* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geology study cards
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
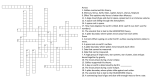
Q: Explain the difference between a convergent and a divergent plate boundary. Q: How is the composition (what it’s made of) of the core of the Earth different than the composition of the Lithosphere and Mantle? A: A convergent plate boundary comes together and collides. A divergent plate boundary separates or divides. A: The Core has a much higher concentration of Iron making it more dense. The Lithosphere and mantle have more oxygen and silicon. Q: What are tectonic plates and what layer of the Earth are they made of? Q: Order the following layers from the deepest to the top layer. Mantle, inner core, outer core, lithosphere, asthenosphere. A: Tectonic plates are the sections of Earth’s Lithosphere that move around causing slow and rapid changes to Earth’s surface. A: Deepest: Inner core, outer core, mantle, asthenosphere, lithosphere: Top layer Q: What are the three major differences between the inner core and outer core? Q: Explain and demonstrate two plate boundaries where earthquakes can happen. A: The inner core is solid with a higher temperature and higher pressure. The outer core is liquid with a lower temperature and lower pressure. A: Earthquakes can occur at a transform boundary (rub hands side by side). They can also happen at a convergentsubduction plate boundary (push one hand under the other hand). Q: Describe 3 things that can happen at a Convergent plate boundary. Q: Explain how a mid-ocean ridge forms, including the type of plate boundary. A: Regular folded mountains can form, volcanic mountains can form (at a subduction boundary) and Earthquakes can occur (at a subduction boundary) A: A mid-ocean ridge forms at a divergent plate boundary when two plates pull apart. The magma between the plates pushes up and cools off. Q: What process causes the plates to move? Use your hands to show this process. Q: How is an ocean plate different from a continental plate? A: Convection currents in the asthenosphere cause the plates to move. A: An ocean plate is thinner and more dense compared to a continental plate. An ocean (spin hands in a circular motion) plate can push under a continental plate through the process of subduction. Q: Explain the relationship between Earthquakes and Tsunamis. Q: What type of plate boundary forms a mountain range with no volcanoes? (use the hand motion) A: Tsunamis are extremely powerful waves caused by a strong Earthquake that occurs underwater. A: A convergent-collision boundary forms mountains without volcanoes. This happens when two continent plates collide (push hands together and then up) Q: Explain how volcanoes form. Include the type of plate boundary where they form most. Q: Describe 3 pieces of evidence Alfred Wegener used to support his theory of Continental drift. A: Volcanoes form at a convergentsubduction plate boundary. When the ocean Answer: Any of the following: Puzzle piece fit of South America & Africa plate pushes under and melts, the new magma Identical Fossils on opposite continents creates pressure. This pressure can cause a Similar rocks found on opposite continents volcanic eruption!! Glaciers discovered in very warm locations. Q: At what 2 plate boundaries are igneous rocks most likely to form? Explain. A: Igneous rocks can form at divergent plate boundaries where magma cools off. The can also form at convergent-subduction plate boundaries where volcanoes form. Q: How do geologists know about the inner layers of the Earth? A: Geologists study seismic wave vibrations produced by Earthquakes. The vibrations change speed when they move through different layers. Q: Explain how an igneous rock can become a metamorphic rock. Q: What processes cause an igneous rock to eventually become a sedimentary rock? A: If the Igneous rock is exposed to high A: The rock must undergo weathering and temperature (heat) and intense pressure it will form sediment. Then, the sediment must be become a metamorphic rock. compacted with pressure and cemented into a sedimentary rock. Q: How can a sedimentary rock become an igneous rock? A: If the sedimentary rock melts into magma and then cools and crystallizes it will become an Igneous rock.