* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
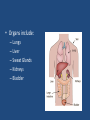
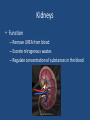
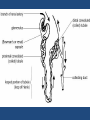
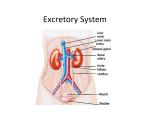
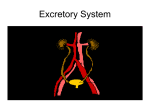
Excretion •Excretion is the process by which waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials are eliminated from an organism • Organs include: – Lungs – Liver – Sweat Glands – Kidneys – Bladder Lungs • CO2 diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli of the lungs • Excess water from AEROBIC respiration is also brought to the lungs • Both are removed from the body by the process of exhalation Liver • Disposal of Hemoglobin – Old Red Blood Cells are destroyed – Hemoglobin is released which is then turned into bile pigments – These pigments are stored in the gall bladder and are later released into the small intestine where they can be removed from the body through feces • Disposal of Nitrogenous wastes – Nitrogenous compounds are broken down and turned into UREA – Urea is then absorbed into the blood system and transported to the kidneys – Removed through URINARY SYSTEM Sweat Glands • Structure – Small, coiled tubular glands in DERMIS of skin – Ducts lead to openings in the epidermis called PORES • Function – Water, salts, and urea diffuse into glands from blood – Eliminated from body, SWEAT – PERSPIRATION: The formation of sweat • Temperature Regulation – Acts as a way of controlling our body temps – Sweat absorbs heat and carries the heat to the outside of our bodies – Sweat evaporates into the air, thereby cooling the body – Used in maintenance of homeostasis Kidneys • Function – Remove UREA from blood – Excrete nitrogenous wastes – Regulate concentration of substances in the blood Nephron • Functional unit of the kidney • Arteries turn into small balls of capillaries –GLOMERULUS • Glomerulus enclosed in cup like structure known as the BOWMAN’S CAPSULE • Extending from Bowman’s Capsule is a long, coiled tubule surrounded by capillaries • Filtration – Water, Salts, Urea, Amino Acids, and Glucose diffuse out of blood in the Glomerulus and into Bowman’s Capsule • Re-absorption – After leaving Bowman’s Capsule, some of the water, salts, etc. enter back into the bloodstream through ACTIVE TRANSPORT • URINE , made up of water, salts, and urea, is left over and travels to the URETER • The Urine travels through the Ureter into the BLADDER – Stores urine • Sphincter muscle leads to URETHRA – Leads outside the body Diseases of the Excretory System • Kidney Disease – Variety of conditions where kidneys and nephrons are unable to do their jobs effectively – Unable to remove nitrogenous wastes – Can be caused by a high protein diet • Gout – Form of arthritis – Uric Acid crystals form and float in bloodstream – Get deposited in joints (Big Toe) – Cause pain and stiffness