* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Appendicular Skeleton
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
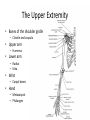
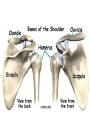
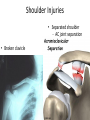
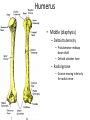
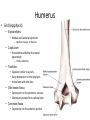
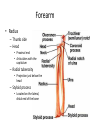
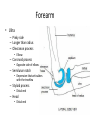
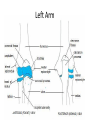
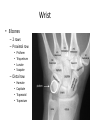
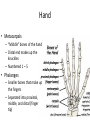
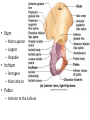
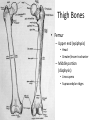
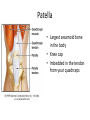
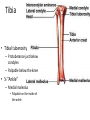
The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton THE UPPER EXTREMITY The Upper Extremity • Bones of the shoulder girdle – Clavicle and scapula • Upper arm – Humerus • Lower arm – Radius – Ulna • Wrist – Carpal bones • Hand – Metacarpals – Phalanges Shoulder Girdle • Only forms one joint with the axial skeleton • Clavicle – Sternoclavicular joint • Where the sternum meets the clavicle Shoulder Girdle • Scapula – Shoulder blade – 3 borders • Superior (top) • Vertebral (by the spine) • Axillary (side near the armpit) – Spine • Ridge along the posterior portion of the bone – Acromion process • Articulates with clavicle • Process that is located at the end of the spine – Coracoid process • Projection on the anterior portion of the scapula • Only 2 major projections Shoulder Injuries • Separated shoulder - AC joint separation • Broken clavicle Humerus • Long bone that makes up the upper arm • Upper end (epiphysis) – Head • Smooth rounded end that fits into glenoid fossa – Anatomical neck • Groove immediately inferior to the head – Greater and lesser tubercles • Greater is lateral to the head • Lesser is inferior (below) the greater – Intertubercular groove • Groove b/t greater and lesser tubercles – Surgical neck • Region below the tubercles that leads to the diaphysis • Common to fracture Humerus • Middle (diaphysis) – Deltoid tuberosity • Protuberance midway down shaft • Deltoid attaches here – Radial groove • Groove moving inferiorly for radial nerve Humerus • End (epiphysis) – Eipicondyles • Medial and lateral projections – Medial is larger of the two – Capitulum • Rounded head below the lateral epicondyle – Radius attaches – Trochlea • Appears similar to a pully • Deep depression in the epiphysis • Articulates with the ulna – Olecranon fossa • Depression on the posterior survace • Olecranon process forms elbow here – Coronoid fossa • Depression on the anterior portion Forearm • Radius – Thumb side – Head • Proximal end • Articulates with the capitulum – Radial tuberosity • Projection just below the head – Styloid process • Located on the lateral, distal end of the bone Forearm • Ulna – Pinky side – Longer than radius – Olecranon process • Elbow – Coronoid process • Opposite side of elbow – Semilunar notch • Depression that articulates with the trochlea – Styloid process • Distal end – Head • Distal end Left Arm Wrist • 8 bones – 2 rows – Proximal row • • • • Pisiform Triquetrum Lunate Scapate – Distal row • • • • Hamate Capitate Trapezoid Trapezium Hand • Metacarpals – “Middle” bones of the hand – Distal end makes up the knuckles – Numbered 1 – 5 • Phalanges – Smaller bones that make up the fingers – Separated into proximal, middle, and distal (finger tip) The Appendicular Skeleton THE LOWER EXTREMITY The Lower Extremity • Hip – Coxal bones (pelvis) • Thigh – femur • Lower leg – Tibia – Fibula • Foot – Tarsal bones – Metatarsals – Phalanges Coxal Bones • Pelvic girdle – Combination of the sacrum and the coxal bones bound together by ligaments – Supports the trunk of the body and allows for leg attachment • Coxal bones – Each bone is made up of 3 fused bones • Illium • Ischium • Pubis • Ilium – Most superior – Largest – Palpable • Ischium – Strongest – Most inferior • Pubus – Anterior to the ischium Coxal Bones • Horizontally divided into 2 parts – Pelvic inlet • a.k.a. pelvic brim • Above the inlet – False pelvis • Runs from the tip of the ilium to the pelvic inlet • Below the inlet – True pelvis • Boundary of the pelvic outlet • Pubic symphysis – Where the coxal bones meet Thigh Bones • Femur – Upper end (epiphysis) • Head • Greater/lesser trochanter – Middle portion (diaphysis) • Linea apera • Supracondylar ridges Thigh Bones • Distal end (epiphysis) – Lateral/medial condyles – Lateral/medial epicondyles – Adductor tubercle – Trochlea – Intercondyloid fossa • notch Patella • Largest sesamoid bone in the body • Knee cap • Imbedded in the tendon from your quadrceps Tibia • Shin bone • Lateral/medial condyles – Upper end of bone – Concave surface to articulate w/ femur • Intercondylar eminence – Spine between condyles – Attachment for ACL and PCL • Crest – Sharp ridge on the anterior – Part of the shin you can feel Tibia • Tibial tuberosity – Protuberance just below condyles – Palpable below the knee • ½ “Ankle” – Medial maleolus • Palpable on the inside of the ankle Fibula • Smaller than tibia • Deeper of the two bones – Always on the outside of the lower leg • Proximal end articulates with the tibia – @ lateral condyle – Creates part of the knee joint • Distal end (other ½ of the “ankle” – Articulates with the tibia – Lateral malleolus Foot • Constructed similar to the hand – Adapted to support weight • Two way arch construction – Longitudinal arch • Medial/lateral longitudinal arches – Transverse arch • Metatarsals & the distal row of tarsals Foot • Flat foot (fallen arches) – Ligaments and muscles hold bones in place – Keeps the arch intact – Foot, knee, eventually back • Very small number of individuals have a true “flat foot” – Usually over-pronation • High arch – Charcot Marie Tooth disorder (CMT) Foot Bones • Tarsal Bones – Talus • Articulates w/ the tibia – Calcaneus • Heel – Navicular • Distal row – Cuniform bones • 1-3 starting at 1st metatarsal – Cuboid • Metatarsals – 1-5 (big toe out) • Phalanges (1-5) – Proximal – Middle* – Distal 3 2 1