* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 101: Lecture 12 Work and Energy
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Physics 101: Lecture 12
Work and Energy
z
z
Chapter 6: Work and Energy
Reminders:
ÎExam I, Tuesday September 30th at 5 PM
ÎSee PHY101 Web page for room assignments
ÎDo not forgot to bring your UB ID card !
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 1
Work & Energy
z
z
z
An important concept in physics
ÎAlternative approach to mechanics
Many applications beyond mechanics
ÎThermodynamics (movement of heat)
ÎQuantum mechanics...
Very useful tools
ÎYou will learn new (sometimes much easier) ways to
solve problems
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 2
Work done by a Constant Force
z
The work done on an object by a constant (i.e.
displacement independent) force F is given by
W = Fs s
Unit : [W] = N m = J (Joule)
s : magnitude of displacement
Fs : magnitude of the force in the direction of the
displacement (Fs=F cosΘ)
W can be positive or negative:
W = + Fs s if Fs points in the same direction as s
W = - Fs s if Fs is opposite of s
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 3
Lecture 9, Preflight 1 & 2
You are towing a car up a hill with constant velocity.
The work done on the car by the normal force is:
1. positive
2. negative
3. zero
FN
V
T
correct
W
The normal force is perpendicular to the
displacement, hence, does no work.
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 4
Concept Question
You are towing a car up a hill with constant velocity.
The work done on the car by the gravitational force is:
1. positive
2. negative
3. zero
FN
V
T
correct
W
With the surface defined as the x-axis, the x component
of gravity is in the opposite direction of the
displacement, therefore work is negative.
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 5
Concept Question
You are towing a car up a hill with constant velocity.
The work done on the car by the tension force is:
1. positive
2. negative
3. zero
FN
correct
V
T
W
Tension is in the same direction as the displacement.
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 6
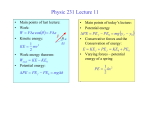
Work/Kinetic Energy Theorem:
Work done by a constant net force:
Wnet = Fnet s = m a s = m (vf2 –v02)/2
KE = m v2/2 is called the kinetic energy of an object.
{Net Work done on an object}
=
{change in kinetic energy of object}
Wnet=∆KE
z
= KEf - KE0 = ½ m vf2 – ½ m v02
Also works for a variable force !
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 7
Work done by Gravity
z
Object falling vertically upward or downward :
Wgravity = Fgravity s = m g (h0-hf)
PE = m g h is called gravitational potential energy
Object falling downward: Wgravity > 0
Object moving upward: Wgravity < 0
Gravity is an example for a conservative force:
work done is independent of path or
force does no net work on object moving around a closed path.
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 8
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
z
or
Total mechanical energy of an object remains constant
provided the net work done by non-conservative forces
is zero:
Etot = KE + PE = constant
KEf + PEf = KE0 + PE0
=> ∆KE + ∆PE = 0
Otherwise, in the presence of a net work done by
non-conservative forces (e.g. friction):
Wnc = ∆KE + ∆PE = KEf – KE0 + PEf-PEo
Physics 101: Lecture 12, Pg 9