* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12_Oracle Database Architecture
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
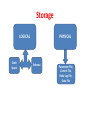
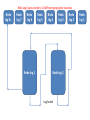
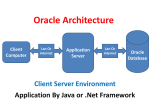
Oracle Database Architecture Ashima Wadhwa Oracle Versions • • • • E.F.T. Codd implement rules for RDBMS. Oracle 7 ( Implements 7 Rules) Oracle 8 (First stable version of Oracle) 9i (integrated with java and supports all utilities which are used By Java.) • 10G (Data Grid) • 11i called Oracle Financials Strong competitor for SAP and ERP. Data is Defined as • A value for an attribute of an entity. • Entity is Real World Thing which exist and can be described in terms of one or more attributes. • Database is Organized value of all SAME type of entity. Memory of ORACLE( Data Dict.) • Arrangement of system table stores data about data called as METADATA. Storage LOGICAL Table Space PHYSICAL Schema Parameter File, Control File, Redo Log File, Data File Oracle Database Architecture Instance SGA Shared pool Server process PGA User process DBWR Parameter file Password file LGWR Control files Redo log files Data files Database Archived log files Oracle Database Architecture • An Oracle database is a collection of data treated as a unit. • The purpose of a database is to store and retrieve related information. • A database server is the key to solving the problems of information management. In general, a server reliably manages a large amount of data in a multiuser environment so that many users can concurrently access the same data. • All this is accomplished while delivering high performance. • A database server also prevents unauthorized access and provides efficient solutions for failure recovery. Oracle Database Architecture • The database has logical structures and physical structures. Because the physical and logical structures are separate, the physical storage of data can be managed without affecting the access to logical storage structures. Physical Database Structures • Physical database structures of an Oracle database, includes : • Datafiles • Redo log files • Control files • Parameter Files Data files • Every Oracle database has one or more physical data files. The data files contain all the database data. The data of logical database structures, such as tables and indexes, is physically stored in the data files allocated for a database. The characteristics of data files are: • A data file can be associated with only one database. • Data files can have certain characteristics set to let them automatically extend when the database runs out of space. • One or more data files form a logical unit of database storage called a tablespace. Control File • Every Oracle database has a control file. A control file contains entries that specify the physical structure of the database. For example, it contains the following information: • Database name • Names and locations of data files and redo log files • Time stamp of database creation Redo Log File • Oracle used redo base recovery and allow to recover only committed transaction till the point of failure. • The redo base recovery in oracle is implemented through the redo log file. • When system fails then oracle read history from these redo log file and guaranties the recovery till the point of failure. • These files are created at the creation of oracle db. • The files are reusable and used as round robin passion. • Maximum size is 50Mb. Redo Log Copies stored to 10 different geographic locations Redo log N.. Redo log 7 Redo log 6 Redo log 1 Redo log 5 Redo log 4 Redo log 3 Redo log 2 Log Switch Redo log 2 Redo log 1 Parameter Files • Parameter files contain a list of configuration parameters for that instance and database. • Oracle recommends that you create a server parameter file as a dynamic means of maintaining initialization parameters. A server parameter file lets you store and manage your initialization parameters persistently in a server-side disk file. Logical Database Structures • • • • • • The logical storage structures, includes : Tablespace Data blocks Extents Segments Schema Tablespaces • A database is divided into logical storage units called tablespaces, which group related logical structures together. For example, tablespaces commonly group together all application objects to simplify some administrative operations. • Each database is logically divided into one or more tablespaces. One or more datafiles are explicitly created for each tablespace to physically store the data of all logical structures in a tablespace. The combined size of the datafiles in a tablespace is the total storage capacity of the tablespace. Oracle Data Blocks • At the finest level of granularity, Oracle database data is stored in data blocks. One data block corresponds to a specific number of bytes of physical database space on disk. The standard block size is specified by the DB_BLOCK_SIZE initialization parameter. In addition, you can specify up to five other block sizes. A database uses and allocates free database space in Oracle data blocks. Extents • The next level of logical database space is an extent. An extent is a specific number of contiguous data blocks, obtained in a single allocation, used to store a specific type of information. Segments • Above extents, the level of logical database storage is a segment. A segment is a set of extents allocated for a certain logical structure. The following table describes the different types of segments. Types of segments Data segments - store the table (or cluster) data. Index segments - store the index data. Temporary segments - temporary work area e.g. for sorting, executing SQL statements. Undo (rollback) segments - store undo information. When you roll back changes made to the database, undo records in the undo tablespace are used to undo the changes. Schema • Schema is set of objects own by User Account. • Each schema has user account but each user don’t need schema. • A user account is account with database having privileges to perform predefined activities on data. • Schema may not exist with user account but user account is exist without schema. • Purpose : Maintenance of object like backup & recovery, implementation of security and access level. Queries??