* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Palpebral fissure
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
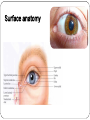
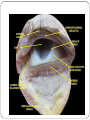
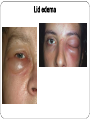
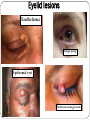
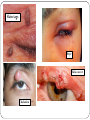
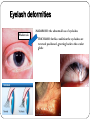
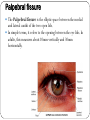
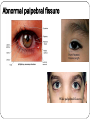
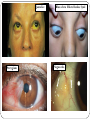
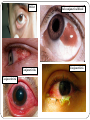
Eye examination Dr Sajad Ahmad Salati MBBS MS MRCS Surface anatomy Schematic diagram of cut-section Eyebrow deformities Hypothyroidism Systemic lupus erythematosus Lid edema Eyelid lesions Xanthelasma Benign polyp Epidermal cyst Moluscum contagiousum Skin tags Stye Skin cancer Chalazion Eyelash deformities Madarosis MADAROSIS : the abnormal loss of eyelashes TRICHIASIS :In this condition the eyelashes are reversed positioned, growing back to the ocular globe Eyelid deformities PTOSIS Ptosis is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid Ptosis Exophthalmos Exophthalmos is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in an orbital tumor). Exophthalmos Rt Exophthalmos Palpebral fissure The Palpebral fissure is the elliptic space between the medial and lateral canthi of the two open lids. In simple terms, it refers to the opening between the eye lids. In adults, this measures about 10mm vertically and 30mm horizontally. Abnormal palpebral fissure Wide palpebral fissures Examination of conjunctiva/sclera The conjunctiva and sclera are examined with a penlight. The lower lid is pulled down gently. The patient is asked to look up to examine the lower palpebral conjunctiva (lining the posterior surface of the lids), the inferior cul-de-sac or fornix, and the inferior bulbar conjunctiva (covering the eyeball itself).The patient is instructed to look down and the upper lid elevated gently so that the superior bulbar conjunctiva may be observed. Abnormal findings Sclera and bulbar conjunctiva •Yellow: Jaundice •Blue sclera: •Pterygium: Triangular thickening of conjunctiva growing across cornea. •Pinguecula:Yellowish triangular nodule in the conjunctiva on either side of cornea (Aging) •Bitot's spots: Vitamin A def. •Sub-conjunctival haemorrhage : Sharply demarcated red area , may involve the entire conjunctiva (Cough, idiopathic) Palpebral conjunctiva •Pallor: Anemia •Polycythemia: Suffused conjunctiva with tortuous full vessels •Conjunctivitis: Red edematous with pus; diffuse dilatation of vessels maximal peripherally •Ciliary injection: Radiating vessels or reddish violet flush around limbus (Acute iritis, acute glaucoma) Jaundice Pterygium Blue sclera Ehlers Danlos Synd Pinguecula Pallor Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis Subconjunctival bleed Conjunctivitis Pupils Pupil is the central aperture in the centre of iris. Normal size : 3-4mm Colour : Grayish black Number : Normally one ( more than one is called polycoria) Location : Normally almost central , slightly nasal . Eccentric is called correctopia. Normal P Pupils E Equal R Reactive L Light Polycoria Correctopia Anisocoria Anisocoria is a condition characterized by an unequal size of the eyes' pupils. Affecting 20% of the population, it can be an entirely harmless condition or a symptom of more serious medical problems. Visual Acuity Test ( Snellen’s Test) Using the foot as a unit of measurement, (fractional) visual acuity is expressed relative to 20/20. Otherwise, using the metre, visual acuity is expressed relative to 6/6. The Visual Acuity Test represents the smallest size that can be reliably identified. Interpretation of VA results VA of 20/20 means that a person can see detail from 20 feet distance , the same as a person with normal eyesight would see from the same distance. If a person has a visual acuity of 20/40, that person is said to see detail from 20 feet the same as a person with normal eyesight would see it , if 40 feet away. It is possible to have vision superior to 20/20: the maximum acuity of the human eye without visual aids (such as binoculars) is generally thought to be around 20/10 (6/3). Testing poor vision: • • • If the patient is unable to read the largest letter <(20/200) Move the patient closer e.g. 5/200 If patient cannot read: count fingers (CF) hand motion (HM) Light perception (LP) No light perception (NLP)