* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diagnosis And Treatment Of Prescription Opioid Dependence
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
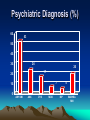
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Prescription Opioid Dependence Steven W. Clay, D.O. Associate Professor, Department of Family Medicine Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Athens, OH 45701 Overview • • • • • 1. Goals of Our Out-Patient Program 2. Presenting the Program 3. Diagnosis 4. Buprenorphine 5. Results So Far 1. Goals of Our Out-Patient Program • Turning Lives Around – Detoxification from Prescription (& Illicit) Opiates – Involvement in 12 Step / Other Programs – Treatment of Co-Morbidity Rural Ohio Setting • Medicaid or No Insurance • In-Patient Programs: Not Interested • Out-Patient Treatment: Maybe Available in Several Weeks to Months • Drug Screens Only With Cash Up Front • 20 + Twelve Step Meetings Per Week (Alcohol or Drugs OK) 2. Presenting the Program • “Our services in Addiction Medicine are limited to those needing help with: – 1. Possible substance abuse or addiction. – 2. Getting off addictive drugs with as little discomfort as possible. – 3. Buprenorphine treatment for narcotic addiction recovery.” • Weeding Out • “We are NOT a pain treatment center.” • “We are NOT an in-patient drug treatment center.” • “We REQUIRE you to have a personal physician or we will help you find one.” • “We REQUIRE a signed written treatment contract.” The Rules • Patients Must follow the rules we set • Including: – Attendance at counseling – Attendance at 12 Step meetings” • Those who break the contract will no longer be seen at our office. • “If you are NOT prepared to follow the Rules, come back when you are ready!” Patient Education • Detox. Only: 97% Relapse By 1 yr. • Reasons for becoming an addict: – Genetic, Environmental – Need to Re-Learn How to Live Without Drugs • Need for complete treatment: – 12 Step & Other Support 3. Diagnosis of Addiction Disorders • • • • • • Risk Factors Interview Collateral Information Establish Use and Consequences Coexisting Physical / Psych Dz. DSM-IV / Other Diagnostic List Addiction Diagnosis • Dependence / Addiction: -Preoccupied with Acquiring / Use -Compulsive use Despite Adverse Consequences -Chronicity and Relapse Establish Readiness For Change • • • • 1. Pre-Contemplation 2. Contemplation 3. Preparation 4. Action Prochaska and DiClemente Stages and processes of self-change of Smoking…J of Consult and Clin Psy 1983 Treatment Matching • ASAM Criteria For Treatment Matching: – Consequences of Use – Family / Other Support – Financial Support – Physical / Psychiatric Co-Morbidity – Relapse Potential Mee-Lee and Shulman The ASAM Placement Criteria and Matching Patients to Treatment in Principles of Addiction Medicine 2nd Ed. ASAM 2003 Treatment Matching • Office Follow-Up to In-Patient Treatment Based Upon Illness Severity • Most Followed as Out-Patients Due to Unavailable: – Treatment Centers – Money – Insurance Prescription Opiate Addiction Patient Presentation • In Contrast to Alcohol / Other Drug Addiction Patients: – Opiate Addicts Frequently Admit Problem and Ask for Help. – Friends, Family Refer Patients – The Word Goes Out in the Addiction Community 4. Buprenorphine • Subutex: – Buprenorphine SL • Suboxone: – Buprenorphine / Naloxone SL – 4 / 1 Ratio Buprenorphine Clinical practice Guidelines SAMHSA 2000 Buprenorphine • • • • Opioid Partial Agonist High Affinity Mu Binding Will Displace Many Other Opiates Maximum Effect About 30-40 mg Methadone Equivalent • SL Absorption Acceptable Buprenorphine Clinical practice Guidelines SAMHSA 2000 Naloxone • Opioid Antagonist • Will Displace Other Opiates and Initiate Withdrawal • Poor SL Absorption • If Taken IV With Buprenorphine, Will Negate Agonist Actions Buprenorphine Clinical practice Guidelines SAMHSA 2000 Transfer to Buprenorphine • Last Week Dose Is What Counts • From Methadone: Taper By Program: – 5-10 mg Per Week of Daily Dose – Goal 30-40 mg Per Day • From Oxycodone (etc.): – Many Stop or Taper Before Being Seen – Adjust Daily Dose to PO Equivalent – Snorted (X 0.6), IV (X 1.5) Transfer to Buprenorphine • Suboxone Used Initially: – Less Risk in Office (Theft) • Half to One 8/2 SL Tablet After: – 48 Hrs. Without Methadone – 24 Hrs. Without Oxycodone (Etc.) • Follow With 8/2 to 16/4 SL Daily • Information Given and Contract Signed Follow-up Care • 1-2 Weeks Initially • MUST: – Go To 12 Step Meetings – Keep Appointments – Not Use • Occasional Dosage Adjustments • Then Seen Monthly Non-Compliance • • • • • Relapse is Part of the Disease Most Admit Mistakes I Usually Will Give One Second Chance Look For Progress Not Perfection Limited Use of Urine Toxicology Screens Due to Cost Tapering Buprenorphine • Decrease By ½ Dose Monthly • Some Can Rapidly Come Off: 1-2 Weeks • Some Take Months • Variation Based on Patient Preference and Involvement in 12 Step Programs 5. Results So Far Results So Far • Opiate Addicts Presenting to University Medical Associates Addiction Medicine • Inclusion Criteria: – Opiate Use > 20mg / Day Methadone – Non-Pregnant – Willing to Follow Rules • 41 Consecutive Opiate Addicts Placed on Buprenorphine Results • Mean Age 33, Range 18 to 56 • 63% Male -SAMHSA 2002 Drug Use Survey: Illicit Drug Use 62.1% Male • Mean Methadone Equivalent Dose Per Day = 88.5 mg (%) Family History: Alcohol, Drug & Psych Disorders 35 34 30 25 22 20 14 15 10 10 10 5 5 5 0 0 NEG A D AD P AP DP ADP Psychiatric Diagnosis (%) 60 53 50 40 24 30 20 17 20 7 10 5 0 ANY SMI ANX DYS MDD BIP SAMHSA SMI Drugs/Pain Prior to Opiates (%) 60 60 50 40 30 20 20 15 10 5 0 POLY PAIN P+P NO PR Opiate Progression (%) 80 70 73 60 50 40 30 20 7 5 15 10 0 PRES PR 2 STR STR STR 2 PR Opiate of Choice (%) 60 58 50 40 32 30 20 10 5 2.5 2.5 Oxy + H Other 0 Oxycod Oth pres Heroin Administration Route (%) 60 51 50 40 29 30 20 12 7 10 2.5 0 PO Snrt IV Chew Tea Detoxed. Before Treatment (%) 80 75 70 60 50 40 30 20 20 5 10 0 0 NONE METHDONE INPT OUTPT 12 Step Attendance (%) 45 44 40 35 30 25 29 20 20 15 10 7 5 0 FREQ OCCAS NONE UNKN Results (%) 60 53 50 40 30 22 20 15 10 10 0 TAPER COMPLETE RELAPSE UNKNOWN O.B.O.T. in S.E. Ohio • • • • Mean Age 33 63% Male Mean Methadone Equiv. 88 mg 34% Negative Family History Addiction/Psych Disorders • 54% Some Mental Illness O.B.O.T. in S.E. Ohio • • • • • • 80% Common Drug Use Progression 90% Prescription Addiction 75% No Previous Detoxification 64% At Least Tried 12 Step Programs 63% Tapering or Completed Program 37% Relapsed or Presumed Relapsed