* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun PPT
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
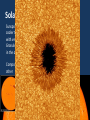
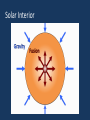
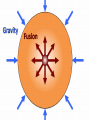
The Sun? The Sun is a star! There are an incredible amount of stars in the universe. Yay! What is a star…? A star is a huge sphere of very hot, glowing gas. Stars produce their own light and energy by a process called nuclear fusion. Fusion happens when lighter elements are forced to become heavier elements. When this happens, a tremendous amount of energy is created causing the star to heat up and shine. Stars come in a variety of sizes and colors. Our Sun is an average sized yellowish star. Stars which are smaller than our Sun are reddish and larger stars are blue. Useful Links: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/universe/stars-article/ http://www.universetoday.com/24351/what-is-a-star/ http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/know_l2/stars.html The Sun – Our Star • One of many stars in the Milky Way, but extremely important to us…why? – Energy, understanding other stars Solar Data • The diameter of the Sun is thus 109 times as great as the Earth's diameter. • About 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the sun. • The mass of the sun is 1.989 x 1030kilograms, about 332,000 times the mass of the Earth. • Volume of the Sun is about 1.5 million times that of Earth’s • Mean density of Sun = 1408 (kg/m3) • Mean density of Earth = 5514 (kg/m3) Solar Parts • A ball of gas, which can be generally thought of as having four “layers”: – Solar interior (core, radiation zone, convection zone) – visible surface (photosphere) • ‘visible’ ‘layer’ – two atmospheric components • chromosphere • corona Solar Activity Sunspots: dark regions on the Sun that are slightly cooler than surrounding surface, and are associated with very strong magnetic activity. Granules: ‘boiling effect’ cause by circulation of energy in the convection zone. - size of Earth and only last 8-10 minutes Composition surface = 74% Hydrogen, 25% Helium, 1% other Sunspots • Observed throughout antiquity (try looking at the sun at its lowest point in the sky, or through a cloud bank and you can occasionally see them unaided) • Deduction of Solar Rotation rate and differential rotation nature from sunspot observation • Dark spot? Not really. Many X brighter than Full Moon. Its relative. • Plage = lighter areas around the sunspots Chromosphere • Layer above the photosphere • Not visible to the naked eye • Hot, low density gas produces an emission spectrum • Appears red due to concentration of hydrogen gases The Corona • Only visible when the solar disc is covered (during a solar eclipse or with a coronagraph) • Very hot, High energy, low density particles escape the gravitational pull of the Sun • Released as streams of ions and radiation outward from the Sun Sunspots Prominences/Flares • http://www.space.com/25287-major-solarflare-eruption-video.html • http://www.space.com/25291-sun-sticks-outa-tongue-of-super-heated-plasma-video.html • http://youtu.be/wisdfag6WIQ Prominences/Flares • Flares are massive eruptions from the surface of the Sun resulting in huge amounts of charged particle energy ejected into space (CMEs – Coronal Mass Ejections) • Threating to astronauts, damaging to communication systems • Kill shot? Radio/X-Ray/UV radiation • Prominences are large looping structures of solar material tapped by magnetic fields. Aurora Borealis/Australis Colors Solar Interior Missing Matter -> Energy • Matter is converted to energy according to Einstein's famous formula: – E = mc2 • c = speed of light (3x108m/s) • M = mass (kg) • E = energy (Joules [J]) – A Joule is a unit of energy equivalent to the energy needed to apply a force of 1 Newton through a distance of one meter. How much energy in matter? The equivalent of energy that would be produced by burning 1000 tons of coal!! Solar Fusion • 4 million tons of Hydrogen converted to energy every second in Solar core! • This consumes 600 million tons of Hydrogen “fuel” every second! • How long can such fuel consumption keep up before the Sun run’s out? • At present rate: about another 100 billion years!! Conclusion? Solar Fusion • The Sun can last for a long time, however it will not last for another 100 billion years • In about 4.5 billion years, the Sun will swell into a Red Giant star. • This will happen b/c the Sun has run out of Hydrogen fuel in its core, resulting in less outward pressure and gravitational contraction, leading to increased pressure/temp. and fusion of heavier elements.