* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
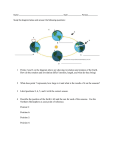
Journal 8/31/16 Why do you think God made the seasons? Why not have made the world so we get fertile crops all year round? Objective Homework To learn about the wobble in the Earth's orbit Read book section 1.4 Pages 12 - 16 Notes: The Tilt of the Earth As we go around the sun, something causes weather to warm up and cool down in predictable patterns. We call this the seasons. None of this should be new. What might be new, however, is what causes this change. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth As we go around the sun, something causes weather to warm up and cool down in predictable patterns. We call this the seasons. None of this should be new. What might be new, however, is what causes this change. The seasons are NOT caused by the Earth getting closer and farther from the sun. (If you put this on a test, you will get NEGATIVE points) Rather, the seasons are caused by a 23.5° tilt of the Earth’s rotational axis from vertical. This causes sunlight to hit at different angles, which gives it different strength to warm the Earth. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth Let’s illustrate this. Imagine the circle below is the Earth. Sunlight comes from the right. A B C We want to examine what’s happening with the sunlight at points A, B, and C. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth Let’s illustrate this. Imagine the circle below is the Earth. Sunlight comes from the right. A B C At C, the sun is shining straight down. This creates the most heat. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth Let’s illustrate this. Imagine the circle below is the Earth. Sunlight comes from the right. A B C At B, the light from the sun is hitting the Earth at an angle. This is less efficient and less heat is absorbed. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth Let’s illustrate this. Imagine the circle below is the Earth. Sunlight comes from the right. A B C At A, the light from the sun barely grazes past the Earth. Almost none of it will be absorbed! Notes: The Tilt of the Earth So why does this cause seasons? Shouldn’t it just mean that the farther you get from the equator, the colder it gets? No, because that tilt changes which way it faces depending on the season. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth So why does this cause seasons? Shouldn’t it just mean that the farther you get from the equator, the colder it gets? No, because that tilt changes which way it faces depending on the season. In summer, we here in the US follow the path of the dotted line over the course of a day. You can see that this gets us pretty close to the direct-sunlight area. Thus, it gets hot. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth By winter, we’ve moved around to the other side of the sun. Now we can see that sunlight hits at only a very bad angle during the day. This means we don’t absorb as much sunlight and thus it’s cold. Notes: The Tilt of the Earth But there’s more! Not only is the Earth tilted, but the way it’s tilted wobbles. We call this wobble “precession”. Precession is hard to explain, so let’s look at a visual example. (Summarize what you’re seeing here in your own words.) Notes: The Tilt of the Earth This “wobble” in the Earth’s spin is slow. It will take the Earth 26,500 years to wobble all the way around just once. As the Earth wobbles, the “north star” - the star the axis points at changes. Right now it’s Polaris, but back in the time of the Egyptians, it was a star called Thuban. Seasons Mini-Lab We’re going to do a lab to prove how the seasons are caused by the tilt of the sun and not by how close we are to the sun. This is going to be done as a computer simulation. Take close notes! http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion1/animations/seasons_e cliptic.html http://www.sepuplhs.org/students/iaes/simulations/SEPU P_Seasons_Interactive.swf http://astro.unl.edu/classaction/animations/coordsmotion /daylighthoursexplorer.html Exit Question What would happen to seasons if the Earth's orbit were tilted by a few more degrees? a) There would be no seasons at all b) The seasons would be less extreme in temperatures c) The seasons would be more extreme in temperatures d) The weather would change from hot to fast and back in less time. e) Not enough information f) None of the above