* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Adventures of a Sound Wave…
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
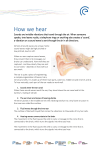
The Adventures of a Sound Wave…. What is your person listening to (if music, what kind? What song? Frequency? Amplitude?) Use this line to DESCRIBE it. Then, draw your frequency vibrations in box 6 and your amplitude vibrations box 7. _______________________________________________________________________________ (4 points) Extra Credit Name: __________________________________________ Period: ______ Use the following information and pages 509-513 in the Glencoe book to create a cartoon strip of energy being transferred by a sound wave through the ear and to the brain. Each box of the cartoon strip is outlined below: Title _____/7 Gathered by outer ear _____/7 Sent through ear canal _____/7 Draw/label sound wave to show Frequency vibrations (clearly label wavelength to match your frequency) ___/7 5. Draw/Label sound wave to show Amplitude (clearly label amplitude to represent your sound) _____/7 6. To ear drum _______/7 1. 2. 3. 4. 7. Ear drum begins to vibrate ____/7 8. Middle of ear (**3 bones) ______/7 9. Inner ear (show all HOW it interprets the sound) _____/7 10. Nerves ______/7 11. Brain ______/7 12. Closing(more than just a “the end”) _____/7 ___/8 Coloring ____/4 Creative (haha funny) The relationship between the ear and sound waves to explain hearing is as follows: Sound waves are gathered by the outer ear which is shaped to help capture the sound waves (energy transferred in particles of air) and send them through the ear canal, which transfers them to the eardrum. The vibrations of air particles cause the eardrum to vibrate. If the vibrations follow each other slowly (low frequency) the sound is heard as a low pitch. If the vibrations follow each other in rapid succession (high frequency), the sound is heard as a high pitch. Sound waves with large amplitudes push on the eardrum with more force and are heard as loud sounds. Sound waves with small amplitudes push on the eardrum with less force and are heard as soft sounds. Vibrations from the ear drum are transmitted to three small bones of the middle ear, which transmit the vibrations to the inner ear. The vibrations in the liquid of the inner ear cause the tiny hairs to vibrate. The vibrating tiny hairs transmit the energy to nerves attached to the hairs. The nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain and interpreted as hearing. anvil - (also called the incus) a tiny bone that passes vibrations from the hammer to the stirrup. cochlea - a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure; it is lined with cilia (tiny hairs) that move when vibrated and cause a nerve impulse to form. eardrum - (also called the tympanic membrane) a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves reach it. Eustachian tube - a tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside. When you "pop" your ears as you change altitude (going up a mountain or in an airplane), you are equalizing the air pressure in your middle ear. hammer - (also called the malleus) a tiny bone that passes vibrations from the eardrum to the anvil. nerves - these carry electro-chemical signals from the inner ear (the cochlea) to the brain. outer ear canal - the tube through which sound travels to the eardrum. pinna - (also called the auricle) the visible part of the outer ear. It collects sound and directs it into the outer ear canal semicircular canals - three loops of fluid-filled tubes that are attached to the cochlea in the inner ear. They help us maintain our sense of balance. stirrup - (also called the stapes) a tiny, U-shaped bone that passes vibrations from the stirrup to the cochlea. This is the smallest bone in the human body (it is 0.25 to 0.33 cm long).