* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GEOMETRY PRACTICE Test 2 (3.5-3.6) Answer
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
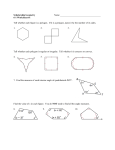
GEOMETRY PRACTICE Test 2 (3.5-3.6) SHOW ALL WORK TO PROVE ANSWERS 1. Find the value of the variable if and not to scale. 1 2 3 The diagram is 6. Find the missing angle measures. The diagram is not to scale. l 4 112° x° 120° y° 5 6 7 79° m 8 2. The sum of the measures of two exterior angles of a triangle is 277. What is the measure of the third exterior angle? 7. The jewelry box has the shape of a regular pentagon. It is packaged in a rectangular box as shown here. The box uses two pairs of congruent right triangles made of foam to fill its four corners. Find the measure of the foam angle marked. SHOW ALL work to earn credit. 3. Find . The diagram is not to scale. 96° 118° 115° x 104° x A 4. A nonregular hexagon has five exterior angle measures of 55, 58, 69, 57, and 55. What is the measure of the interior angle adjacent to the sixth exterior angle? 5. How many sides does a regular polygon have if each exterior angle measures 72? 8. Find the measures of an interior angle and an exterior angle of a regular polygon with 6 sides. 9. Write the equation 9x + 3y = –9 in slope-intercept form. Then graph the line. The diagram is not to scale. 10. Write a two-column proof. Given: Prove: 11. q 5 1 3 4 2 p 4 137 o 6 5 6 7 8 r 1 2 11. Find the measure of each interior and exterior angle of the figure on the right. 12. Identify the form of the equation –3x – y = –2. To graph the equation, would you use the given form or change to another form? Explain.= 8 3 13. Explain how to tell whether a polygon is convex. 14. Which statement is false? Explain. A. An equiangular polygon has all angles congrue B. A regular polygon is both equilateral and equiangular. C. An equilateral polygon has all sides congruent. D. A polygon is concave if no diagonal contains points outside the polygon. . 9 7 15. Write a two-column proof. Given: Prove: are supplementary. 1 2 3 l 4 5 6 7 16. For a regular n-gon: a. What is the sum of the measures of its angles? b. What is the measure of each angle? c. What is the sum of the measures of its exterior angles, one at each vertex? d. What is the measure of each exterior angle. e. Find the sum of your answers to parts b and d. Explain why this sum makes sense. 18. Graph . 19. The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem states: The sum of the measures of the angles of an n-gon is ____. 20. Complete this statement. A polygon whose sides all have the same length is_____ 21. Complete this statement. A polygon whose sides all have the same length and angles have the same measure is_____. 22. Write an equation in point-slope form then write in slope-intercept form of the line through point P(–4, 6) with slope –3. 8 m 117. Complete this statement. The sum of the measures oof the exterior angles of an n-gon, one at each vertex, is ____. 23. Complete this statement. A polygon whose angles all have the same measure is ____. 24. At the curb a ramp is 13 inches off the ground. The other end of the ramp rests on the street 91 inches straight out from the curb. 25. Write an equation in slope-intercept form of the line through points S(–2, –6) and T(4, 3). 26. Graph the line that goes through point (–2, 2) with 3 slope . 5 27. Write an equation in point-slope form, y – y1 = m(x – x1), of the line through points (5, –2) and (2, 10) Use (5, –2) as the point (x1, y1). b. 28. Write a two-column proof. 6 y 4 Given: Prove: and a are supplementary. b c 2 –6 –4 –2 –2 r d 2 4 6 x 2 4 6 x 2 4 6 x –4 e –6 f g s h c. 6 y 4 2 29. Write a two-column proof? Given: Prove: and –6 –4 –2 –2 –4 are supplementary. –6 K A d. B J C D 6 y 4 2 E F G H L –6 –4 –2 –2 –4 –6 5 30. Graph y = x – 1. 4 31. Write an equation in point-slope form of the line through point K(–1, 6) with slope –4. 32. Write an equation for the vertical line that contains point E(10, 1). 33. Write the equation for EACH graph a. 34. Find the x- and y- intercepts for the following equation 5x – 8y = 40. Then graph. 35. Nancy and Jaime wanted buy their parents gifts for Christmas which was 2 months away. They both worked at Carl’s Jr. earning minimum wage. Nancy figured she could save $12 a week and she already had $52 in her piggy bank at home. Jaime decided to work extra hours and save $26 a week. Unfortunately he did have any money to start with. Write equations and graph each situation. y 6 Which had more money saved in 2 months (8 weeks)? 4 2 –6 –4 –2 –2 –4 –6 2 4 6 x Estimate how long it would take for each of them to have the same amount of money. GEOMETRY Answer Section PRACTICE Test 2 (3.5-3.6) SHORT ANSWER 1. ANS: –4 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 3-1.2 Properties of Parallel Lines TOP: 3-1 Example 5 2. ANS: 83 REF: 3-1 Properties of Parallel Lines STA: CA GEOM 2.0| CA GEOM 4.0| CA GEOM 7.0 KEY: corresponding angles | parallel lines | PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: angle | triangle | exterior angle | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem 3. ANS: 73 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: pentagon | exterior angle | sum of angles of a polygon 4. ANS: 114 PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums KEY: hexagon | angle | exterior angle 5. ANS: 5 sides REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums TOP: 3-5 Example 3 6. ANS: x = 109, y = 60 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: sum of angles of a polygon PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums TOP: 3-5 Example 4 7. ANS: 72° REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: exterior angle | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: 1 DIF: L2 OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums TOP: 3-5 Example 5 8. ANS: m (interior) = 120 m (exterior) = 60 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: angle | pentagon | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: Polygon Exterior Angle-Sum Theorem | exterior angle | interior angle 9. ANS: y = –3x – 3 y 6 4 2 –6 –4 –2 2 4 6 x –2 –4 –6 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane OBJ: 3-6.1 Graphing Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 3 KEY: slope-intercept form | point-slope form | graphing 10. ANS: a. Vertical angles. b. Transitive Property. c. Alternate Interior Angles Converse. PTS: OBJ: TOP: KEY: 11. ANS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-2 Proving Lines Parallel 3-2.1 Using a Transversal STA: CA GEOM 2.0| CA GEOM 4.0| CA GEOM 7.0 3-2 Example 1 two-column proof | proof | reasoning | corresponding angles | multi-part question PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-4 Parallel Lines and the Triangle Angle-Sum Theorem OBJ: 3-4.2 Using Exterior Angles of Triangles STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: Triangle Angle-Sum Theorem | exterior angle 12. ANS: Standard form. Answer may vary. Sample: You could use the given form. Find the intercepts and use them to draw the line. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane OBJ: 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines KEY: graphing | point-slope form | standard form of a linear equation | slope-intercept form | writing in math OTHER 13. ANS: A polygon is convex if the points of all the diagonals are inside or on the polygon. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.1 Classifying Polygons STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: classifying polygons | concave | convex | writing in math 14. ANS: D; a polygon is convex, not concave, if no diagonal contains point outsides the polygon. PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: polygon | writing in math | reasoning | interior angle | Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem ESSAY 15. ANS: [4] [3] [2] [1] correct idea, some details inaccurate correct idea, some statements missing correct idea, several steps omitted PTS: 1 DIF: L4 REF: 3-2 Proving Lines Parallel OBJ: 3-2.1 Using a Transversal STA: CA GEOM 2.0| CA GEOM 4.0| CA GEOM 7.0 KEY: two-column proof | proof | extended response | rubric-based question | parallel lines | supplementary angles 16. ANS: [4] a. 180(n – 2) b. c. d. 360 e. [3] [2] [1] This makes sense because an interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle are supplementary. parts a–d correct; small error in part e parts a–d correct three correct answers PTS: 1 DIF: L4 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems OBJ: 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: exterior angle | Polygon Exterior Angle-Sum Theorem | extended response | rubric-based question MULTIPLE CHOICE 17. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 18. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 19. ANS: OBJ: B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 Polygon Exterior Angle-Sum Theorem C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.1 Graphing Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 2 graphing | standard form of a linear equation D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 KEY: 20. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 21. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 22. ANS: OBJ: 23. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 24. ANS: OBJ: 25. ANS: OBJ: 26. ANS: OBJ: 27. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 28. ANS: OBJ: TOP: KEY: 29. ANS: OBJ: TOP: 30. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 31. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 32. ANS: OBJ: KEY: 33. ANS: OBJ: 34. 35. Polygon Angle-Sum Theorem B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 polygon | classifying polygons | equilateral B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 polygon | classifying polygons | equilateral C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines KEY: slope-intercept form B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-5 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems 3-5.2 Polygon Angle Sums STA: CA GEOM 12.0| CA GEOM 13.0 polygon | classifying polygons | equilateral B PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines KEY: word problem | problem solving | slope-intercept form D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines KEY: slope-intercept form | slope D PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines KEY: graphing | slope-intercept form | slope | y-intercept D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 5 point-slope form A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-1 Properties of Parallel Lines 3-1.2 Properties of Parallel Lines STA: CA GEOM 2.0| CA GEOM 4.0| CA GEOM 7.0 3-1 Example 3 proof | two-column proof | supplementary angles | parallel lines | reasoning A PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 3-2 Proving Lines Parallel 3-2.1 Using a Transversal STA: CA GEOM 2.0| CA GEOM 4.0| CA GEOM 7.0 3-2 Example 1 KEY: parallel lines | reasoning | supplementary angles A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.1 Graphing Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 1 slope-intercept form | graphing D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 4 point-slope form C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.2 Writing Equations of Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 6 vertical line D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: 3-6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane 3-6.1 Graphing Lines TOP: 3-6 Example 2