* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 142 Lecture 19
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
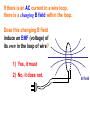
Quiz# 2 deals with answering questions about (and calculating values for) charged particle beams being accelerated and deflected by E and B fields. A recap of some in-class problems/questions dealing with charged particles accelerating across a potential difference and/or being steered or deflected by Electric or Magnetic fields is posted for you at http://csce.unl.edu/~ddaes/Quiz2Review.ppt You might also want to review the textbook’s Assigned problems: Ch.19: P 56, 76 Ch.20: P 17,18 Ch.22: P 17 If there is an AC current in a wire loop, there is a changing B field within the loop. Does this changing B field induce an EMF (voltage) of its own in the loop of wire? 1) Yes, it must 2) No, it does not. B field 1) Yes, it must AC current produces a changing B field. A changing B field induces an EMF in a loop, even the loop that produces the changing B field This is called self-inductance Self-Induction in Daily Life When you turn off your toaster by unplugging it current changes rapidly to zero rapidly changing B field produced very large voltage induced in wires of toaster spark voltage difference large enough for electrons to flow through air If you unplug your computer while it is still on, large voltages may be generated, possibly destroying the CPU chip. A solenoid has an inductance of 87.5mH and a resistance of 0.250. Find: The time constant for this circuit: = L/R = 87.510-3H/0.250 = 0.350 seconds and how long it takes for the current to reach ½ its maximum once connected to a 3volt battery. 6A = 12A(1-e-t/) ½ = e-t/ ln(½) = -t/0.350sec t = 0.2426 sec How much energy is stored in this solenoid at full current? A lamp with a 60W bulb is plugged into a 120v outlet. a)What are the rms and peak currents through the lamp? b)What is the bulb’s resistance? A lamp with a 60W bulb is plugged into a 120v outlet. a)What are the rms and peak currents through the lamp? P I rms R 2 but requires a value for R b)What is the bulb’s resistance? A lamp with a 60W bulb is plugged into a 120v outlet. a)What are the rms and peak currents through the lamp? P I rms R but requires a value for R P I rmsVrms Irms=60W/120v = 0.5 A 2 b)What is the bulb’s resistance? A lamp with a 60W bulb is plugged into a 120v outlet. a)What are the rms and peak currents through the lamp? P I rms R but requires a value for R P I rmsVrms Irms=60W/120v = 0.5 A 1 while I rms I peak so I peak 2I rms 1.414 0.5A 2 2 b)What is the bulb’s resistance?