* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Global 10 Greece
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
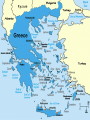
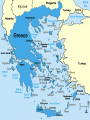
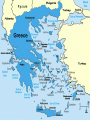
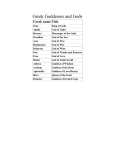
Aim: How was Ancient Greece Shaped by its Geography? Do Now: 1. Based on the DBQ work from yesterday how does Ancient Greek Geography differ from the Geography of the civilizations we have previously studied? 2. In your opinion what are three key features of Ancient Greek geography? – Explain your reasoning. Geography Located in Southeastern Europe Composed of many mountains, isolated valleys, and small islands Prevented a large Empire Aegean and Mediterranean were a valuable link to the rest of the world Became skilled sea traders Exchanged goods, ideas, and technology Early Civilizations Minoans built the first civilization on the island of Crete Traded with Egypt, and Mesopotamia Gained new Ideas and Technology Mycenaeans conquered Crete around 1400 B.C. Learned writing and other skills from the Minoans Rise of City-States Divided into mountains by isolated valleys Hundreds of scattered islands exist off of its coast Polis: Greek city state The Polis Made up of two parts Hilltop acropolis with Marble temples Flatter ground held the main city with a wall Governments in the City-States Kings at first Overtime landowning nobles gained power Created an Aristocracy or a government ruled by the landholding elite Most Powerful were Sparta and Athens Ways of life in these two City-States varied greatly Sparta Family life was sacrificed to the Polis At 12 they were enrolled in separate companies with other boys their age Slept outside and underwent heavy military training until the age of 24 After that they became frontline soldiers Kept prepared for battle for entire life Older men expected to models for the younger Military and Training Slept outside on reed mats Expected to stand and die rather than retreat Women Prohibited from wearing jewelry or ornate clothes Exercised rigorously to give birth to healthy children Hardly oppressed Saw it as a privilege to be a daughter or mother to a brave warrior Athens Developed from a monarchy into an Aristocracy Nobles controlled most aspects of government Merchants and soldiers resented their power Felt service entitled them to more rights Athenian law prevented foreign citizens from becoming Athenian citizens Solon Leader (archon) given free hand to make reforms Outlawed debt slavery Opened high offices to more citizens Granted citizenship to some foreign citizens Citizenship remained limited and led to tyrants Tyrants: People who gained power by force More Reform Eventually nobles lost a great deal of power in Greece, and the aristocracy was weakened Poor citizens given a greater voice Made all male citizens over 30 a governing body that debated laws Rights Overall Very limited Only male citizens could participate in government Tens of thousands were slaves without political rights, and freedoms Women Viewed as unable to reason and think as well as men Had no share in public life Religious Beliefs Polytheistic Believed Gods Lived on Mount Olympus in Northern Greece Honored Their Gods with Temples and Festivals. Consulted Priests , Priestesses , and Oracles to Discover the will of the Gods Religion was important but not as much as in other civilizations Some felt universe was regulated by natural laws not the Gods The Gods A quick overview ZEUS Most Powerful of the Gods Known as God of the Sky and Ruler of Olympus Weakness was the charms of women Ruled over affairs of Humans and other Gods Hera Wife of Zeus Goddess of Marriage Aphrodite Daughter of Zeus Goddess of Love Athena Daughter of Zeus Goddess of Wisdom Gave Athens its Name Dionysus Primarily a Fertility God Presided over Vineyards Grapes and Wine Was one of the 12 Great Gods Apollo God of Sun Considered Bright and Rational Associated with Arts of Music and Medicine Poseidon God of the Sea Hades God of the Underworld First Ruled underworld alone Later ruled with wife Persephone, Queen of the Underworld