* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle III
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
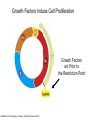
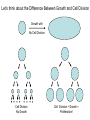
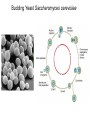
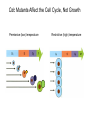
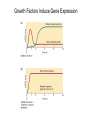
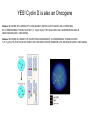
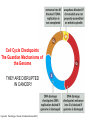
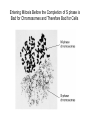
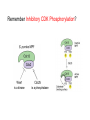
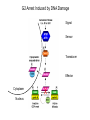
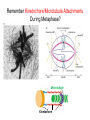
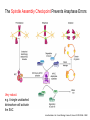
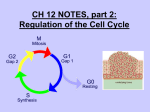
Growth Factors Induce Cell Proliferation Growth Factors act Prior to the Restriction Point Modified from The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Let’s think about the Difference Between Growth and Cell Division Growth with No Cell Division Cell Division No Growth Cell Division + Growth = Proliferation! Growth with No Cell Division: A Differentiated Neuron Cell Division with No Growth: Early Development OOCYTE GROWS WITHOUT DIVIDING (MONTHS) FERTILIZATION FERTILIZED EGG DIVIDES WITHOUT GROWING (HOURS) 1 mm sperm tadpole feeds, grows and bcecomes an adult frog A Typical Solid Tumor…Needs to Grow The size of a tumor first detectable by X-ray: 108 cells The size of a tumor first palpable: 109 cells The size of tumor at death of patient: 1012 cells Unregulated Proliferation: Cancer! Budding Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc Mutants Affect the Cell Cycle, Not Growth Permissive (low) temperature Restrictive (high) temperature Mammalian Cells Growing in Cell Culture Amino Acids Arginine Cystine Glutamine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine Vitamins Salts Miscellaneous Biotin Choline Folate Nicotinamide Pantothenate Pyridoxal Thiamine Riboflavin NaCl KCl NaH2PO4 NaHCO3 CaCl2 MgCl2 Glucose Penicillin Streptomycin Phenol red Whole serum Specific growth factors 1961Hayflick and Moorhead Showed that human fibroblasts die after a finite number of divisions in culture. This is called “The Hayflick Limit” Some Commonly Used Cell Lines Cell Line* Cell Type and Origin 3T 3 fibroblast (mouse) BHK 21 fibroblast (Syrian hamster) MDCK epithelial cell (dog) HeLa epithelial cell (human) PtK 1 epithelial cell (rat kangaroo) L6 myoblast (rat) PC 12 chromaffin cell (rat) SP 2 plasma cell (mouse) *Many of these cell lines were derived from tumors. All of them are capable of indefinite replication in culture and express at least some of the differentiated properties of their cell of origin. BHK 21 cells, HeLa cells, and SP 2 cells are capable of growth in suspension; the other cell lines require a solid culture substratum in order to multiply. Growth Factors Induce Cell Proliferation Growth + Cell Cycle Progression: But How? Growth Factors act Prior to the Restriction Point Modified from The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Growth Factors Induce Gene Expression Growth Factors Induce Oncogene Expression As Early Response Genes Growth Factors Induce Cyclin D Expression They also act by inhibiting CKIs We actually have: 3 D-type cyclins 2 E-type cyclins 2 A-type cyclins 3 B-type cyclins And the D-type cyclins respond to different cues Growth Factors Get the Cell Cycle Going Growth Factors Induce Cyclin D Expression ONCOGENES!!!! So, is Cyclin D an oncogene? YES! Cyclin D is also an Oncogene Disease: INVOLVED IN B-LYMPHOCYTIC MALIGNANCY (PARTICULARLY MANTLE-CELL LYMPHOMA) BY A CHROMOSOMAL TRANSLOCATION T(11;14)(Q13;Q32) THAT INVOLVES CCND1 AND IMMUNOGLOBULIN GENE REGIONS (BCL1 ONCOGENE). Disease: INVOLVED IN A SUBSET OF PARATHYROID ADENOMAS BY A CHROMOSOMAL TRANSLOCATION T(11;11)(Q13;P15) THAT INVOLVES CCND1 AND THE PARATHYROID HORMONE (PTH) ENHANCER (PRAD1 ONCOGENE). Translocations Cause One Gene to be Controlled by Another Cell Cycle Checkpoints The Guardian Mechanisms of the Genome THEY ARE DISRUPTED IN CANCER! Figure 8.4 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Entering Mitosis Before the Completion of S phase is Bad for Chromosomes and Therefore Bad for Cells Caffeine Abrogates the Replication Checkpoint The point: the combination of cellular stress and an inactive Checkpoint is very detrimental to cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell © 1994 by Bruce Alberts et al How do Cell Cycle Checkpoints Work? Zhou and Elledge Nature 408, 433 - 439 (2000) Remember Inhibitory CDK Phosphorylation? is a kinase is a phosphatase G2 Arrest Induced by DNA Damage Signal Sensor Transducer Effector Cytoplasm Nucleus Remember Kinetochore/Microtubule Attachments During Metaphase? Microtubule Kinetochore Remember the Metaphase to Anaphase Transition? Lara-Gonzalez et al. Current Biology Volume 22, Issue 22 2012 R966 - R980 Mitotic Defects Leading to Aneuploidy Weaver BA, Cleveland DW. Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;18(6):658-667. The Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Prevents Anaphase Errors Very robust: e.g. A single unattached kinteochore will activate the SAC Lara-Gonzalez et al. Current Biology Volume 22, Issue 22 2012 R966 - R980 Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Genes that are Mutated and/or Misregulated in Human Cancers Weaver BA, Cleveland DW. Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;18(6):658-667.