* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epidemiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
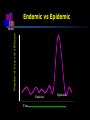
Endemic - Epidemic - Pandemic R>1 R=1 R<1 Time Endemic Transmission occur, but the number of cases remains constant Epidemic The number of cases increases Pandemic When epidemics occur at several continents – global epidemic Number of Cases of a Disease Endemic vs Epidemic Endemic Time Epidemic Epidemiology : Definition :( study of disease occurrence and distribution in the community) . In other word Epidemiology means The study of distribution and determinants of health related states or events in specialized population and the application of the study to control of heath problems . Uses of epidemiology : Identify the aetiology or the cause of the disease and the risk factor that increases a person's `risk for a disease. To determine the extent of a disease found in the community. What is the burden of a disease in the community ,this is critical for planning health series. Study the natural history and prognosis of the disease. To evaluate new preventive and therapeutic measures and new modes of health care delivering. To provide the foundation for the developing public policy and regulating decisions related to environmental problems Chronic or Non Communicable Diseases (NCDs) Chronic diseases are the major cause of deaths worldwide . Increase rate of NCDs in low and intermediate income countries . Interventions are effective and can reduce burden of disease . Some of NCDs have infectious etiology, helicobacter pylori bacteria is the causative agent for stomach cancer . The 10 leading causes of death in the world, 2000 and 2012 Ischemic heart disease, stroke, lower respiratory infections and chronic obstructive lung disease have remained the top major killers during the past decade. Top 15 CAUSES of death in USA 1. Heart Disease 2. Cancer 3. Lung Disease 4. Accidents 5. Stroke 6. Alzheimer's 7. Diabetes 8. Influenza-Pneumonia 9. Nephritis/Kidney 10. Suicide 11. Blood Poisoning 12. Liver Disease 13. Hypertension/Renal 14. Parkinson 15. Homicide Causes of death in developing countries Causes of death in developed countries HIV-AIDS Ischaemic heart disease Lower respiratory infections Cerebrovascular disease Ischaemic heart disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Diarrhea Lower respiratory infections Cerebrovascular disease Childhood diseases Malaria Tuberculosis Lung cancer Car crash Stomach cancer Hypertensive heart disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Tuberculosis Measles Suicide Developed vs. developing economies] Top causes of death, according to the World Health Organization report for the calendar year 2001: Epidemiology of Chronic Non Communicable Diseases (NCDs) Chronic disease : All impairments or deviations from normal which have one or more of the following characteristics: 1. Permanent . 2. Leave residual disability . 3. Caused by a non-reversible pathology . 4. Required special training of the patient for rehabilitation . 5. Required long period of supervision, observation or care . Problems in etiological investigations of NCDs 1. Absence of a known agent . 2. Multifactor's nature of etiology . 3. Long latent period . 4. Indefinite onset . 5. Differential effect of factors on incidence and course of the disease . Prevention of NCDs received little attention by policy makers, medical professionals, and general public because 1. The extent is less sufficiently examined. 2. Long delay between cause and effect . Primary prevention is possible for most NCDs Due to the following facts : 1. Large population differences in incidence and mortality of NCDs . 2. Dynamic national trends in incidence and mortality rates of most NCDs . 3. Rapid changes in risk of many NCDs among migrants population . 4. Positive results of intervention trials . 5. Identification of modifiable risk factors of many NCDs . Causes of shift of epidemiological studies toward the NCDs rather than acute infectious and nutritional deficiency diseases 1. Demographic changes : Decrease in infant mortality rate . Decrease in infertility rate . both leads to population aging . 2. Urbanization and socioeconomic ransformation A. B. C. D. E. F. Changes in community relationships . Changes in life style . Decreases concerns about moral believes . Human mobility . Expansion of education . Participation of women in labor force . 3. Changes in nutritional pattern A. B. Rapid increase in food energy availability and consumption . Obesity is emerging as a major public health problem . 4. Other causes : A. Smoking epidemic . B. Increase in alcohol consumption . C. Sedentary life style . Preventive health care Level Definition Primary prevention Methods to avoid occurrence of disease either through eliminating disease agents or increasing resistance to disease. Examples include immunization against disease, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise regimen, and avoiding smoking. Secondary prevention Methods to detect and address an existing disease prior to the appearance of symptoms. Examples include treatment of hypertension (a risk factor for many cardiovascular diseases), cancer screenings Tertiary prevention Methods to reduce negative impact of symptomatic disease, such as disability or death, through rehabilitation and treatment. Examples include surgical procedures that halt the spread or progression of disease