Questions 1. What is biological diversity? 2. Why should we value it? 3. Which threats exist to biodiversity? 4. What suggestions does the film make for protecting biodiversity? Which other suggestions could be made? 2005 Millennium Ecosystem Assessment “Everyone in the world depends completely on Earth’s ecosystems and the services they provide, such as food, water, disease management, climate regulation, spiritual fulfillment, and aesthetic enjoyment. Over the past 50 years, humans have changed these ecosystems more rapidly and extensively than in any comparable period of time in human history, largely to meet rapidly growing demands for food, fresh water, timber, fiber, and fuel. This has resulted in a substantial and largely irreversible loss in the biodiversity of life on Earth” Fourth Global Biodiversity Outlook 2013 “Current trends are bringing us closer to a number of potential tipping points that would catastrophically reduce the capacity of ecosystems to provide ... essential services.” 2. Protection of Biodiversity • Definition of Biodiversity • Threats to Biodiversity and Loss of Biological Diversity • Consequences of Biodiversity Loss • Protection 3. International Legal Instruments • Regulatory Techniques – direct/indirect – In-situ conservation – Ex-situ conservation • Global Instruments (examples) – Convention on International Trade with Endangered Species (CITES) (e.g. Elephants) – Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) – Ramsar Convention on Wetlands – UNESCO World Heritage Convention Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) Objectives 1) conservation of biological diversity, 2) sustainable use of its components and 3) fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources Precautionary Principle: Compare! Rio Declaration, 15: “where there are threats of serious or irreversible damage, lack of full scientific certainty shall not be used as a reason for postponing costeffective measures to prevent environmental degradation” CBD, Preamble: “where there is a threat of significant reduction or loss of biological diversity, lack of full scientific certainty should not be used as a reason for postponing measures to avoid or minimize such threat such a threat.” Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) • Commitments (Art.5-20) • Ecosystem Approach – Requires consideration of the whole ecosystem rather than its separate elements – Primarily based upon the understanding that the various elements of ecosystems are in an interactive relationship at different spatial and temporal scales. Focuses on ecosystems rather than separate species – Pays attention to the many links within and amongst them – Adopting a long-term timeframe • Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020, including Aichi Biodiversity Targets COP 10 Decision X/2.Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 20112020 Strategic Goal A: Address the underlying causes of biodiversity loss by mainstreaming biodiversity across government and society Strategic Goal B: Reduce the direct pressures on biodiversity and promote sustainable use Strategic Goal C: To improve the status of biodiversity by safeguarding ecosystems, species and genetic diversity Strategic Goal D: Enhance the benefits to all from biodiversity and ecosystem services • Strategic Goal E: Enhance implementation through participatory planning, knowledge management and capacity building Access to Genetic Resources/Bioprospecting/Benefit Sharing • Art. 15 • Nagoya Protocol (2010) Biosafety • Cartagena Protocol, January 29, 2000 – Art. 19.3 CBD – Biotechnology and its Risks – Precaution – Biosafety and Trade back