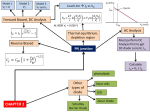
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Example quiz questions
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
1. When the magnitude of forward bias voltage of pn diode increases, what happens to the junction capacitance of the diode? (increases, decreases, remains constant): why? 2. For a given current voltage V of the forward biased Silicon diode, what happens to the diode current when the temperature increases? (increases, decreases, remains constant): why? 3.In order to reverse bias a pn junction where should where should we apply higher potential: to p or to n region? why? 4. Which part of the depletion region is wider in p+-n diode? (the one at the n side, the one at the p+ side, both are equally wide): why? 5. What happens with small signal transconductance gm of a bipolar transistor in active rgn. of operation when the collector current increases? (gm increases, decreases, remains constant): why? 6. Which of the terminals has the highest potential for npn transistor in saturation? (base terminal, emitter terminal, collector terminal): why (provide the conditions for this rgn. of operation)? 7. Which of the terminals has the highest potential for npn transistor in active region of operation? (base terminal, emitter terminal, collector terminal): why (provide the conditions for this rgn. of operation)? 8 Consider an npn transistor in an active rgn. of operation. Assume that the VBE = 0.65V. In which case the collector current will be larger: for VCE = 2V or for VCE = 6V ? why? 9. When the magnitude of forward bias voltage of pn diode increases, what happens to the diffusion capacitance of the diode? (increases, decreases, remains constant): why? 10. Which part of the depletion region is wider in n+-p diode? (the one at the n side, the one at the p side, both are equally wide): why? 11. Which of the terminals has the lowest potential for pnp transistor in saturation? (base terminal, emitter terminal, collector terminal): why (provide the conditions for this rgn. of operation)? 12 For a circuit on Fig. 1 below, calculate the current IREF knowing that Io is 1mA and both transistors are identical and have β=100. VCC VCC IREF R Io Fig.1 The circuit for the problem 12