* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MAFS.912.G-C.1 - Understand and apply theorems about circles
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
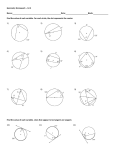
Standard 1 : Understand and apply theorems about circles This document was generated on CPALMS - www.cpalms.org Geometry - Additional Cluster Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. Number: MAFS.912.G-C.1 Title: Understand and apply theorems about circles Type: Cluster Subject: Mathematics Grade: 912 Domain: Geometry: Circles Related Standards Code MAFS.912.G-C.1.1 MAFS.912.G-C.1.2 MAFS.912.G-C.1.3 MAFS.912.G-C.1.4 Description Prove that all circles are similar. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. Related Access Points Access Point Access Point Number MAFS.912.G-C.1.AP.1a: MAFS.912.G-C.1.AP.2a: MAFS.912.G-C.1.AP.3a: Access Point Title Compare the ratio of diameter to circumference for several circles to establish all circles are similar. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii and chords. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle. Related Resources Formative Assessment Name All Circles Are Similar: Description Students are given two circles with different radius lengths and are asked to prove that the circles are similar. Students are asked to describe the relationship between a central angle and an inscribed angle that intercept the Central and Inscribed Angles: same arc. Circles with Angles: Students are given a diagram with inscribed, central, and circumscribed angles and are asked to identify each type of angle, determine angle measures, and describe relationships among them. Circumscribed Circle Construction: Students are asked to use a compass and straightedge to construct a circumscribed circle of an acute scalene triangle. Constructing a Tangent Line: Students are asked to complete and justify the construction of a line tangent to a circle from an exterior point. Inscribed Angle on Diameter: Students are asked to find the measures of two inscribed angles of a circle. Inscribed Circle Construction: Students are asked to use a compass and straightedge to construct an inscribed circle of an acute scalene triangle. Inscribed Quadrilaterals: Students are asked to prove that opposite angles of a quadrilateral, inscribed in a circle, are supplementary. page 1 of 4 Similar Circles: Students are given two circles with different radii and are asked to prove that the circles are similar. Tangent Line and Radius: Students are asked to draw a circle, a tangent to the circle, and a radius to the point of tangency. Students are then asked to describe the relationship between the radius and the tangent line. Using a Compass To Construct a Tangent Line: Students are asked to construct a tangent line to a given circle from a given exterior point. Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast Name Description All Circles Are Similar- Especially What better way to demonstrate that all circles are similar then to use pizzas! Gaines Street Pies explains how all pizza pies are similar through transformations. Circular Pizza!: Lesson Plan Name Are All Circles Similar? : Circle to Circle: Geometry Problems: Circles and Triangles: Geometry Problems: Circles and Triangles: Description This lesson allows students to prove that all circles are similar using transformations. Students will need prior knowledge of similarity, transformations, and the definition of a circle. The lesson begins with a warm up regarding dilations, then poses the question: Are all circles similar? The students are guided through the proof using a translation and dilation. The teacher emphasizes the details in the proof. The lesson closes with an exit ticket. Students use coordinate based translations and dilations to prove circles are similar. This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to use geometric properties to solve problems. In particular, the lesson will help you identify and help students who have the following difficulties solving problems by determining the lengths of the sides in right triangles and finding the measurements of shapes by decomposing complex shapes into simpler ones. The lesson unit will also help students to recognize that there may be different approaches to geometrical problems, and to understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of those approaches. This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to use geometric properties to solve problems. In particular, the lesson will help you identify and help students who have the following difficulties: Solving problems by determining the lengths of the sides in right triangles. Finding the measurements of shapes by decomposing complex shapes into simpler ones. The lesson unit will also help students to recognize that there may be different approaches to geometrical problems, and to understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of those approaches. Inscribing and Circumscribing Right Triangles: Off on a Tangent: Seeking Circle Angles: Seeking Circle Segments: The Seven Circles Water Fountain : Why are Circles Similar?: This lesson is designed to enable students to develop strategies for describing relationships between right triangles and the radii of their inscribed and circumscribed circles. Students learn and apply vocabulary, notation, concepts, and geometric construction techniques associated with circles and their tangents to a historical real-world scenario, the Mason-Dixon Line, and a hypothetical real-world scenario, the North-South Florida Line. Students will start this lesson with a win-lose-draw game to review circle vocabulary words. They will then use examples on a discovery sheet to discover the relationships between arcs and the angles whose vertex is located on a circle, in the interior of the circle, and exterior to the circle. They will wrap up the lesson in a class discussion and questions answered on white boards. Students will start this lesson with a "Pictionary" game to review circle vocabulary terms. They will then use computers and GeoGebra to discover the relationships between portions of segments that intersect in the interior of the circle, and exterior to the circle. They will wrap up the lesson in a class discussion and consensus on rules (formulas). This lesson provides an opportunity for students to apply concepts related to circles, angles, area, and circumference to a design situation. A lesson plan that shows students how to prove all circles are similar using the three transformations (reflection, dilation, translation) on a unique circle. The lesson takes students through multiple step transformations to show proof of circle similarity. A Socratic discussion is used as closure to aid in comprehension of circle similarity Educational Game Name Circle Up!: Tangled Web: An Angle Relationships Game: Description This interactive game helps you learn about angles and segments, lines and arcs in a circle and how they are related. You will compete against yourself and earn points as you answer questions about radius, diameter, chord, tangent line, central angles and inscribed angles and intercepted arcs. You are a robotic spider tangled up in an angular web. Use your knowledge of angle relationships to collect flies and teleport through wormholes to rescue your spider family! Problem-Solving Task Name Circumcenter of a triangle: Description This task shows that the three perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle all meet in a point, using the characterization of the perpendicular bisector of a line segment as the set of points equidistant from the two ends of the segment. Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task focuses on a remarkable fact which comes out of the construction of the inscribed circle in a triangle: the angle bisectors of the three angles of triangle ABC all meet in a point. II: Inscribing a triangle in a circle: This problem introduces the circumcenter of a triangle and shows how it can be used to inscribe the triangle in a circle. page 2 of 4 Locating Warehouse: This problem solving task challenges students to place a warehouse (point) an equal distance from three roads (lines). Neglecting the Curvature of the Earth: This task applies geometric concepts, namely properties of tangents to circles and of right triangles, in a modeling situation. The key geometric point in this task is to recognize that the line of sight from the mountain top towards the horizon is tangent to the earth. We can then use a right triangle where one leg is tangent to a circle and the other leg is the radius of the circle to investigate this situation. Placing a Fire Hydrant: This problem solving task asks students to place a fire hydrant so that it is equal distance from three given points. Right triangles inscribed in circles I: This task provides a good opportunity to use isosceles triangles and their properties to show an interesting and important result about triangles inscribed in a circle: the fact that these triangles are always right triangles is often referred to as Thales' theorem. Right triangles inscribed in circles II: This problem solving task asks students to explain certain characteristics about a triangle. Tangent Lines and the Radius This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. of a Circle: Tangent to a circle from a point: This problem solving task challenges students to describe and compare different angles. Two Wheels and a Belt: This task combines two skills: making use of the relationship between a tangent segment to a circle and the radius touching that tangent segment, and computing lengths of circular arcs given the radii and central angles. Virtual Manipulative Name Description Circumscribe a Circle About a In this GeoGebraTube interactive worksheet, you can watch the step by step process of circumscribing a circle about a triangle. Using paper and pencil along with this resource will reinforce the concept. Triangle: Tutorial Name Constructing Tangent Lines: Description This GeoGebraTube interactive worksheet shows you the step by step method for constructing tangent lines to a circle from a point outside the circle. Use the slider to see each step, and read below the illustration to follow the steps. Worksheet Name Description Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task shows how to inscribe a circle in a triangle using angle bisectors. I: Assessment Name Sample 1 - High School Geometry State Interim Assessment: Sample 3 - High School Geometry State Interim Assessment: Description This is a State Interim Assessment for 9th-12th grade. This is a State Interim Assessment for 9th-12th grade. Student Resources Title Circle Up!: Circumcenter of a triangle: Description This interactive game helps you learn about angles and segments, lines and arcs in a circle and how they are related. You will compete against yourself and earn points as you answer questions about radius, diameter, chord, tangent line, central angles and inscribed angles and intercepted arcs. This task shows that the three perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle all meet in a point, using the characterization of the perpendicular bisector of a line segment as the set of points equidistant from the two ends of the segment. Circumscribe a Circle About a In this GeoGebraTube interactive worksheet, you can watch the step by step process of circumscribing a circle about a triangle. Using paper and pencil along with this resource will reinforce the concept. Triangle: Constructing Tangent Lines: This GeoGebraTube interactive worksheet shows you the step by step method for constructing tangent lines to a circle from a point outside the circle. Use the slider to see each step, and read below the illustration to follow the steps. Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task shows how to inscribe a circle in a triangle using angle bisectors. I: Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task focuses on a remarkable fact which comes out of the construction of the inscribed circle in a triangle: the angle bisectors of the three angles of triangle ABC all meet in a point. II: Inscribing a triangle in a circle: This problem introduces the circumcenter of a triangle and shows how it can be used to inscribe the triangle in a circle. page 3 of 4 Locating Warehouse: This problem solving task challenges students to place a warehouse (point) an equal distance from three roads (lines). Neglecting the Curvature of the Earth: This task applies geometric concepts, namely properties of tangents to circles and of right triangles, in a modeling situation. The key geometric point in this task is to recognize that the line of sight from the mountain top towards the horizon is tangent to the earth. We can then use a right triangle where one leg is tangent to a circle and the other leg is the radius of the circle to investigate this situation. Placing a Fire Hydrant: This problem solving task asks students to place a fire hydrant so that it is equal distance from three given points. Right triangles inscribed in circles I: This task provides a good opportunity to use isosceles triangles and their properties to show an interesting and important result about triangles inscribed in a circle: the fact that these triangles are always right triangles is often referred to as Thales' theorem. Right triangles inscribed in circles II: This problem solving task asks students to explain certain characteristics about a triangle. Tangent Lines and the Radius This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. of a Circle: Tangent to a circle from a point: This problem solving task challenges students to describe and compare different angles. Two Wheels and a Belt: This task combines two skills: making use of the relationship between a tangent segment to a circle and the radius touching that tangent segment, and computing lengths of circular arcs given the radii and central angles. Parent Resources Title Circumcenter of a triangle: Description This task shows that the three perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle all meet in a point, using the characterization of the perpendicular bisector of a line segment as the set of points equidistant from the two ends of the segment. Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task shows how to inscribe a circle in a triangle using angle bisectors. I: Inscribing a circle in a triangle This problem solving task focuses on a remarkable fact which comes out of the construction of the inscribed circle in a triangle: the angle bisectors of the three angles of triangle ABC all meet in a point. II: Inscribing a triangle in a circle: This problem introduces the circumcenter of a triangle and shows how it can be used to inscribe the triangle in a circle. Locating Warehouse: This problem solving task challenges students to place a warehouse (point) an equal distance from three roads (lines). Neglecting the Curvature of the Earth: This task applies geometric concepts, namely properties of tangents to circles and of right triangles, in a modeling situation. The key geometric point in this task is to recognize that the line of sight from the mountain top towards the horizon is tangent to the earth. We can then use a right triangle where one leg is tangent to a circle and the other leg is the radius of the circle to investigate this situation. Placing a Fire Hydrant: This problem solving task asks students to place a fire hydrant so that it is equal distance from three given points. Right triangles inscribed in circles I: This task provides a good opportunity to use isosceles triangles and their properties to show an interesting and important result about triangles inscribed in a circle: the fact that these triangles are always right triangles is often referred to as Thales' theorem. Right triangles inscribed in circles II: This problem solving task asks students to explain certain characteristics about a triangle. Tangent Lines and the Radius This problem solving task challenges students to find the perpendicular meeting point of a segment from the center of a circle and a tangent. of a Circle: Tangent to a circle from a point: This problem solving task challenges students to describe and compare different angles. Two Wheels and a Belt: This task combines two skills: making use of the relationship between a tangent segment to a circle and the radius touching that tangent segment, and computing lengths of circular arcs given the radii and central angles. page 4 of 4