* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download information systems 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Personal information management wikipedia , lookup
Expert system wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
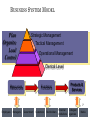
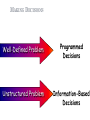
INFORMATION SYSTEMS 1 OBJECTIVES Importance of information systems 4 levels of users (filtering info) Information system types Different decision types 2 WHY? Understand your role in a system better Know what systems are available to you Be a better user to the IT group Make good IT management decisions Info Systems cost A LOT of money (Cost Vs Benefit Ratio) 3 THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE - GOOD Access to a world market Improve quality Aid employee communication Reduce costs Increase productivity Improve company morale Serendipitous Surfing: Politics 4 COST, RISK, AND CHANGE - BAD IT solutions can be expensive and time consuming Element of risk in the implantation of IT Implementing IT means change 5 INFORMATION QUALITY Quality (GIGO) Accessibility Completeness Timeliness Relevance (Information overload) BUSINESS SYSTEM MODEL Plan Organize Lead Control Strategic Management Tactical Management Operational Management Clerical Level Resources Products & Services Functions 7 Employees Managers Government Customers Stockholders Financial Institutions Colleges/ agencies Media FILTERING INFORMATION The right information - the right decision maker - the right time - the right form. • • • • Clerical Level (Transaction Handling) Operational Level (Exception Reports) Tactical Level (What-if Reports) Strategic Level (One-time Reports, What-if Reports or Trend Analyses) 8 MAKING DECISIONS Well-Defined Problem Programmed Decisions Unstructured Problem Information-Based Decisions 9 WHAT CAN INFO SYSTEM DO? Input Source Data Inquiry Response to prompt Instruction Message Change Processing Retrieve Record Update Summarize Select Manipulate Output Hard copy Soft copy Control Storage Data Text Images Other digital information 10 INFORMATION SYSTEM TYPES Manual system No hardware No software 11 TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEMS (TPS) Activities: Transaction handling Record-keeping Action documents Scheduled reports Primarily support: MIS DSS EIS Clerical personnel Operational-level managers Inflexible 12 MIS VS. DP MIS offers greater flexibility MIS integrates the information flow MIS caters to information needs of all management levels MIS are more timely and have online inquiry capabilities Boosts system security Management focused reports MIS uses an integrated database 13 DECISIONS SUPPORT SYSTEMS Interactive Integrated set of hardware and software tools Produce information to support decision-making process 14 DSS VS. MIS MIS DSS structured problems designed to support a set of applications Semi-structured and unstructured problems can be adapted to any decision environment 15 DSS CHARACTERISTICS Helps decision maker Semistructured & unstructured problems Most effective for tactical & strategic management levels Interactive and user-friendly; little IT help needed 16 more. . . DSS CHARACTERISTICS Uses models, simulations, & analytical tools Readily adaptable to any decision environment Interacts with a corporate database Not used for pre-established production schedule Often makes helpful charts EX: Forecasting; Chase MIS statistics warehouse analysis DSS TOOL BOX Applications Development Quick application building Support a one-time decision Data Management Data Warehousing (combine and offer preset relationships) Data Mining (search warehouse for new relationships) 18 more. . . DSS TOOL BOX Modeling Decisions involve many factors Uncertainty and risk present Statistical Analysis Risk Analysis Trend Analysis Planning What-If Goal Seeking 19 more. . . DSS TOOL BOX Inquiry Graphics Consolidations Application-Specific 20 EIS – DSS WITH A TWIST Executive Information System Just DSS for executives Each tool is designed specifically to support decision making at the executive levels of management Primarily the tactical and strategic levels 21 EXPERT SYSTEMS An Expert System is an interactive system Responds to questions Asks for clarification Makes recommendations Helps the user in the decision-making process Simulates human thought process Reasons, draws inferences & makes judgments (heuristic knowledge) Information acquired from live domain experts Highest form of knowledge-based systems, not an assistant system 22 EXPERT SYSTEM EXAMPLE Printer - Replace technical support people Diagnosis help (you relate symptoms and it asks for more info) Assistant system (call center; life ins quotes) Knowledge base contains Means of identifying problem Possible solutions How to progress from problem to solution 23 INTELLIGENT AGENTS Type of artificial intelligence Agent may work on: An ongoing goal An action triggered by an event A one-time goal Internet intelligent agents growing Scan internet for best price Sort through e-mail for call center Scan internet or a few databases for best vacation possibility 24 INFORMATION SYSTEMS Manual Data Processing – Filing cabinet MIS – Timely inquiries, focused reports DSS – interpret unstructured facts, what if Expert Systems – move user through process Intelligent Agents – event triggers 25 OBJECTIVE SUMMARY Different decision types 4 levels of users (filtering info) Clerical, operational, tactical, strategic information system types Structured, semi-structured, unstructured Manual, DP, MIS, DSS, EIS, Expert system, Intelligent Agent (AI) Importance of information systems 26 THANK YOU 27