* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EKG review 2 student
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
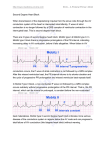
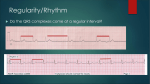
EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PROGRAM UNIVERSTIY OF WISCONSIN HOSPITAL AND CLINICS EKG REVIEW #2 1. What is considered to be the beginning of Ventricular repolarization? 2. What is the area called that marks the end of depolarization and the beginning of repolarization of the ventricles. 3. Describe where the NEGATIVE and the POSITIVE are for the following LEAD I LEAD II LEAD III 4. Fill in the blanks for counting 300 ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ Can the rhythm be both irregular and regular to use this method? 5. How many LARGE boxes are there in 6 seconds? 6. A T wave should be ___________ of entire QRS. 7. ST segment depression suggests ________________ depression is described as greater or equal to ___________ ST segment elevation suggests ____________ elevation is described as greater or equal to ________ 8. What are the two AV valves and where are they located? 1 9. What is the formula for cardiac output? 10. What THREE things is Stroke volume dependant on? 11. Describe absolute refractory period 12. How do you tell the difference between sinus arrhythmia and sinus arrest? 13. Why does a PVC, no matter what type, always make the rhythm irregular? 14. Describe Compensatory Pause 15. List the characteristics of a classic PVC 16. Describe an interpolated PVC-include compensatory pause 17. Describe an end-diastolic PVC-include compensatory pause 18. Describe a Retrograde PVC-include compensatory pause 19. What does Bigeminy, Trigeminy and Quadrigeminy mean? 2 20. Describe Uniformed and Mulitformed PVCs 21 Describe R on T phenomenon 22. You are analyzing a wide, bizarre early beat. This beat might be 23. Describe the differences of the above two beats QRS direction of initial wave of QRS Compensatory pause Direction of T wave P present Pulse 24. What is the difference between a Ventricular escape beat and a PVC 25. What is the difference between a Ventricular escape beat and Ventricular escape rhythm? 26. Describe the EKG characteristics of (include rate) Acclerated idioventricular Ventricular escape rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia 27. Three types of VT (from an EKG standpoint ) are 28. Describe PEA 29. Describe the “p waves” or lack of P waves and PR intervals in Junctional rhythms. Do all THREE versions. 3 30. What is the difference between a Junctional escape beat and a PJC 31. What is the difference between a Junctional escape beat and Junctional escape rhythm? 32. Describe the EKG characteristics of (include rate) Acclerated Junctional Junctional escape rhythm Jucntional Tachycardia 33. What are the THREE common characteristics of all PACs? 34. Describe the PR interval and the QRS of all three types of PACs 35. The rate range for Atrial Tachycardia is usually AT usually starts with a __________ How many consecutive impulses need to be present to be called AT? ________ Usually conduction of P:QRS is what ratio? 36. In WAP, discuss Irregular vs Regular and why? P waves PR interval 37. A tachycardic WAP is really a ___________ 38. In MAT, which wave of the EKG do we asses for greater than 100? 39. When assessing A flutter, you do not comment on which three EKG waves/segments? 40. TRUE/ FALSE Atrial Flutter ATRIAL rate is 250-350 ++ Usually more F waves than QRS A QRS will always stomp out a flutter wave 4 41. Which two Atrial Rhythms have no atrial kick? What is the significance of no atrial kick? 42. Your patient is in Atrial Fib and you are analyzing his rhythm. Can you comment on his P waves? PR interval, ST segment, T waves? 43. A Fib great than 100 is called A Fib less than 100 is called 44. The TWO Hallmarks of A fib are 45. Which two leads are the best for analyzing BBB? 46. Describe the QRS duration and a Normal T wave direction in BBB. 47. Which portion of the QRS do you look at to diagnose left vs right BBB? 48. SVT with BBB may look just like what rhythms? 48.a. What is the only thing abnormal (EKG wise) about First Degree heart block? 49. Describe the EKG characteristics of Mobitz I ODB 50. Describe the EKG characteristics of Mobitz II ODB 51. Where does the “block” occur with Mobitz 1 ODB and Mobitz II ODB? 5 52. Your patient is having more Ps than QRS, the ratio is 2:1, what is the best way to determine if your patient is in Mobitz I or Mobitz II? 53. What is the difference between HGB and ODB? 54. Your patient is having more Ps than QRS, the ratio is 4:1, what is the best way to determine if your patient is in Mobitz I or Mobitz II? 55. Some Third Degree heart blocks have a normal QRS, some wide, Why? 56. Describe the relationship of the P wave to the QRS in Third Degree Heart block. 57. Complete this sentence….BAD is _______________ 58. What is the difference between Third Degree and Block Acceleration Dissociation? 59. Which Heart block is most capable of producing Ventricular Asystole? 60. Which blocks do not receive Atropine and why? EKG review 2 student 6