* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download genetics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
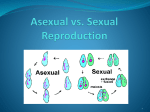
GENETICS 7.14A THE STUDENT IS EXPECTED TO DEFINE HEREDITY AS THE PASSAGE OF GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT GENERATION KWL ON GENETICS • KNOW • WANT TO LEARN • LEARNED VIDEO CLIP What is genetics? NEW VOCABULARY • Traits – An organism’s physical characteristics • DNA – “DeoxyriboNucleic Acid”. Genetic material that carries information about the organism • Genes – A section of DNA on a chromosome that has genetic information for one trait • Chromosome - A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. DRAW IT WHERE IS THE GENETIC MATERIAL FOUND IN THE CELL? CLASS TRAIT SURVEY # of students: _________ Number of students with trait Total number of students in class X 100 = Class percentage % PERSONAL TRAITS PICTURE EXAMPLES QUESTIONS • Who do you have these traits in common with? • How did you get the traits you have? • Why do you think you have some traits in common with your classmates? DOMINANT VS. RECESSIVE • A dominant allele is a strong form of a gene whose traits always show up in the organism if it is present. It is represented by a capital letter. • The recessive allele is a weak form of a gene that can be hidden or covered up if the dominant allele is present. It is represented by a lower case letter. GREGOR MENDEL THE “FATHER OF GENETICS” • He identified traits by studying the heredity of pea plants • The process in which characteristics or traits are passed from parents to offspring is called heredity • Genetics is the scientific study of heredity SEXUAL AND ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 7.14 The student knows that reproduction is a characteristic of living organisms and that the instructions for traits are governed in the genetic material VIDEO CLIP Where do your genes come from? SEXUAL REPRODUCTION VS • Two parents • Sex cells: sperm and egg • Sperm and egg join = fertilization • Offspring look different from parent ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION • One parent • No sex cells • Offspring produced by cell division • Offspring identical to parent (same DNA) SENTENCE STEMS • One characteristic of asexual reproduction is… • One characteristic of sexual reproduction is… • One characteristic sexual and asexual reproduction have in common is… ADVANTAGES / DISADVANTAGES ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION SEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Advantages: • Advantages: • Does not require a mate for reproduction to take place • Can increase population rapidly • Disadvantages: • Diversity of offspring • Offspring less likely to have mutations show up • Disadvantages: • Lack of diversity in offspring • Requires a mate to reproduce • Reproduce genetically identical to parents, the offspring inherit any mutations of the parents • Slower population growth TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Binary Fission • Organism divides in half • Two identical daughter cells produced • Daughter cells are half the parent’s size • Daughter cells grow, then divide too • Example: Bacteria TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Budding • Small bud grows out of parent cell • Two different sized cells made (with identical DNA) • Bud breaks off and grows • Example: yeast and hydra VIDEO CLIPS • Sexual reproduction • Asexual Reproduction