* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid gland
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
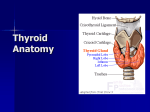
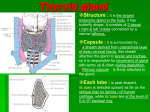
Thyroid gland By Dr. Adel Sahib Al-Mayaly دعاء الصباح Blood supply • Thyroid is a vascular organ rich in blood supply. • Two main sources of arterial supply:• 1- External carotid artery;- sup. Thyroid artery. • 2- Subclavian artery;- inferior thyroid A. • 3- Thyroideae ima A. ;- brachiocephalic art. Blood supply Superior Thyroid Artery • the first branch from the anterior aspect of the external carotid. • It descends downward for a short distance it pierces the pretracheal fascia & divides into ant. & post. Branches. • The external laryngeal n. lies behind the art, & it leaves the art. just above the upper pole to supply cricothyroid muscle Inferior thyroid artery • from the thyrocervical trunk. • arches upwards and medially behind the carotid sheath arches upwards and medially behind the carotid sheath. • It divides outside the pretracheal fascia into • branches that pierce the fascia. • The recurrent laryngeal nerve has a variable relationship to the artery • Relation of RLN to IThA Venous Drainage • 1-Superior thyroid vein:• follows the superior thyroid artery and enters drains to the internal jugular vein. • 2- Middle thyroid vein:• Crosses anterior to the common carotid artery to drain into the internal jugular vein. • The inferior thyroid vein:• Drain into brachiocephalic vein. Parathyroid glands Overview • Parathyroid glands normally lie behind the lobes of the thyroid gland. • There are usually four glands two on each side. • Each weighs about 50 mg. • They are brownish-yellow, which helps to distinguish them from the deep red of the thyroid gland. • Superior Gland • It is the more constant in position. • it is usually within the thyroid’s pretracheal fascial capsule. • At the middle of the back of the thyroid lobe, level with the first tracheal ring and above the inferior thyroid artery. • • Inferior Gland • is less constant in position. • It is usually within the pretracheal fascial sheath behind the lower pole but it may. • be in the gland itself. Blood Supply • Both upper and lower parathyroid by an anastomosis between the superior and inferior arteries. • Their minute veins join thyroid veins. Lymph drainage • As for lymph drainage of the thyroid gland Cervical plexus Cervical plexus • It is formed by the ventral primary divisions of the first four cervical nerves. • Each nerve, except the first, divides into the superior branch and the inferior branch. • C1 joins the upper branch of C2 • the adjacent upper and lower branches of C2 and C3 fuse • Each nerve receives a gray ramus communicans from the superior cervical ganglion. Cervical plexus • The loops lie on the surfaces of the levator scapulae and the scalenus medius muscles • It is covered by the upper part of SCM muscle. • The plexus lies behind the prevertebral layer • of deep cervical fascia. • The plexus supplies the skin and the muscles of the head, the neck, and the shoulders. • Branches Cutaneous branches • 1- The lesser occipital nerve (C2), which supplies the back of the scalp and the auricle • 2- The great auricular nerve (C2 and 3), which supplies the skin over the angle of the mandible • 3- The transverse cervical nerve (C2 and 3), which supplies the skin over the front of the neck • 4-The supraclavicular nerves (C3 and 4). • The medial, and intermediate, and lateral branches • supply the skin over the shoulder region. Muscular (Deep) branches • 1- Communicating branch:- from C1 to the hypoglossal nerve. • It carries motor fibres to genniohyoid & thyrohyoid muscles & to remaining infrahyoid muscles. • 2- Muscular branches:- from all roots to prevertebral muscles. Cervical plexus • 3- proprioceptive branches:- from C2,3 to SCM & C3,4 to trapezius m. • 4- Descending cervicalis ( descending root of ansa). • 5- Phrenic nerve:- C3,4,5 • It runs vertically downward over scalenus anterior m. behind subclavian v. to enter mediastinum to supply diaphragm.