* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fight obesity with effective and guaranteed tools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
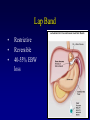
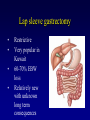
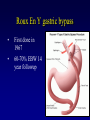
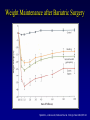
Fight obesity with effective and guaranteed tools Haitham Al-Khayat, MD Consultant general and bariatric surgeon New Dar Al-Shifa hospital t Obesity Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems. Obesity is the 2nd most common cause of death from a modifiable behavioral risk factor Obesity related comorbidity • • • • • • Type II DM Hypertension Cardiac diseases Strokes Hyperlipidemia Respiratory diseases • • • • Degenerative osteorthritis • • • Depression GERD Nephrotic syndrome Infertility Venous stasis ulcers Pseudotumor cerebri Causes of obesity Behavior Genetics Environment Environment portion size Nonoperative treatment how does it add up?? Nonoperative treatment how does it add up?? Diet Exercise Behavioral therapy + Drug therapy ?????? . Why Surgery? • • • Diet and exercise are not effective long term in the morbidly obese Surgery is an accepted and effective approach Surgical risk is acceptable vs. risk of long-term obesity Surgery is effective Surgery is effective Pre-operative Medications Post-operative Medications Surgical treatment of obesity Indication of surgical options Patient selection BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 OR BMI 35 - 40 kg/m2 with significant comorbidity High risk health problems Ineffective documented dietary attempt The Gastrointestinal system Operative approaches Restrictive Procedures Adjustable silastic gastric banding (ASGB) Sleeve gastrectomy Gastric plication Combined Procedures Roux-en-Y gastric bypass ( GBP ) Lap Band • • • Restrictive Reversible 40-55% EBW loss Lap sleeve gastrectomy • • • • Restrictive Very popular in Kuwait 60-70% EBW loss Relatively new with unknown long term consequences Roux En Y gastric bypass • • First done in 1967 60-70% EBW 14 year followup Results of bariatric surgery • • • • Weight loss Resolution or improvement in comorbidity Increased longevity Improved QOL Health Social Personal Work General Complications of Weight-Loss Surgery • Post-operative depression • Food issues • Changes in relationships • Hair loss • Usually temporary • Cause: protein, vitamin A, mineral • Excess skin Weight loss program team • • • • • • Surgeon Nurse practitioner Dietitian Anesthesiologist Nurses Cardiologist SAFETY and RESULTS Final words * Surgery is only a tool * Patients must commit to lifelong changes in diet and behavior * Think seriously about options * We are here to help Defining the Problem The Problem • Prevalence of obesity in U.S. increased from 12% to 21% between 1991 and 2001 = 15 million people • Obesity is the 2nd most common cause of death from a modifiable behavioral risk factor • 111,909 excess deaths annually Mokdad AH et al. JAMA. 2003;289:76-79 Flegal KM et al. JAMA 2005;293:1861-1919 Excess U.S. Medical Costs Related to Abnormal Body Weight Int J Obesity 2005;29:334-339 Relative risk of health problems associated with obesity Greatly increased (relative risk >>3) Moderately increased (relative risk 2-3) Diabetes Coronary heart disease Gall bladder disease Osteoarthritis (knees) Hypertension Hyperuricemia and gout Dyslipidemia Insulin resistance Slightly increased (relative risk 1-2) Cancer (breast cancer in postmenopausal women, endometrial cancer, colon cancer) Reproductive hormone abnormalities Breathlessness Polycystic ovary syndrome Sleep apnea Impaired fertility Low back pain Increased anesthetic risk Fetal defects arising from maternal obesity The Effect of Obesity on the Development of Health Risks Age-adjusted relative risk of type 2 diabetes 50 100 Men1 42 40 93 Women2 75 30 50 40 20 12 25 10 2.2 8.1 1.0 0 <23 25 31 35 0 1.0 <22 25 31 35 BMI 1Chan JM et al. Diabetes Care 1994;17:961-969; 2Colditz G et al. Ann Intern Med 1995;122:481-486. Fed up with how her diet is going Charlene takes a more serious aim at her target weight Weight Maintenance after Bariatric Surgery Sjöström L, Lindroos AK, Peltonen M et al. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:26 Conclusions • Bariatric surgery is an effective means to achieve clinically significant, permanent weight loss with low rates of complications. • Bariatric surgery results in significant improvement in health risks associated with obesity. • Surgical weight loss increases life-span. • Surgical therapy is cost-effective.