* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PULMONARY RADIOLOGY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
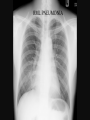
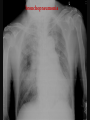
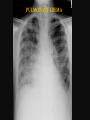
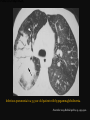
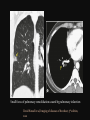
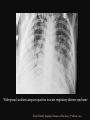
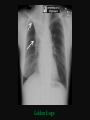
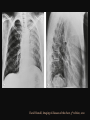
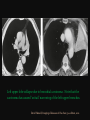
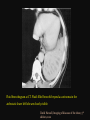
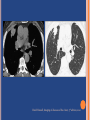
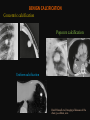
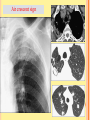
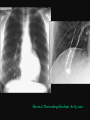
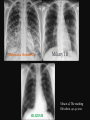
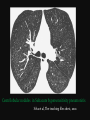
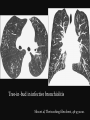
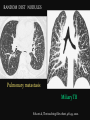
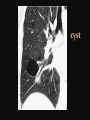
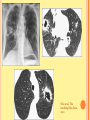
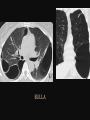
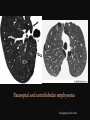
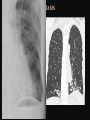
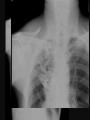
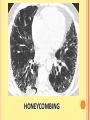
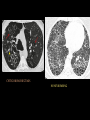
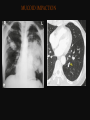
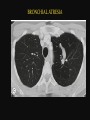
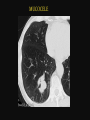
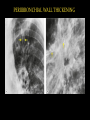
PULMONARY RADIOLOGY พญ. ปาณยา ทุมสท้าน ภาควิชาร ังสีวท ิ ยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น PULMONARY OPACITY “area that preferentially attenuates the x-ray beam” Area that more opaque than the surrounding area CLASSIFIED INTO Airspace opacities Atelectasis (collapse) Nodules and masses Linear and band like opacities Cysts and bullae Nodular and reticulonodular opacities and honeycombing AIRSPACE OPACITIES Acinar shadow Consolidation Solitary airspace opacity Multifocal airspace opacity DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF AIRSPACE OPACITES SOLITARY AIRSPACE OPACITY Pneumonia Atelectasis Infarction Hemorrhage Neoplasms - BAC - Lymphoma Radiation fibrosis Pulmonary contusion, vasculitis, drug reaction, etc. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF AIRSPACE OPACITES MULTIFOCAL AIRSPACE OPACITIES Exudate and transudates Hemorrhage Pneumonia, OP, infarction, connective tissue disease and vasculitis, inhalation of noxious gases or liquids, drug reaction, alveolar proteinosis Pulmonary contusion/hematoma, infarction, vasculitis Neoplasm BAC, lymphangitic carcinomatosa, metastases, lymphoma RML PNEUMONIA bronchopneumonia PULMONARY EDEMA RadioGraphics, Infectious pneumonia in a 35-year-old patient with hypogammaglobulinemia. November 2009 RadioGraphics, 29, 1909-1920. Small focus of pulmonary consolidation caused by pulmonary infarction David Hansell et al, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 Widespread, uniform airspace opacities in acute respiratory distress syndrome David Hansell, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 ATELECTASIS Most frequent cause is bronchial obstruction Bronchial obstruction in adult Usually the result of a bronchial neoplasm or mucus plug Occasionally, FB aspiration, broncholiths, extrinsic compression e.g. enlarged LNs, aortic aneurysm Passive atelectasis Discoid atelectasis ( Platelike or linear atlectasis) A form of adhesive atelectasis Usually abuts the pleura and is perpendicular to pleural surface Golden S sign David Hansell, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 Left upper lobe collapse due to bronchial carcinoma. Note that the carcinoma has caused ‘rat tail’ narrowing of the left upper bronchus. David Hansell, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 Fluid bronchogram at CT. Fluid-filled bronchi beyond a carcinoma in the atelectatic lower left lobe are clearly visible. David Hansell, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 ROUND ATELECTASIS A form of chronic atelectasis that resembles a mass Main DDx is BCA “bronchi and vessels curving into the periphery and converging toward a mass and area of pleural thickening (Comet tail sign)” David Hansell, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE/MASS Pulmonary nodule : lesion up to 3 cm in diameter. DDx of SPN/mass 1. Neoplasm 2. BCA, metastasis, lymphoma, carcinoid tumor, hamartoma, etc Inflammatory 1. 2. Infection: TB, fungus, round pneumonia, lung abscess, septic emboli Non infection: RA, Wegener granulomatosis SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE/MASS DDx of SPN/mass Congenital 3. Pulmonary AVM, sequestration, lung cyst, bronchial atresia with mucoid impaction Miscellaneous 4. Organizing pneumonia, pulmonary infarction, round atelectasis, etc. Mimics of SPN 5. External object Bone island or rib, healing rib fracture Pleural plaque Loculated pleural fluid PATIENT WITH A KNOWN EXTRATHORACIC MALIGNANT NEOPLASM Patients with CA of H&N, bladder, breast, cervix, bile ducts, esophagus, ovary, prostate, or stomach with SPN Patients with known salivary glands, adrenals, colon, kidney, thyroid, thymus or uterus “primary lung CA were more likely than metastasis” “fairly even odds” Patients with known melanoma, sarcoma, or testicular cancer “solitary metastasis is more likely than primary lung CA” Features which can be diagnostically helpful Calcification Fat density within a nodule Ground glass opacity Size Shape Cavitation Air bronchogram and bubblelike lucencies Enhancment BENIGN CALCIFICATION Concentric calcification Popcorn calcification Uniform calcification David Hansell et al, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 David Hansell et al, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 Fat in hamartoma David Hansell et al, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 DENSITY OF THE NODULE March 2007 RadioGraphics, 27, 391-408. SIZE AND SHAPE David Hansell et al, Imaging of diseases of the chest, 5th edition, 2010 FLEISCHNER SOCIETY RECOMMENDATIONS MacMahon et al. Radiology 237:395, Nov 2005 Contrast enhancement Rate of growth Adjacent bone destruction Air crescent sign Silva et al. The teaching files chest. 82-83. 2010. MULTIPLE PULMONARY NODULES Neoplasm metastatic CA or sarcoma, lymphoma, BAC Hamartomas, laryngeal papillomatosis Inflammatory Infective Granulomas (TB, histoplasmosis, nocardiosis) Lung abscesses, septic emboli,etc. Noninfective RA, Wegener granulomatosis Congenital : AVM Miscellaneous Hematomas, pulmonary infarction, mucoid impaction Metastasis thyroid CA Miliary TB Silva et al, The teaching files chest. 40-41, 2010. SILICOSIS Centrilobular nodules in Subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis Silva et al, The teaching files chest, 2010. Tree-in-bud in infective bronchiolitis Silva et al, The teaching files chest, 46-47,2010. RANDOM DIST NODULES Pulmonary metastasis Miliary TB Silva et al, The teaching files chest, 48-49, 2010. ABNORMAL LUCENCY LESION Cyst, cavity, bleb, bulla, emphysema CYST; any round circumscribed space that is surrounded by an epithelial or fibrous wall of variable thickness CAVITY; a gas-filled space, seen as a lucency or low-attenuation area, within pulmonary consolidation, a mass, or a nodule usually produced by the expulsion or drainage of a necrotic part of the lesion via the bronchial tree Cavity is not a synonym for abscess. BLEB; a small gas-containing space within the visceral pleura or subpleural lung, not > 1 cm in diameter CT: a thin-walled cystic airspace contiguous with the pleura BULLA; An airspace measuring > 1 cm – usually several centimeters – in diameter sharply demarcated by a thin wall that is no greater than 1 mm in thickness. usually accompanied by emphysematous changes in the adjacent lung. Bullous emphysema is bullous destruction of the lung parenchyma usually on a background of paraseptal or panacinar emphysema EMPHYSEMA; permanently enlarged airspaces distal to the terminal bronchiole with destruction of alveolar walls CT; focal areas or regions of low attenuation, usually without visible walls.[ cyst Silva et al, The teaching files chest, 2010 BULLA BLEB EMPHYSEMA IMAGE : WIKIPEDIA Paraseptal and centrilobular emphysema Imagingconsult.com BRONCHIECTASIS HONEYCOMBING CYSTIC BRONCHIECTASIS HONEYBOMBING LINEAR AND BAND-LIKE OPACITIES Mucoid impaction Septal lines Bronchial wall (peribronchial) thickening MUCOID IMPACTION BRONCHIAL ATRESIA MUCOCELE PERIIBRONCHIAL WALL THICKENING RETICULONODULAR OPACITIES Acute Lower zone Pulmonary edema, pneumonia (Mycoplasma, viral, opportunistic) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, RA, scleroderma, drug reaction, HP, Mid- or upper zone Pulmonary TB or fungal disease, Pneumoconiosis, HP NODULAR AND RETICULONODULAR PARTERN Pulmonary fibrosis THANK YOU ALL FOR YOUR ATTENTION