* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GEOELECTRIC STRUCTURE BENEATH A 14 KM TRANSECT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
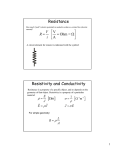
GEOELECTRIC STRUCTURE BENEATH A 14 KM TRANSECT ACROSS THE BOUNDARY BETWEEN NAKURU AND KERICHO COUNTIES AND ITS RELATION TO THE GROUNDWATER OCCURRENCE IN THE AREA Geo-electric resistivity survey was conducted along a 14km transect at the boundary between Kericho and Nakuru counties to observe the structure beneath and its relation to ground water occurrence. The study area is located between Latitude 35.5820700 to 35.792290o and Longitude 0.1556140 to 0.2557630. The area consists of volcanic rocks which include Pliocene trachytes, phonolites and basalts, Holocene basalts flows, pyroclastic and volcanic soils, Holocene colluvium deposits, pebbles sheets and basalts and Neogene (undifferentiated sediments intercalated in volcanics. In order to understand the aquifer distribution in the area and subsurface lithology, 58 Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES) were probed within the study area and data obtained were then interpreted using EarthImager 1D software, RES2DINV software and Surfer 11. The top most layers have high resistivity values ranging from 130 ohm meter to 430 ohm meter which is then underlain by pockets of low resistivity values of less than 100 ohm meter. Bottom layers have got very high resistivity values of up to 1390 ohm meter and probably infer fresh bedrock of basalts. Generally, the resistance variation in the area is related to the geology of the subsurface, revealing the stratigraphic layering and the rock characteristics in terms of weathering/fracturing. Major fault lines found, conform to the major incised valleys and streams transecting while minor structural lineaments are observed to assume the general trend of the weathering profile. Additionally where fractures are present in a geologic medium, the bedrock is expected to be more strongly weathered to a greater depth and can greatly influence its hydrogeological characteristics. The present study has proved the use of resistivity method as an excellent tool to delineate groundwater potential zones and subsurface lithology.