* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Phillips Curve: Short Run and Long Run
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
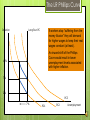
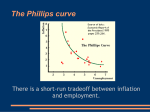
2.4 E (HL only) The Phillips Curve: Short Run and Long Run Inflation and Unemployment using AS/AD YF Inflation AS1 Expansionary fiscal or monetary policy will lead to a rise in AD, thus more GDP, thus less u/e 3.75% 2% U/E AD2 AD1 Y1 Y2 Real National Income CPI % (Inflation) The Phillips Curve It suggested that if governments wanted to reduce unemployment it had to accept higher inflation as a trade-off. 2.5% Money illusion – wage rates rising but individuals not factoring in inflation on real wage rates. 1.5% 4% 6% PC1 Unemployment (%) The Phillips Curve Problems: 1970s – Inflation and unemployment rising at the same time – stagflation Phillips Curve redundant? Or was it moving? The LR Phillips Curve Inflation Long Run PC If workers stop “suffering from the money illusion” they will demand for higher wages to keep their real wages constant (at least). An inward shift of the Phillips Curve would result in lower unemployment levels associated with higher inflation. 15% 7% 2% PC3 7% PC1 PC2 Unemployment The Phillips Curve Where the long run Phillips Curve cuts the horizontal axis would be the rate of unemployment at which inflation was constant – the so-called Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) = NRU The Phillips Curve To reduce unemployment to below the natural rate would necessitate: 1. 2. Influencing expectations – persuading individuals that inflation was going to fall i.e. tight money policy Boosting the supply side of the economy - increase capacity (pushing the PC curve outwards) The Phillips Curve Supply side policies have been focused on: Education: Welfare benefits: Boosting the number of those staying on at school Boosting numbers going to university Lifelong learning Vocational education The working family tax credit Incentives to work Labour market flexibility