* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter ??
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
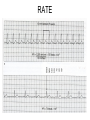
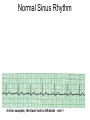
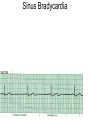
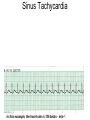
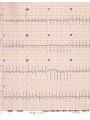
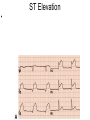
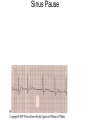
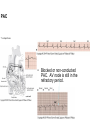
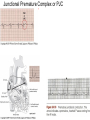
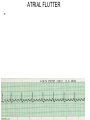
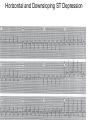
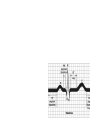
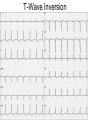
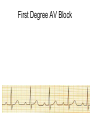
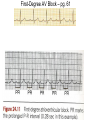
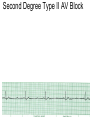
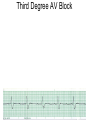
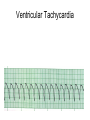
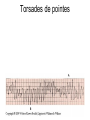
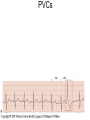
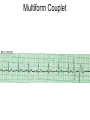
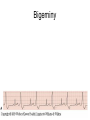
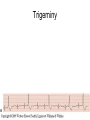
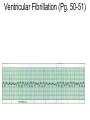
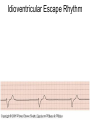
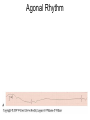
ECG Review for practical 1: For the practical you will be required to provide an answer for each ECG that includes the name of the ECG, what is the disorder, why it is abnormal, and give the rate when required. Be specific. Don’t overwrite with excess unnecessary information. We will review in class on _______.Until then go through these slides and fill in the needed information via your notes. If you do not have this filled out you will not be allowed to stay for the review. RATE Normal Sinus Rhythm In this example, the heart rate is 68 beats · min–1. Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia In this example, the heart rate is 136 beats · min–1. See Figure 11.3, Page 120 for reference Myocardial Infarction Note the Q wave may be the only remaining evidence of the MI Reprinted, by permission, from E. Stein, 1992, Rapid analysis of electrocardiograms, 2nd ed. (Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger), 150. Significant Q Wave ST Elevation • Sinus Pause Premature Atrial Contraction Biphasic P wave in this case. PAC *= ectopic focus • Blocked or non-conducted PAC. AV node is still in the refractory period. Junctional Premature Complexes Inverted P wave in this case Junctional Premature Complex or PJC • ATRIAL FLUTTER • Rate Atrial Fibrillation Horizontal and Downsloping ST Depression Upsloping ST Depression T-Wave Inversion T wave inversion First Degree AV Block First-Degree AV Block – pg. 61 Second Degree Type I AV Block Second Degree Type II AV Block Third Degree AV Block Ventricular Tachycardia Runs of Ventricular Tachycardia Torsades de pointes PVCs Multiform Couplet Bigeminy Trigeminy Ventricular Fibrillation (Pg. 50-51) Idioventricular Escape Rhythm Asystole Agonal Rhythm