* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch_ 1-2 guided reading key
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
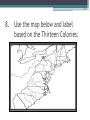
Ch. 1 & 2 Guided Reading KEY Section 1 – Converging Cultures Ch. 1 – Section 1 1. CIVILIZATION: • Highly organized society marked by: ▫ advanced knowledge of trade ▫ government ▫ the arts ▫ science ▫ written language. 2. JAMESTOWN • First lasting colony in Virginia ▫ Funded by: Joint-stock company (next slide) Ch. 1 – Section 1 3. JOINT-STOCK COMPANY • Funded Jamestown • A group of private investors who pooled their money to support big projects. 4. PROPRIETARY COLONY • A colony owned by an individual who could govern it any way he wanted by: ▫ appointing government officials ▫ coining money ▫ imposing taxes ▫ raising an army 5. How did the types of settlements influence the way each was governed? • Settlements of religious people were governed largely by those associated with the church. • Less religious settlements were governed using the principle of separation of church & state, either by land owners or by governing council. CH. 1 – Section 1 6. TRIANGULAR TRADE • Trade among the colonies: ▫ England ▫ Caribbean sugar planters Africa 7. SLAVE CODES • Laws that kept African captives from: ▫ owning property ▫ receiving an education ▫ moving about freely or ▫ meeting in large groups 8. Use the map below and label based on the Thirteen Colonies: Section 2 – Dissent and Independence 9. MERCANTILISM • Set of ideas about the world economy. • Mercantilists believed that to become wealthy and powerful, a country had to accumulate gold and silver by selling more goods than it bought. 10. How did the Enlightenment and the Great Awakening affect the established order? • It split churches into various Factions. It also reinforced the concept of individualism. ▫ Enlightenment – period of time where philosophers believed that both the physical world & human nature operated in an orderly way according to natural laws. ▫ Great Awakening – movement during the 1700s that stressed dependence on God. 11. Describe the French and Indian war in one sentence. • The French and British Faught over the Ohio River Valley, after the war extended to Europe, the British triumphed ending with the Treaty of Paris. 12. THE INTOLERABLE ACTS Name Year Description Stamp Act 1765 Townshend Acts 1767 Required stamps to be bought and placed on most printed material. Direct Tax Repealed in 1766 Put a customs duty on glass, lead, paper, paint, and tea Gave customs officers right to arrest Led to Boston Massacre Tea Act 1773 Coercive Acts 1774 Created Favorable Business terms for struggling British East India Company. Led to Boston Tea Party Punished Massachusetts and other colonies from challenging British Authority 13. Why did the colonies declare independence? • Laws and taxes imposed on the colonies were enacted without representation. 14. Use the map and label below based on the Revolutionary War: 15. YORKTOWN • Where the last major battle of the Revolutionary War was Fought. Section 3 – The Constitution 17. Compare and contrast the Great Compromise with the Three-Fifths Compromise • Great Compromise stated that Congress would be divided into two houses. ▫ The house gives representation based on population and the senate would have equal representation. • The Three-Fifths Compromise stated that every five enslaved people in state would count as three free persons. 18. POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY • Government subject to the will of the people or rule by the people. • Before the Civil War, the idea that people living in a territory had the right to decide by voting if slavery would be allowed there. 19. FEDERALISM • Political system in which power is divided between the national and state governments. 20. How much of the legislature is needed to override a veto? • Two-thirds 21. RATIFICATION • Formal approval • To change the constitution, states must ratify or pass it with 9 of the 13 states. 22. Use the graphic below to define both FEDERALIST and ANTIFEDERALIST. VERSUS • Constitution would create a federal system • Large landowners • Impose taxes on foreign goods • Concerned that Federal government would be too strong. Section 1 – The New Republic 23. BILL OF RIGHTS • First 10 amendments to the Constitution 24. What is the different between enumerated and implied powers? • Enumerated powers are specifically mentioned in the Constitution • Implied powers are not specifically mentioned in the Constitution but necessary for the government. 25. CANDIDATE NAME ELECTION OF 1800 CANDIDATE IMPORTANT ISSUES PARTY RAISED John Adams Federalist Alien & Sedition Acts were not popular Thomas Jefferson DemocratRepublican Tied with Aaron Burr revealed a flawed system Aaron Burr DemocratRepublican House decided to make Jefferson President & Burr Vice President WINNER: Jefferson 26. JUDICIAL REVIEW • Power of the Supreme Court to determine whether laws of Congress are constitutional and to strike down those that are not. 27. Why is the Supreme Court decision Marbury v. Madison important? • It established the Court’s right to judicial review, the power to decide the constitutionality of laws 28. How did the decisions of the Marshall Court strengthen the federal government? • The Supreme Court interpreted the Constitution broadly to support federal power 29. How did the Industrial Revolution change American society? • The North became a manufacturing center, transportation revolution, growth of cities and immigration, increased demand for slave labor, increasing sectional divisions. 30. NATIVISM • A preference for native-born people and a desire to limit immigration. 31. LABOR UNIONS • An organization of workers formed for the purpose of advancing its members’ interests. Section 2 – Growing Division and Reform 32. What issue did the Missouri Compromise solve and which states was added to the union? • It temporarily settled the dispute over the westward expansion of slavery. ▫ Maine was added as a free state ▫ Missouri was added as a slave state. 33. SPOILS SYSTEM • Practice of handing out government jobs to supporters; replacing government employees with the winning candidate’s supporters. 34. What caused the nullification crisis? • The imposition of tariffs that hurt an already struggling South Carolina economy. Ch. 2-2 35. TRAIL OF TEARS • President Jackson sent an army to Georgia to forcibly move the Cherokee. • Roughly 2000 Cherokee died in camps and on a westward journey about 2000 more died. • This became known as Trail of Tears 36. WHIGS • A political party that wanted to expand the federal government, encourage industrial and commercial development and create a centralized economy. 37. TEMPERANCE • Moderation in or abstinence from alcohol. 38. Write two sentences about the Women’s Movement using the words: Lucretia Mott, Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Seneca Falls Convention • Student responses… 39. How did Northerners’ views on abolition differ from those of Southerners? • In the North, there was some support, some opposition and some indifference. Abolition was widely opposed in the South. ▫ Abolition immediate end to slavery Section 3 – Manifest Destiny and Crisis Ch. 2-3 40. MANIFEST DESTINY • Idea popular in the United States during the 1800s that the country must expand its boundaries to the Pacific Ocean. 41. ANNEXATION • Incorporating a territory within the domain of a country. 42. Which states were admitted to the union under the presidency of James K. Polk? • Texas and Oregon 43. Describe the war with Mexico and include the terms: bear Flag Republic, General Winfield Scott, Mexico City and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. • War with Mexico began with the statehood of Texas. • Polk sent Taylor to Texas hoping Mexico would attack first. ▫ After they did, there was an uprising in California and we named the region the Bear Flag Republic. ▫ Then, General Winfield Scott seized Mexico City forcing the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. 44. SECESSIONS • Withdrawal from the Union. 45. How are the Fugitive Slave Act, the Underground Railroad and Harriet Tubman related? • The Fugitive Slave Act allowed the capture of Blacks without allowing them to testify on their own behalf. • This gave rise to Civil Disobedience and the Underground Railroad. • Harriet Tubman - 46. Draw a picture of the transcontinental railroad. 47. What was the main goal of the newly formed Republican Party? • Stop Southern Planters from becoming an aristocracy (high social class) that controlled the government. 48. CONFEDERACY • Nation declared to have been formed by the southern states that seceded from the Union in 1860-1861 49. Why was Jefferson Davis significant? • He was the president of the Confederacy. Section 4 – The Civil War 50. Why did the call for military volunteers lead more states to secede? • Many people in these states were not willing to take up arms against fellow southerners. 51. ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES NORTH SOUTH The Union had a weak Robert E. Lee and an Army, but powerful advanced Army. Navy. Industry gave an important economic advantage. Had Farming, but very little industry Well organized government with President Abraham Lincoln. A loose government with Jefferson Davis as President 52. EMANCIPATION PROCLAMATION • A decree given by Abe Lincoln freeing all enslaved persons in states still in rebellion after January 1, 1863. 53. Why do you think African Americans were willing to volunteer to fight in the Civil War? • Student responses… 54. GETTYSBURG ADDRESS • A speech given by President Lincoln to dedicate the Gettysburg Cemetery. He reminded everyone that all men are created equal. 55. On their respective pictures, write descriptions of each General. • Gave Sherman Charge of • Southern the West • General • Took control of the • Loses Civil War – troops couldn’t control vast • Northern Army 56. THIRTEENTH AMENDMENT • Banned slavery in the United States 57. Why was Appomattox Courthouse significant? • It is where Lee surrendered to Grant Section 5 - Reconstruction 58. RECONSTRUCTION • The reorganization and rebuilding of the former Confederate states after the Civil War. 59. What was the Wade-Davis bill? • Required the majority of the adult white men in the former Confederacy to take an oath of allegiance to the Union. Ch. 2-5 60. POCKET VETO • Indirectly vetoing a bill by letting a session of Congress expire without signing the bill. 61. FREEDMEN’S BUREAU • Given the task of freeing and clothing war refugees in the South using surplus Army supplies. 62. Write three characteristics of President Andrew Johnson. Why do you think he was so mad all the time? • Democrat • Loyal to Union • Southern Ch. 2- 5 63. BLACK CODES • Laws passed in the South just after the Civil War aimed at controlling freedmen and enabling plantation owners to exploit African American workers. 64. FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT • Granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the US and declared that no state could deprive a person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law. 65. What are carpetbaggers and scalawags? • Carpetbaggers were Northerners who moved South • Scalawags were Southerners that supported Reconstruction 66. How and where was the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) founded? • Started in 1866 in Pulaski, Tennessee 67. COMPROMISE OF 1877 • An agreement that stated that Republicans agreed to withdraw the remaining federal troops from the South 68. What type of economy was the “New South” based upon? • Strong industry 69. TENANT FARMERS • Farmer who works land owned by another and pays rent either in cash or crops. 70. How would you change this assignment to help you learn the material in a more effective way? • Student responses…