* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computer Networking
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
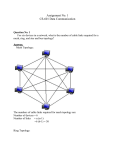
Computer Networks part I Computer Networking Networking began its infancy in the mid -1960’s. by the US Department of Defence (DoD). The original intention of networking was being developed to withstand a nuclear war. 2 Computer Networking WE ARE DEALING WITH MACHINES INSTEAD OF PEOPLE IN TODAY’S WORLD. OUR PRIVACY IS AFFECTED AND ALMOST ALL OF OUR PERSONAL INFORMATION CAN BE FOUND IN THE “VIRTUAL WORLD” . 3 Computer Networking • A collection of computing devices connected in order to communicate and share resources. Connections between computing devices can be physical using wires or cables or wireless using radio waves or infrared signals. • Typically classified according to: – Reach and complexity – Protocols and topologies 4 What is a Network? • A network consists of 2 or more computers connected together, and they can communicate and share resources (e.g. information) 5 BENEFITS OF A NETWORK • Information sharing: Authorized users can use other computers on the network to access and share information and data. This could include special group projects, databases, etc. • Hardware sharing: One device connected to a network, such as a printer or scanner, can be shared by many users. • Software sharing: Instead of purchasing and installing a software program on each computer, it can be installed on the server. All of the users can then access the program from a single location. • Collaborative environment: Users can work together on group projects by combining the power and capabilities of diverse equipment. 6 Network Topologies Introducing Topologies • Topology refers to physical or logical arrangement of network • Physical topologies are – Single Node – Bus – Star – Ring – Mesh – Tree – Hybrid 8 Logical Topologies • Refers to the way in which data are transmitted between nodes • Describes the way: – Data are packaged in frames – Electrical pulses are sent over network’s physical media • Logical topology may also be called network transport system 9 Single Node Topology • Single device, at times device called dumb terminal is connected to the server • Devices operates on files from server and returns them back after completing task 10 Single Node Topology • Advantages: – Easy to install, configure and manage – Least expensive – Single cable is required • Disadvantages: – Network consists of single device – Dumb terminal is dependent on server 11 SIMPLE PHYSICAL TOPOLOGIES 12 A Bus topology consists of a single cable—called a bus— connecting all nodes on a network without intervening connectivity devices Bus topology network 13 Bus topology • All devices are connected to a common cable called backbone/trunk • Operates in daisy chain fashion • Medium is shared that’s why creates collision 14 Bus topology • Advantages: – Installation of devices is easy – Works better for smaller network – Less expensive • Disadvantages: – If backbone breaks, entire network gets down – Difficult to isolate problems – Limited number of devices can be attached 15 Star topology Every node on the network is connected through a central device A typical star topology network 16 Star Topology • Advantages: – Easy to install, configure, manage and expand – Centralized management – Addition or removal of device does not affect the whole network • Disadvantages: – Requires more cable – Failure of hub affects entire network – More Expensive 17 Ring Topology • Devices are connected in a closed loop • All devices have equal access to media • Device waits for its turn to transmit • Most common type is Token Ring network 18 Ring topology Each node is connected to the two nearest nodes so the entire network forms a circle One method for passing data on ring networks is token passing A typical ring network 19 Ring Topology • Advantages: – Reliable and offers greater speed – No collisions – Handles large volume of traffic • Disadvantages: – More cabling is required compared to bus topology – One faulty device affects the entire network – Addition of devices affect network 20 Dual Ring Topology • Consists of two independent primary and secondary rings • Secondary ring is redundant, used only when primary stops functioning 21 Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) • Logical topology whose standard was originally specified by ANSI in mid-1980s and later refined by ISO 22 Mesh Topology • Used in WANs to interconnect LANs • Every device is connected to every other device • Use routers to determine the best path of communication 23 Mesh Topology Types Full mesh Partial mesh • Full mesh topology – All devices are connected to each other • Partial mesh topology - Some devices are connected to only those with whom they exchange most of the data 24 Mesh Topology • Advantages: – Improves fault tolerance – Failure of one link does not affect entire network – Centralized management is not required • Disadvantages: – Difficult to install and manage – Each link from one device to other requires individual NIC – Expensive 25 Tree Topology - I • Combines the characteristic of linear bus and star topology • Devices are wired to root hub • Twisted pair cable is commonly used • Lowest level devices are smaller computers 26 Tree Topology • Advantages: – Easy to expand the network – Point-to-point wiring for each device – Fault detection is easy • Disadvantages: – Difficult to configure – If backbone breaks, entire network goes down – More expensive 27 Hybrid Topology • Combines two or more different physical topologies • Commonly Star-Bus or Star-Ring • Also known as special topology and useful for corporate offices 28 Hybrid Topology • Advantages: – Used for creating larger networks – Handles large volume of traffic – Fault detection is easy • Disadvantages: – Installation and configuration is difficult – More expensive than other topologies – More cabling is required 29 Hybrid Physical Topologies Hybrid topology Complex combination of the simple physical topologies Star-wired ring Star-wired bus Daisy-Chained Hierarchical hybrid topology 30 Hybrid Physical Topologies Star-wired ring Star-wired topologies use physical layout of a star in conjunction with token ring-passing data transmission method A star-wired ring topology network 31 Hybrid Physical Topologies Star-wired bus In a star-wired bus topology, groups of workstations are starconnected to hubs and then networked via a single bus A star-wired bus network topology 32 Hybrid Physical Topologies Daisy-Chained A Daisy chain is linked series of devices A daisy-chained star-wired bus topology 33 Hybrid Physical Topologies Hierarchical hybrid topology Uses layers to separate devices by priority or function A hierarchical ring topology 34