* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Systems Software - Shawlands Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
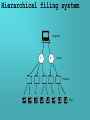
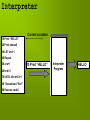
Systems Software Operating Systems What you will know Common features of an Operating System HCI, File Management, error reporting, memory management Modes of processing Interactive & Real-time Device Drivers Types of filing system Flat & Hierarchal Types of access Random & Sequential What is software? Software is the term that we use for all the programs and data that we use with a computer system. Two types of software Program The instructions that the computer follows (e.g. a word processor or a game). Data What the programs process (e.g. a word processing document or a saved game) More on software There are two types of program software. Applications software Programs designed to carry out a manual task (Word Processors, Databases, Graphics etc.) Systems Software Programs used to organise the computer, handle its devices, manage memory etc. The Operating System is Systems Software Operating Systems The operating system (OS) is the most important program used by the computer. The OS organises many things within the computer. Operating Systems (OS) The OS is stored on hard disc and loaded into RAM when the computer starts up. Some computers store their OS in ROM so that it cannot be erased by accident. The operating system controls and monitors the operation of the computer system. The filing system is part of the OS and it controls the loading and saving of programs and data from backing storage. Examples of OS Windows Linux Mac OS Unix for large file servers and networks Standard Functions of the OS User interface (HCI) The OS provides the means of the user communicating (interacting) with the computer system Features such as windows, icons, menus, commands, etc. are all provided by the operating system 1011 0110 Open word processor OS Standard Functions of the OS Controls input/output The access to all devices attached to the computer is controlled by the OS. For example, the OS can stop two programs trying to use the same device at the same time. Standard Functions of the OS Manages memory Controls where programs and data are placed in the main memory. Error Reporting The operating system lets the user know if any mistakes have occurred E.g. No paper in printer Modes of Processing Interactive Accepting input from a human. Interactive computer systems are programs that allow users to enter data or commands. Most popular programs, such as word processors and spreadsheet applications, are interactive. In interactive processing, the application responds to commands as quickly as it can once they have been entered. Sometimes there is a delay while the processor finishes another task. Modes of Processing Real-Time Real-time operating systems are systems that respond to input immediately. Automatic teller machines for banks are an example of real-time processing. Real-time systems are used for tasks such as navigation, in which the computer must react to a steady flow of new information without interruption. Interactive Systems with Background Job Capability Some operating systems allow a background process to occur at the same time as a foreground interactive process. The foreground process is the one that accepts input from the keyboard, mouse, or other input device. Background processes cannot accept interactive input from a user. For example, some word processors print files in the background, enabling you to continue editing while files are being printed. Device Drivers A device driver is a program which is an add-on to the operating system in a computer It is used to allow communication between a particular device and the computer. A scanner or a printer are examples of devices that may need drivers. Filing System The filing system manages backing storage It controls access to all types of backing storage devices It will prevent two programs trying to access the same files at the same time. Data stored in backing storage in areas called Directories (Windows call them folders) Hierarchical filing system Computer C:/ D:/ Drives Folders Files Hierarchical filing system A filing system in which directories have files and subdirectories beneath them. A hierarchical filing system is one that uses directories to organise files into a tree structure. Work on same topic can be grouped together Easier to find files as they are in their own directory Files can have the same name as long as in different directories Access Types Random/Direct Access Retrieves the data you want straight away. CD-ROM drive, Hard disc drive, Floppy disc drive. Sequential Access Move through record after record to find the data you want. Magnetic tape Systems Software What you will know Other examples of systems software Common features of HLL Types of language Special Purpose General Purpose Translators Compiler Interpreter Systems Software The operating system is just one example of systems software. Other examples of systems software are: Anti-virus tools Disk utilities Programming tools Printer manager utilities All these are examples of programs. Programs can be written in a number of different ways... High Level Languages Common Features Written similar to English Common internal structures loops, IF & Case statements Built in error checking Portable (can be moved to different machines) Most designed for special purpose… Types of Language General purpose Written for a wide variety of tasks. They can be used for any type of application however may make particular tasks difficult to do. Special Purpose Special purpose high level languages are written for particular types of task. For example: Basic, Pascal, C, etc Make tasks easier to carry out. Translators High Level languages need to be changed into machine code. This is done using a translator Types of translator: Compiler Interpreter Assembler Interpreter Translates line by line Each HLL statement is translated, converted and turned in to machine code. Immediately executes HLL programs Is used during build and testing. Needs to be translated every time program is executed Interpreter Current Location 10 Print “HELLO” 20 Print names$ 30 LET a=a+1 40 Repeat 50 a=a+1 60 b=b+2 70 UNTIL Not d+23=1 80 “Screenload “file1” 90 Execute code2 10 Print “HELLO” Interpreter Program HELLO Compiler A program that translates source code (HLL) into machine code in one go. Final program only translated once. Compiled program runs faster then interpreted one. Other machines don’t need translator to execute program. Takes time to produce program Difficult to detect errors Compiler Compiled Program (Machine Code) Source Code Compiler Program Assembler Assembly language has the same structure and set of commands as machine code, but it allows a programmer to use names instead of numbers. Uses less memory than HLL Program execution fast compared to HLL Written for one type of processor won't run on another. Harder to program Assembler LDA #28 011000011100 PRN #76 101001001100 CLE #1 Assembler JMP #8 Assembly Language 100100000001 110100001000 Machine Code