* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Generalization - WordPress.com
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
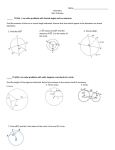
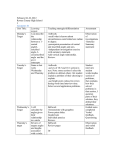
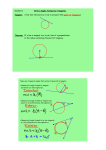
THE ASHTON SCHOOL WEEKLY LESSON PLAN TEMPLATE Teacher _____________Bethany Miller Week of: Subject ______Geometry____________ Grade: ___ 10A/B _____March 24-28 Standard(s) G.MG.3 Apply geometric methods to solve problems. G.C.1 Prove that all circles are similar G.C.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. G.C.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. G.C.4 Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle G.C.5 Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. G.CO.12 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically Essential Questions What are the properties of similar polygons? How are proportions used to make drawings of large objects small enough to fit on paper? Assessment (Formative and Summative) Homework, exit slips, individual and group work. Lesson Plan Outline Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Observa tions G.C.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. G.C.5 Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. Homework review G.C.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. G.MG.3 Apply geometric methods to solve problems. G.C.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. G.C.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. G.CO.12 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods G.C.4 Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle G.C.4 Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. Homework review Homework review Homework review Homework review Introduce New Introduce central angle, arc, minor arc, Information Introduce arcs and chords and their bisectors Introduced inscribed angle and intercepted arc. Introduce tangent, point of tangency, and common tangent Introduce definition of secant and intersections on or inside a circle Weekly Goals (Benchmarks & Indicators) Accessing Prior Knowledge (APK) and sometimes R (review) major arc, semicircle, congruent arcs, adjacent arcs, and arc length Application Guided practice through in class examples. Continued application through homework problems Generalization Find the measure of the angle using the measure of the arc. Adapted from the GANAG schema - Guided practice through in class examples. Continued application through homework problems Find the bisector of the arc and compare it with the chord. Guided practice through in class examples. Continued application through homework problems Guided practice through in class examples. Continued application through homework problems Guided practice through in class examples. Continued application through homework problems Find the measure of the inscribed angle. Find the point of tangency on the circle. How does an intersection outside the circle affect the measure. Improving Student Learning One Teacher at a Time by Jane E. Pollock ©2007