* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Batteries (Level 2) File - Totton College
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Uninterruptible power supply wikipedia , lookup
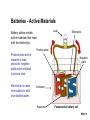
1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems The Battery Electrical systems require electrical power to function. Alternator provides electrical power when engine is running. Battery provides electrical power when engine is stationary. A large amount of battery power is required to start an engine. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Active Materials Load Battery plates contain active materials that react with the electrolyte. Electrolyte Positive plate Positive plate active material is lead peroxide, negative plate active material is porous lead. Electrolyte is made from sulphuric acid and distilled water. Negative plate Container Separator Fundamental battery cell Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Cell Construction Plates Positive plates Lead straps / connectors Plates contain grids that hold the active material and provide an electrical path. Plate Groups Alternate positive and negative plates are grouped together, and connected by straps. Grid Separators Separators Insulate the plates from each other, but allow electrolyte to flow freely. Negative plates Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Cells An element contains plate groups and separators, and is commonly known as a cell. Each cell produces about 2V, so 6 cells are required for a 12V battery. Cells are connected in series by lead straps. Straps across end cells are part of the terminals. Battery terminals Lead straps Cell (x6) Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Batteries - Discharging and Charging Automotive – Electrical Systems (described using conventional current flow techniques) Discharging Discharging occurs when current flows out of a battery. Current is produced when a load is placed across battery terminals. Battery converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Charging Charging occurs when current flows into battery. Requires an external voltage that is higher than the battery voltage. On a vehicle, the charging voltage is provided by an alternator. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Chemical Action Electrolyte chemically reacts with lead plates. Discharging Electrolyte hydrogen combines with positive plate oxygen to form water. Electrolyte sulphate combines with lead on plates to form lead sulphate. Charging Current flow reverses chemical action. Sulphate is forced back into electrolyte and combines with hydrogen, while oxygen returns to the positive plate to form lead peroxide. Process continues while voltage is applied, until all lead sulphate is converted. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Ratings Labels on battery case indicate battery ‘rating’. Capacity - Ampere-Hour Rating Amount of current a battery can supply over a given period of time (20 hours) @ 27°C (80°F). Capacity - Cold Start Rating Current battery can provide over a set period of time (30s) @ -18°C (0°F). HEAVY DUTY 085 DIN EQUIV 54317 AMP HOUR .44 AH CCA SAE 370 AMPS IEC 245 AMPS CCA DIN 210 AMPS OTHER EQUIV RESERVE CAPACITY 62 MINS Capacity - Reserve Capacity Rating Time battery can supply 25A @ 27°C (80°F) before the individual cell voltages drop below 1.7V. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Case Case is made of polypropylene (plastic) or a hard rubber compound. Dividers help separate cells. Ribs at bottom of each cell collect excess material from plates. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Case Cover is sealed to the top of the case. Openings above each cell for screw-in plugs or snap-in caps, in lowmaintenance batteries. Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Terminals and Cables Battery Terminals Battery has terminals for cable connections. Positive terminal is usually bigger. Common types are: Battery Cables Cables connect to battery using cable ends. Battery cables carry large currents and are very thick. Cables should be kept short for ease of routing. Postor Side Lug terminal L terminal Next > 1. Batteries and Fuses Automotive – Electrical Systems Batteries - Maintenance Free Batteries Sealed for life, no need to top-up with electrolyte. Built-in relative density indicator. Green = fully charged. Black = requires charging. Yellow = electrolyte low. Reservoir to collect evaporated water. Next >