* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWI ALL 2010-2011
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
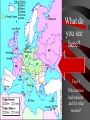
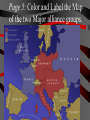
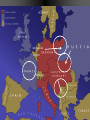
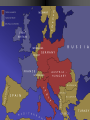
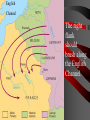
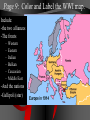
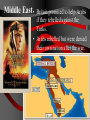
Basic #12 Vocabulary Alliance – an agreement between nations to come to one another’s defense Archduke Franz Ferdinand – crown prince of Austria whose assassination sparked WWI Balkans – Southeastern Europe Belgium – neutral nation invaded by Germany to being World War I Black Hand – secret society committed to ending Austrian rule in Slavic lands (Balkans) Imperialism – to dominate another country politically, economically, and culturally Basic #12 Vocabulary Cont… Kaiser Wilhelm II – leader of Germany who helped instigate WWI Militarism – glorification of the military, which caused the buildup of European militaries Nationalism – love of one’s country Neutrality – policy of not supporting either side in a war Powder Keg – an explosive situation Serbia – nation where Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated Basic #12 Vocabulary Cont… Schlieffen Plan – Germany’s plan to fight a war with France & Russia. It involved a surprise attack on France by going thru Belgium. Slavs – the race of people living in Eastern Europe (Bosnia, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia) Triple Alliance – defensive treaty between Germany, Italy, and Austria-Hungary Triple Entente – France, Russia, and Britain’s defensive treaty against Germany Ultimatum – a final set of demands Basic #12 Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Which cause of WWI describes a country’s obsession with building up its armed forces in preparation for war? Which cause of WWI describes the tangled friendships and rivalries between the European powers? What happened to Otto von Bismark’s power? Which nations were part of the Triple Alliance? Which nations were part of the Triple Entente? Which cause of WWI describes the competition for overseas colonies, power and Empires? Which cause of WWI describes the belief that one’s country is superior to all the others? What do we call the Balkans’ role in the start of WWI? Where are the Balkans? Who were/are the Slavic people? Which country was Austria-Hungary’s rival? Who were the Black Hands? What was the significance of Archduke Franz Ferdinand’s assassination? What do we call Germany’s plan for a quick invasion of France? Which neutral country did Germany run through on their way into France? “The War to End All Wars” - WWI European Tensions Ignited Page #2: When is it justified for a country to go to war? The Powder Keg and the Spark The lead up to World War I What were the long term causes of WWI? • M-Militarism • A -Alliances • I -Imperialism • N -Nationalism 1. Militarism Anglo-German arms race • Militarism—a belief that war in Europe was inevitable. • European nations made – military service mandatory – created large pools of reserve forces • Germany overtook Britain industrially in the 1890s • British policy-their fleet larger than combined fleets of any 2 rival nations • 1898, Kaiser Wilhelm II began expansion of German navy 2. Alliances “We lie in the middle of Europe. We have at least 3 fronts on which we can be attacked…let us endeavor to make otherwise” Triple Alliance vs. Triple Entente -1888 speech by Bismarck • 1870: Balance of power upset by Prussian victory in FrancoPrussian War. • Bismarck feared French revenge • negotiated treaties to isolate France 2. Alliances • • 1881: Alliance of the Three Emperors— Germany, Austria, and Russia in a mutual defense pact Triple Alliance – 1. 2. 3. 1881 Germany Austria Italy Kaiser Wilhelm II removes Bismarck • Kaiser Wilhelm II refused to renew Russian treaty • Germany developed closer ties to Austria • Russia feels threatened Who might Russia look to for a friend? Why? 2. Alliances • France courts Russia and the two became allies Dual Entente • "Splendid Isolation": After 1891, Britain was the only uncommitted power • Which nation might the British be worried about? Why? • Entente Cordial (1904): In the face of British-German naval arms race • Triple Entente, 1907:Britain, France and Russia; to check Triple Alliance What do you see here? Page 3 What nations had tensions and for what reasons? Page 5: Color and Label the Map of the two Major alliance groups. 3. Imperialism • Berlin Conference, 1885: Calms everyone down but… • Kruger Telegram (1902): – triggered British anger at Germany for congratulating Boers on their victories over British troops in South Africa. • The Moroccan Crises (1906 & 1911) – Kaiser urges Moroccan independence despite it being a French colony – Britain/Italy supported France 4. Nationalism • Created a "powder keg" in the Balkans (mountainous region of South Eastern Europe) • Why Now? – The Ottoman Empire (“the sick man of Europe”) looses control over the Balkans – Pan-Slavism, a nationalist movement to unite all Slavic peoples, encouraged the Serbs, Bosnians, Slovenes, and Croats to seek a single Kingdom • Russia was the southern Slavs’ “big brother” and Austria looked to enlarge its empire in the area Ottoman Empire 4. Nationalism First and Second Balkan Wars (1908 & 1913) • Serbia takes land from the Ottoman Turks and from Bulgaria • Serbia wants to create a PanSlavic Nation that could rival the other Great Powers • Austria is worried about Serbian expansion Summary of Long Term Causes • Britain and Germany Naval Arms Race • Germany and France Imperialism in N. Africa • Russia, Ottoman Empire and Austria want control over the Balkans • Two camps: • Triple Alliance Germany/Austria/Italy • Triple Entente Britain/France/Russia • Ottoman “Sick Man of Europe” Page 4: Illustrate the Long Terms Causes of WWI: M A I N -Militarism -Alliances -Imperialism -Nationalism Page #6 Hymn of Hate We will never forgo our hate. Hate by water and hate by land. Hate of the head and hate of the hand Hate of the hammer and hate of the crown Hate of the 70 millions choking down We love as one, we hate as one We have one foe and one alone: England! 1. 2. 3. Who do you think chanted this poem? If you were British, how would you feel about this poem? Which cause of WWI does this song reflect and why? Immediate Causes: The Spark List of Characters: • Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the throne of the Austria • The Black Hand, a secret society committed to ending Austrian rule in Slavic lands Setting: • Sarajevo, Bosnia’s (Slavic area) capital city • June 28, 1914 a royal visit to increase loyalty but also Saint Vitus’ Day, the day Serbians lost their independence to the Ottomans Climax • Gavrilo Princip – 19 yrs. old – member of the Black Hand – fires two bullets at close range into the Archduke and his wife Sophie • Both die in the hospital Page 7 • In your own words, describe what happened in Sarajevo. • What might Austria do? Accusations that Serbia was behind the plot • July 23, 1914 • Austria issues an ultimatum of demands that Serbia must do to avoid war. • The harshest was allowing Austrian police to enter Serbia and look for the Black Hand. Start to Stalemate What is a stalemate? Friends • Serbia is scared of war but does not want to give in to demands. • Russia tells Serbia that it will support Serbia in a war against Austria. • Austria is worried about a war against Russia and asks Germany for help. Germany agrees to defend Austria if need be. July 25, 1914 • Serbia accepts all demands except the one allowing Austrian police into Serbia. War!!! • Austria rejects Serbia’s offer and declares war on Serbia. • Russia mobilizes (get the troops ready for war) along Austrian and German borders. Why would Russia mobilize along the German border??? Basic #13 Vocabulary 1st Battle of the Marne – 1st battle of World War I and started trench warfare Allies – Britain, France, Italy, Russia, Portugal, Greece, Serbia, Romania, Montenegro, and USA Battle of the Sommes – 5 month battle with +1,000,000 soldiers killed, including +60,000 British soldiers in 1 day. Battle of Verdun – 11 month battle with + 500,000 casualties (wounded, killed, or missing-in-action) on both sides Central Powers – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Ottoman Empire Basic #13 Vocabulary Cont… Convoy – a group of merchant ships protected by warships Eastern Front – Battle line between Germany/AustriaHungary and Russia Mobilize/mobilization – to prepare military forces for war New Weapons – inventions of the industrial revolution which greatly increased casualties in war such as tanks, poison gas, submarines, airplanes, & machine guns No Man’s Land – the land between enemy trenches, not many people survived in it for long Over the Top – call given when soldiers were order to attack the opposing trench Shell shocked – when soldiers went crazy from artillery falling on them every few minutes for weeks at a time Basic #13 Vocabulary Cont… Stalemate – a deadlock in which neither side can advance Trench foot – when soldier’s feet would rot as a result of being wet for too long Trench warfare – when opposing sides dig trenches in the earth to protect soldiers from modern weapons U-boats – German submarines Western Front – trenches between Belgium/France and Germany Zeppelins – large gas-filled balloons, used to bomb the English coast Basic #13 Questions 1. What does mobilization mean? 2. Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire were called the 3. France, Britain, Russia, Serbia, Belgium and later Italy and the US were called the 4. The fighting in Belgium and France was known as the __________________. 5. Which famous battle stopped Germany’s advance towards Paris in 1914? 6. When neither army is able to gain ground, we call that a _______________. 7. WWI is most widely known for this type of fighting? 8. Soldiers with wet boots and socks often got a condition called ___________________. 9. When the whistle blew, it was time for soldiers to go _____________________. 10. The area between the two enemy trenches where the fighting took place was called ___________________. 11. Which famous battle was waged by the Germans to capture an ancient French fortress? 12. Which famous battle was launched by the British to relieve the French at Verdun? 13. Soldiers who were psychologically injured by combat were said to be . 14. What five industrialized weapons were first used in the first world war? 15. What were the large airships that dropped bombs on enemy cities? • Germany feared that if they attacked Russia, France would come to their aid. • Schlieffen Plan – deal with a war on two fronts – French and Russians. • The only way to win was to have a lightning quick attack (3 weeks) on France through neutral Belgium towards Paris. • After the French surrender the German Army can turn to deal with the larger but slower Russian Army. Schlieffen Plan Page 8: How was the Schlieffen Plan supposed to work? Draw a map to illustrate this. English Channel The right flank should brush along the English Channel. Belgium??? • Germany invades Belgium in route to France. • Great Britain feels obligated by an 80-year-old treaty to defend Belgium’s neutrality declares war on Germany and sends its small army to France. • France follows Plan 17 that called for an attack straight into the heart of Germany to have a quick victory. Meeting stiff resistance the French army retreats. Italy, Where are you? • Italy refuses to join with its allies of Austria and Germany because it claims that the alliance was a defensive treaty. • So since Germany attacked France, Italy did not have to go to war. • In all warring nations reserves are called up and millions go off to war. Most experts think that the war will be over in the matter of months. Countries in First World War Standing Armies & Reserves in August 1914 Mobilized Forces in 1914-18 Russia 5,971,000 12,000,000 France 4,017,000 8,410,000 Great Britain 975,000 8,905,000 Italy United States 1,251,000 200,000 Which nation had the largest Army in 1914? 5,615,000 4,355,000 Japan 800,000 Romania 290,000 Serbia 200,000 Belgium 117,000 Greece 230,000 Portugal 40,000 100,000 Montenegro 50,000 50,000 Which nation drafted the largest percentage? 800,000 750,000 707,000 267,000 230,000 Germany 4,500,000 11,000,000 Austria-Hungary 3,000,000 7,800,000 Turkey 210,000 2,850,000 Bulgaria 280,000 1,200,000 Stopped!!! • September 3, 1914 • The 1st Battle of Marne: German forces are within striking distance of Paris. The French find out about how and when the Germans will attack. • To stop the Germans the French sent every available soldier by taxi to the front line. The French win this battle and stop the German advance. Race to the Sea • September 13, 1914 • Germans have retreated nearly 60 miles to fortified trenches. The war slows to a stalemate. • Both sides dig extensive trenches 466 miles long from Switzerland to the English Canal. • The so-called Great War has begun. It will be the most deadly war that the world had ever seen. • These trench lines will remain locked in place for the next 3½ years. • This front will be the most deadly and costly area of combat. The Western Front New Players and New Names • In late 1914, the Ottoman Empire joined with Germany and Austria. Later Bulgaria joins as well. • These nations were called the Central Powers for the remainder of the War. • In 1915, Italy switches sides (for the promise of Austrian lands after the war) and joins with France, Britain, Russia, Belgium and Serbia. • These nations were called the Allies for the remainder of the war. Page 9: Color and Label the WWI map. Include: -the two alliances -The fronts – – – – – – Western Eastern Italian Balkan Caucasian Middle East -And the nations -Gallipoli (star) Italy Eastern Front • Russian versus Germans, Austrians and Turks. • Germans beat the Russians and slowly push east. • Why were the Russians losing so badly? Advantages: Disadvantages: • Russia greatly outnumbered the Germans and the Austrians. • Germany’s army was fighting France as well. • Austria was attacking the Serbians and then the Italians (1915). • Short on supplies: food, ammo, guns, clothing and boots. • Russia had all their ports blocked by Germans and Turks. • By 1915 Russia had lost 2 million soldiers. Life in the Trenches Trench Warfare • Trench System: Created to protect the soldiers from enemy fire • Soldiers in Trenches: – Ate and Slept – Wrote home – died Page 10: Draw 2 diagrams of a trench. One from the side and one from the top. Label the following Side view: Barbed Wire Fire step Duck Board Top View: Front Trench No Man’s Land Reserve Artillery Dug-out Routine What did the soldiers do all day? ·Most received only 3 to 4 hours of sleep. ·At night repair groups would venture out to repair the barbed wire. • After it was obvious that no attack was coming soldiers would play cards, nap and write letters Food and Shelter • Most food was dull and sometimes poorly cooked and almost always cold Water, if purified had a bad taste, sometime soldiers had to strain water from blackish puddles Most slept in “dugout” holes made in the side of the trenches • Gear and Supplies Other than the soldiers rifle and uniform the soldier carried the following: – – – – – – – – – – two grenades 220 rounds of ammo wire cutters entrenching tool two sandbags rolled ground sheet Haversack shaving kit message book iron food rations • Total of 66 pounds. -steel helmet -field dressing -Greatcoat -water bottle -Towel -mess tin -extra socks Rats and Barbed Wire Rats • lived on the dead bodies • big as cats Barbed wire • cheap and easy way to guard a trench from attack. Death and Illnesses • Pneumonia and bronchitis • Soldier feet remained wet for too long they could develop “trench foot” that made the foot rot. Machine Guns • Machine guns –600 shots per minute –cooled by a water chamber Artillery and Communication Light artillery could fire 15 to 20 rounds every minute Six of every ten casualties were caused by artillery. “Big Bertha” range of 15 Kilometers. Communications ill equipped for war send a message was via a phone line Sometimes messenger pigeons and runners Shell Shocked • Lack of sleep + Page 17: List the causes of being Shell Shocked. • Noise from Artillery + List the symptom of being Shell Shocked. • Fear of random death = • Shell Shocked How could this effect the daily life of a soldier? Poison Gas • This weapon moved through the air and if the wind changed direction so did the gas. But most gasses were heavier than air and would naturally sink into trenches. • Gas attacks claimed the lives of over 1 million soldiers. Tanks • To fool the enemy from learning about this new weapon these landships were called “water tanks.” • Eight men • converted tractors with guns • 4 MPH • weighted 28 tons • extremely unreliable Air Warfare Planes – Reconnaissance (scouting) – 50 mph – originally had no weapons. • Eventually these planes are mounted with machine guns and have an increased speed. Zeppelins • only aircraft used to attack • Large hydrogen balloons • carried 1 ton of bombs. Page 18: Pick one of these weapons to research. Make a diagram of the weapon and label the parts Give a brief description of the weapon and explain the impact on the war. The Hell of War • Veterans knew when the attacks were coming because: • the officers would check every soldier to make sure that they were adequately supplied. • They also handed out dog tags • fed everyone well. • Sometime a quick shot of rum was give to “increase” bravery. Over the Top A whistle then blew and the first wave when “over the top” into No Man’s Land. They spread out about one yard apart and moved towards the enemy trench. Other waves would quickly follow. The troops had to cross hundreds of yards of barbed wire under fire from artillery, rifles and the deadly machine guns. Those few who made it faced hand-to-hand combat. Success? • If the attack succeeded the enemy would retreat to the reserve trench and seal off the communication trench. • The front usually only moved one trench at a time. • Thousands died for a few hundred yards! • 21 million soldiers were wounded during WWI. Major Conflicts Verdun • Germans attack ancient French fortress. • 300,000 men were killed on both sides. • Germans only gained 4 miles! Somme • British attacked to relieve the French. • 20,000 British soldiers were lost on the first day. • By the end 500,000 men on both sides were lost. • British only gained 5 miles. Page 19: Big Battles • Why did they attack the other trenches? • What were the results of these attacks? • Were the battles worth it? Basic #14 Vocabulary 2nd Battle of the Marne – July 1918, Germany’s last offensive is stopped by US troops Armenian Genocide – when Turks attempt to empty the Ottoman empire of all Armenians by marching them out of the country and kill over 600,000 in the process Armistice – an agreement to end fighting Atrocity - horrible acts against innocent people Conscription – draft, requiring all young men to be ready for military or other service Contraband – military supplies and raw materials needed to make military supplies Basic #14 Vocabulary Cont… Czar Nicholas II – leader of Russia during WWI, whose mismanagement of the war would result in the Russian Revolution Gallipoli Campaign – attempt by Australians and New Zealanders to open a supply line to Russia Lusitania – passenger ship carrying contraband. when attacked by u-boats, 128 Americans died. Middle Eastern Front - British attempts, by TE Lawrence (Lawrence of Arabia), to overcome the Turks with Arab aid Neutrality – when a nation refuses to take sides during a war (ex. Switzerland) Propaganda – spreading ideas to promote a cause or damage an opposing cause Rationing – restricting the amount of stuff people can buy during war times Basic #14 Vocabulary Cont… Russian Revolution – caused Russia to pull out of WWI Self-determination – the right of people to choose their own form of government Total war – using an entire nation’s resources to win the war effort Unrestricted submarine warfare – when u-boats fired on enemy ships with no warning Woodrow Wilson – US President during WWI Zimmerman Telegram – German telegram to Mexico, offering Mexico US territory if Mexico would join WWI on the side of the Central Powers Basic #14 Questions 1. The fighting in Russia and southeastern Europe was known as the _________________. 2. What were the goals of the Gallipoli Campaign? 3. The British officer Lawrence of Arabia was a key player in which major front of the war? 4. What do we call it when the Turks killed millions of their Christian citizens over fears that they would aid the Russians? 5. What strategy did the Germans used to starve out Great Britain (UK)? 6. What is Total War? 7. When you conserve resources for the war, this is called____________. 8. One-sided information used to make a person feel something about an issue is called___________. 9. When a nation refuses to take a side in a conflict it is called __________________. 10. Who was the President of the US during the First World War? 11. The US was outraged when a German U-Boat killing 128 Americans sank the British passenger ship the _________________. 12. Which message from the German Ambassador urged Mexico to declare war on the United States? 13. Who was the leader of Russia through most of WWI? 14. What caused the Russians to pull out of WWI? 15. What battle was Paris saved from a last German offensive by American troops and tanks? Gallipoli (Turkey) • Goal was to knock out the Turks and open a supply line to Russia. • An amphibious assault on the Gallipoli peninsula. • The forces were mostly Australian and New Zealanders. • The Turks had the high ground and no real gains were made. • After 1 year the Allies had lost 250,000 men and withdrew. Asia and the Pacific• Japan- Japan joined the Allies a few weeks after the war started. – Easily capturing German colonies in China and the Pacific. Africa • Germany had 4 colonies in Africa at the start of the WWI. • Only German East Africa held out until 1918 (two weeks after Germany surrendered). Middle East • Britain promised to help Arabs if they rebelled against the Turks. • Arabs rebelled but were denied their own nation after the war. Armenian Genocide • Christians who were part of the Ottoman Empire • Russian-Ottoman front • Some Armenians helped the Russians – their fellow Christian • The Ottomans got mad and deported the entire population • Between 600,000 and 1.5 Million Armenians died. Naval Warfare Dreadnoughts • huge powerful steel battleships • ran on oil • too expensive and often named after famous individual. • This made naval commander reluctant to use them in combat. Submarines (U-Boats) • Submarines were underwater boats that were extremely useful at sinking enemy supply ships. • Because they were technically ships they had to obey the Law of the Sea – If you attack a civilian vessel you must give warning – Give time for the crew to get into life vessels – Call in the position so that the crew can be rescued Atlantic Ocean • Unrestricted Submarine Warfare • Germans used U-Boats (subs) to starve out the British. • Sunk neutral ships as well and angered the US. • U-Boat sunk 3,000 ships in 1917 alone. Page 20: War Around the World • Briefly describe in each box how the war impacted these regions. Where was the US??? • America was Neutral during the first 3 years of the war. • Many Americas believed that the War was a European affair and that the US should stay out of it. American Entry • We didn’t want to get into the war and we weren’t ready (16th largest Army in the World) • Why Join the War? • Unrestricted Submarine Warfare • Lusitania – a British passenger ship (carrying weapons) was sunk – 1,198 civilians lost their lives (128 were Americans) • Zimmerman note – encoded message sent by German Ambassador – asking Mexico and Japan to attack the United States. • This was the last straw and America declared war on April 2, 1917. President Woodrow Wilson Page 21: US ENTRY • Why did American stay out of the war for 3 years? • Briefly describe the 3 reasons why the US entered? • What extra motive did President Wilson have for entering the war? Home Front • Total War: when a nation uses all of its resources for the war effort. • Government took over the economy • Rationing (limiting) goods • Pro-War Propaganda – Love our troops, hate the enemy • Mass conscription • Unemployment nearly zero% • Women join factories – 43% in Russia • People bought war bonds to help fund the war Russian Withdrawal • March 1917 Czar Nicholas II abdicated due to domestic unrest. – By 1917 the Russian Army lost 5.5 million soldiers. • November (October) Revolution and V.I. Lenin takes over Russia Costly Peace for Russia • Lenin signs a peace treaty in March 1918 and signs the Brest-Litovsk peace treaty. • Russia signs over control of Finland, Poland, Ukraine, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. ¼ its pop. 1/5 of land • With Russia out of the war the Germans can move all troops to the Western Front. PAGE 22: RUSSIAN WITHDRAWL 1. Why did Russia withdraw from the war? 2. Why is this such a HUGE deal? Germany’s Last Chance 2nd Battle of Marne • 1918 Germany attacks – 6,000 artillery pieces and veteran troops from the Eastern Front – German pushed through the line and was only 40 miles from Paris. • Allies used 350 tanks and over 140,000 American soldiers to stop the attack. The Bitter Truth: Soldiers’ Poetry • Wilfred Owen (18931918) died a week before the war ended • “Dulce Et Decorum Est” Dulce Et Decorum Est Bent double, like old beggars under sacks, Knock-kneed, coughing like hags, we cursed through sludge, Till on the haunting flares we turned our backs, And towards our distant rest began to trudge. Men marched asleep. Many had lost their boots, But limped on, blood-shod. All went lame, all blind; Drunk with fatigue; deaf even to the hoots Of gas-shells dropping softly behind. Gas! GAS! Quick, boys!--An ecstasy of fumbling Fitting the clumsy helmets just in time, But someone still was yelling out and stumbling And flound'ring like a man in fire or lime.-Dim through the misty panes and thick green light, As under a green sea, I saw him drowning. In all my dreams before my helpless sight He plunges at me, guttering, choking, drowning. If in some smothering dreams, you too could pace Behind the wagon that we flung him in, And watch the white eyes writhing in his face, His hanging face, like a devil's sick of sin, If you could hear, at every jolt, the blood Come gargling from the froth-corrupted lungs Bitter as the cud Of vile, incurable sores on innocent tongues – FINISH THE LAST 4 LINES on Page 23 Dulce Et Decorum Est If in some smothering dreams, you too could pace Behind the wagon that we flung him in, And watch the white eyes writhing in his face, His hanging face, like a devil's sick of sin, If you could hear, at every jolt, the blood Come gargling from the froth-corrupted lungs Bitter as the cud Of vile, incurable sores on innocent tongues,-- My friend, you would not tell with such high zest To children ardent for some desperate glory, The old Lie: Dulce et decorum est Pro patria mori. The End • America started to transport its nearly 2 million new troops. • Central Powers realized defeat and started to surrender: Bulgaria, Turkey, Austria, and finally Germany on Nov. 11, 1918 at 11am. Page 24: Interesting Fact— Research any TOPIC of WWI and write about it! Battles Person Weapon Civilians Personal Family Story Or any other topic approved by teacher