* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Systems by Graphing
Non-negative matrix factorization wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Cayley–Hamilton theorem wikipedia , lookup
Matrix multiplication wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
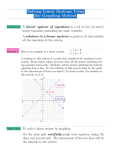
3.1 - Solving Systems by Graphing All I do is Solve! Graph the following pairs of equations: a. y = x + 5 y = -2x + 5 b. y = 3x + 2 y = 3x - 1 c. y = -4x - 2 y = 8x + 4 -2 System of Equations: A set of two or more equations that use the same variables. Solution to a System: A set of values that makes ALL equations true. Is (-3, 4) a solution to the system? Is (3,1) a solution for the following system? ìï y = x - 2 í ïî y = -2x + 7 Types of Solutions 1. Intersecting Lines have ONE unique solution. 1. Coincidental Lines (or same lines) have MANY solutions. 1. Parallel Lines have NO solutions! Solve by Graphing: y 4 x 6 y 2x 10 Graphing Calculator Solve the following systems by graphing: A. y x5 y 2x5 B. y 3x2 y 3x1 C. y 2x 2 4 y x2 2 Solving by Graphing: x 2y 7 2x 3y 0 Classwork (To Be Turned In): What type of solution does each system have? If the solution exist, what is it? 2) 1) 3) 4) 3.2 Solving Systems Algebraically Solving Systems by Substitution The Substitution Method • Not every system can be solved easily by graphing. Sometimes it is not always clear from the graph where the solution is. • We can use an algebraic method called SUBSTITUTION to find the exact solution without a graphing calculator. Solving by Substitution 1. Solve for one of the variables. 2. Substitute the expression of the equation you solved for into the other equation. 3. Solve for the variable. 4. Substitute the value of x into either equation and solve. Solve the system by substitution. ìï 2x - 3y = 6 í ïî x + y = -12 You Try! Solve the system by substitution ìï 3x - y = 0 í ïî 4x + 3y = 26 Solving Systems by Elimination Elimination We can solve by elimination by either Adding or Subtracting two equations to eliminate a variable! Solve by Elimination: ìï 3x - 2y = 14 í ïî 2x + 2y = 6 Solve by Elimination: ìï 4x + 9y = 1 í ïî 4x + 6y = -2 You Try! Solve the systems by elimination: Note: Sometimes with elimination you will have to multiply one or both of the equations in a system. This creates an EQUIVALENT SYSTEM that has the same solution to the original. Solve the system by elimination. Special Solutions Solve each system by elimination. ìï 2x - y = 3 1. í ïî -2x + y = -3 ìï 2x - 3y = 18 2. í ïî -2x + 3y = -6 3.6 Solving Systems with Three Variables 3-variable Systems Systems with 3 variables will have 3 equations. These type of systems are in three dimensions! So it is not going to be easy to find their solution by graphing. We can solve Systems with 3 variables, using Elimination OR Substitution. Solve by Elimination ì x - 3y + 3z = -4 ï í 2x + 3y - z = 15 ï 4x - 3y - z = 19 î SO MUCH WORK!!! Luckily, we have an easier way to do this! When solving system of the equations we can use Matrices!! Writing Systems as a Matrix Equation For Matrix Equations in the form AX = B •A is called the COEFFICIENT MATRIX •X is called the VARIABLE MATRIX •B is called the CONSTANT MATRIX •A Coefficient is a number INFRONT of a variable. •A Variable is a value represented by a letter or symbol •A Constant is a number WITHOUT a variable. Write the following System as a Matrix: ì 2x + y + 3z = 1 ï í 5x + y - 2z = 8 ï x - y - 9z = 5 î Remember that when solving matrix equations: If AX=B then X = -1 A B Solve the Matrix Equation é 2 1 3 ùé x ù é 1 ù ê úê ú ê ú ê 5 1 -2 úê y ú = ê 8 ú ê 1 -1 -9 úê z ú ê 5 ú û ë ûë û ë Write as a Matrix Equations and Solve! ì x+ y+z = 2 ï 2x + y = 5 í ï x + 3y - 3z = 14 î Write the follow systems as Matrix Equations. Then Solve! 1. 2. Unique Solutions Remember, Systems can have 1 solution, NO solutions, or MANY solutions. IF matrix A’s Determinate is 0 then the matrix does NOT have an inverse and the systems does NOT have a unique solution. IF matrix A’s Determine is NOT 0 then the matrix has an inverse and the system has a unique solutions! Unique Solution Determine if there is a unique solution. ìï x + y = 3 í ïî x - y = 7 ìï x + 2y = 5 í ïî 2x + 4y = 8 Example The sum of three numbers is 12. The 1st is 5 times the 2nd. The sum of the 1st and 3rd is 9. Find the numbers. HW 3.6/ Classwork 26. x 2y z 4 2x y 4z 8 3x y 2z 1 29. x 2y 2 2x 3y z 9 4 x 2y 5z 1 27. 4 A 2U I 2 5A 3U 2I 17 A 5U 3 30. 6x y 4z 8 y z 0 4 6 2x z 2 32. 4 x y z 5 x y z 5 2x z 1 y 28. 2l 2w h 72 l 3w h 2w 31. 5z 4 y 4 3x 2y 0 x 3z 8