* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principles of Mathematics 11
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic form wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
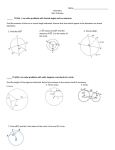
Principles of Mathematics 11 Course Outline Text: MathPower 11: McGraw-Hill Ryerson General Objectives: 1. To develop skills in logical analysis and to present problem solutions in a clear and precise manner. 2. To develop the mathematics necessary to function in society. 3. To develop the mathematics necessary to engage in life long learning. 4. To develop the mathematics necessary to pursue further formal study in mathematically related areas. Unit Objectives: Problem Solving It is expected that students will: 1. use a variety of methods to solve real-life, practical, technical, and theoretical problems 2. solve problems that involve a specific content area such as geometry, algebra, trigonometry, statistics, probability 3. solve problems that involve more than one content area 4. solve problems that involve mathematics within other disciplines 5. analyse problems and identify the significant elements 6. develop specific skills in selecting and using an appropriate problem-solving strategy or combination of strategies chosen from, but not restricted to, the following: guess and check look for a pattern make a systematic list make and use a drawing or model eliminate possibilities work backward simplify the original problem develop alternative original approaches analyse keywords 7. demonstrate the ability to work individually and cooperatively to solve problems 8. determine that their solutions are correct and reasonable 9. clearly explain the solution to a problem and justify the processes used to solve it 10. use appropriate technology to assist in problem solving Number (Number Operations) It is expected that students will: 1. solve consumer problems, using arithmetic operations. 2. solve consumer problems, including: wages earned in various situations property taxation exchange rates unit prices 3. reconcile financial statements including: cheque books with bank statements cash register tallies with daily receipts 4. solve budget problems, using graphs and tables to communicate solutions 5. solve investment and credit problems involving simple and compound interest Patterns and Relations (Patterns) It is expected that students will: 1. apply the principles of mathematical reasoning to solve problems and to justify solutions. 2. differentiate between inductive and deductive reasoning 3. explain and apply connecting words, such as and, or, and not, to solve problems 4. use examples and counter examples to analyse conjectures 5. distinguish between an if-then proposition, its converse and its contra positive 6. prove assertions in a variety of settings, using direct and indirect reasoning Patterns and Relations (Variables and Equations) It is expected that students will 1. represent and analyse situations that involve expressions, equations and inequalities. 2. graph linear inequalities, in two variables 3. solve systems of linear equations, in two variables: algebraically (elimination and substitution) graphically 4. solve systems of linear equations, in three variables: algebraically with technology 5. solve non-linear equations, using a graphing tool 6. solve non-linear equations: by factoring graphically 7. use the Remainder Theorem to evaluate polynomial expressions, the Rational Zeros Theorem, and the Factor Theorem to determine factors of polynomials 8. determine the solution to a system of nonlinear equations, using technology as appropriate Patterns and Relations (Relations and Functions) It is expected that students will: 1. represent and analyse quadratic, polynomial and rational functions, using technology as appropriate 2. examine the nature of relations with an emphasis on functions 3. determine the following characteristics of the graph of a quadratic function: vertex domain and range axis of symmetry intercepts 4. perform operations on functions and compositions of functions 5. determine the inverse of a function 6. connect algebraic and graphical transformations of quadratic functions, using completing the square as required 7. model real-world situations, using quadratic functions 8. solve quadratic equations, and relate the solutions to the zeros of a corresponding quadratic function, using: factoring the quadratic formula graphing 9. determine the character of the real and non real roots of a quadratic equation, using: Ñthe discriminant in the quadratic formula Ñgraphing 10. describe, graph, and analyse polynomial and rational functions, using technology 11. formulate and apply strategies to solve absolute value equations, radical equations, rational equations, and inequalities Shape and Space (Measurement) It is expected that students will: 1. solve problems involving triangles, including those found in 3-D and 2-D applications. 2. solve coordinate geometry problems involving lines and line segments, and justify the solutions. 3. solve problems involving ambiguous case triangles in 3-D and 2-D solve problems involving distances between points and lines 4. verify and prove assertions in plane geometry, using coordinate geometry 3 Shape and Space (3-D Objects and 2-D Shapes) It is expected that students will: 1. develop and apply the geometric properties of circles and polygons to solve problems. 2. use technology with dynamic geometry software to confirm and apply the following properties: the perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord the measure of the central angle is equal to twice the measure of the inscribed angle subtended by the same arc the inscribed angles subtended by the same arc are congruent the angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary a tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency the tangent segments to a circle, from any external point, are congruent the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the inscribed angle on the opposite side of the chord the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is 180(n-2) 3. prove the following general properties, using established concepts and theorems: the perpendicular bisector of a chord contains the center of the circle the measure of the central angle is equal to twice the measure of the inscribed angle subtended by the same arc (for the case when the center of the circle is in the interior of the inscribed angle) the inscribed angles subtended by the same arc are congruent the angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary a tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency the tangent segments to a circle from any external point are congruent the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the inscribed angle on the opposite side of the chord the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is 180(n-2) 4. solve problems, using a variety of circle properties, and justify the solution strategy used Time line: Unit Systems of Equations Linear Inequalities Quadratic Functions Quadratic & Polynomial Equations Functions Reasoning The Circle Coordinate Geometry & Trigonometry Personal Finance Total Time (h) 12 9 10 12 11 10 12 14 10 100 Evaluation: Term Unit Assignments (no more than 3 per unit)….......... Quizzes ............................................................................ Unit Tests ........................................................................ Course Mark Term Work......................................................................... Final Exam......................................................................... 5 20 % 35 % 45 % 100 % 70 % 30 % 100 % Student Expectations: 1. The student must come to class prepared and on time. This means that they have their text book, pencils, erasers, paper, calculator, etc. 2. Be quiet and ready to start working when the bell rings to indicate the start of class. In addition, to remain at work the bell sounds indicating the end of class or until you are dismissed. 3. Evaluation is done on an ongoing basis and as such it is very important that students' work be kept up to date. If you have any difficulties be sure to ask for help as early as possible. 4. All missed tests, quizzes and assignments must be completed! Students who are absent on the day of these events must make arrangements to write the missed evaluation on their return to school. Failure to do this will result in a mark of ZERO. Remember, the onus is on YOU to make up any and all missed work! 5. Late assignments/portfolios will not be accepted! However, the sequential nature of mathematics requires that you make some attempt to complete the work. 6. Students should plan to spend at least one-half hour on homework each night in addition to preparation for exams, or studying. 7. All garbage including used gum is to be placed in the garbage can at the front of the room. 8. No food or drink is allowed inside the classroom.