* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Q1 - Rocky Ford School District
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Hyperbolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
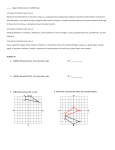
ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically a. Experiment with transformations in the plane. (CCSS: G-CO) We will identify, name and draw points, lines, segments rays and planes and apply basic facts about points lines and planes. i. State precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. (CCSS: GCO.1) 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically d. Make geometric constructions. (CCSS: G-CO) 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically d. Make geometric constructions. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Make formal geometric constructions7 with a variety of tools and methods.8 (CCSS: GCO.12) Make formal geometric constructions7 with a variety of tools and methods.8 (CCSS: GCO.12) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Know Apply Resource Correlation Holt McDougal GeometryCommon Core Edition Teachers Editionpg 6 1.1 Understanding Points, Lines and Planes Academic Vocabulary Point Line Plane Collinear Coplanar Segment Endpoint Ray Opposite rays postulate We will apply length and midpoint of a segment and construct midpoints and congruent segments Apply Synthesis 1.2 Measuring and constructing segements Pg 13 Coordinate Distance Length Congruent segments Construction Between Midpoint Bisect Segment bisector We will name and classify angles. We will also measure and construct angles and angle bisectors. Know Apply Synthesis 1.3 Measuring and Constructing Angles Pg 20 Angle Vertex Interior of an angle Exterior of an angle Measure Degree Acute angle Right angle Obtuse angle Straight angle Congruent angles Angle bisector Page 1 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically 3. Expressions can be represented in multiple, equivalent forms 4. Solutions to equations, inequalities and systems of equations are found using a variety of tools Evidence Outcome a. Experiment with transformations in the plane. (CCSS: G-CO) i. State precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. (CCSS: GCO.1) a.Interpret the structure of expressions.(CCSS: A-SSE) i. TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context.* (CCSS: A-SSE.1) Student-Friendly Learning Objective Level of Thinking Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary We will identify adjacent, vertical, complementary and supplementary angles. We will solve to find measures of pairs of angles and apply in problem solving. Know Apply 1.4 Pairs of Angles pg 28 Adjacent Angles Linear Pair Complementary Angles Supplementary Angles Vertical Angles We will apply formulas for perimeter, area and circumference, rearrange formulas to isolate particular terms and apply in problem solving Apply 1.5 Using Formulas in Geometry pg 36 Perimeter Area Base Height Diameter Radius Circumference pi a.Create equations that describe numbers or relationships. (CCSS: ACED) iv. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations.22 (CCSS: ACED.4) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Page 2 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 3. Objects in the plane can be described and analyzed algebraically a. Express Geometric Properties with Equations. (CCSS: G-GPE) We will develop and apply the formula for midpoint on the coordinate plane. We will apply the Pythagorean theorem to develop the distance formula to find the distance between two points on a coordinate plane. ii. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. (CCSS: G-GPE) 4. Use coordinates and the distance formula to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles.* (CCSS: GGPE.7) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Apply Analysis synthesis Resource Correlation 1.6 Midpoint and distance in the coordinate plane. Pg 43 Academic Vocabulary Coordinate plane Leg hypotenuse Page 3 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically a. Experiment with transformations in the plane. (CCSS: G-CO) We will identify reflections, rotations and translations., represent transformations with functions and graph transformations in the coordinate plane. ii.Represent transformations in the plane using1 appropriate tools. (CCSS: G-CO.2) iii.Describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. (CCSS: G-CO.2) TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Level of Thinking Know Comp Apply Sythesis Resource Correlation 1.7 Transformation in the coordinate plane pg 50 1.7 Tech Lab Explore transformations Tech lab. (Geometry Software required.) (Could also use NCTM online manipulativesgeometry, transformations) Academic Vocabulary Transformation Preimage Image Reflection Rotation translation iv. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not.2 (CCSS: G-CO.2) vi.Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. (CCSS: G-CO.4) vii.Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using appropriate tools.3 (CCSS: G-CO.5) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Page 4 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically PREP for We will apply inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures. We will write counterexamples to disprove conjectures. c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. iii. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) Prove theorems about parallelograms.6 (C CSS: G-CO.11) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Apply Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Resource Correlation 2.1 Using inductive reasoning to make conjectures. Pg 74 Academic Vocabulary Inductive Reasoning Conjecture Counter Example Page 5 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically PREP for We will identify, write and analyze the truth value of conditional statements. We will write inverse, converse, and contrapositive of a conditional statement. c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. iii. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) Prove theorems about parallelograms.6 (C CSS: G-CO.11) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Know Apply Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Resource Correlation 2.2 Conditional Statements pg 81 (2.3 Geometry Lab, Solving Logic Puzzles pg 94. After Conditional Statements) Academic Vocabulary Conditional statement Hypothesis Conclusion’ Truth value Negation Converse Inverse Contrapositive Logically equivalent statements Page 6 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically PREP for We will evaluate if a statement is applying inductive or deductive reasoning and apply the law of detachment and the Law of Syllogism in logical reasoning to make c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. iii. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) Prove theorems about parallelograms.6 (C CSS: G-CO.11) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Apply Evaluate Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary 2.3 Using deductive reasoning to Verify Conjectures Deductive Reasoning Page 7 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically PREP for We will write and analyze biconditional statements and apply in writing definitions of geometry terms. c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. iii. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) Prove theorems about parallelograms.6 (C CSS: G-CO.11) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Level of Thinking Apply Sythesis Evaluate Analysis Resource Correlation 2.4 Biconditional Statements and definitions pg 96 Academic Vocabulary Biconditional statements Definition Polygon Triangle quadrilateral Page 8 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically PREP for We will identify properties of equality and congruence and apply the properties to write algebraic proofs. Know Apply Synthesis 2.5 Algebraic Proof pg 104 proof We will prove geometric theorems about lines and angles by applying deductive reasoning and write proofs in two-column form Anal Synthesis Evaluation 2.6 Geometric Proof pg 110 (Geometry Lab 2.6 Design Plans for proofs pg 117) Theorem Two-column proof c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. ii. iii. 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) Prove theorems about parallelograms.6 (C CSS: G-CO.11) c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) i. Level of Thinking Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org Page 9 ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically c. Prove geometric theorems. (CCSS: G-CO) We will prove geometric theorems about triangles by applying deductive reasoning and write proofs in flowchart and paragraph forms. Anal Synthesis Evaluation 2.7 Flow Chart and Paragraph Proofs pg 118 Flowchart proof Paragraph Proof 1. Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically a. Experiment with transformations in the plane. (CCSS: G-CO) We will identify parallel, perpendicular and skew lines and apply in problem solving. We will identify the angles formed by two lines and a transversal and apply in problem solving. Know Comp Apply 3.1 Lines and angles pg 146 Parallel lines Perpendicular lines Skew lines Parallel planes Transversal Corresponding angles Alternate interior angles Alternate exterior angles Same-side interior angles . Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically c. Prove geometric theorems (CCSS: G-CO) We will prove and apply theorems about angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal and apply in problem solving Apply Analysis Synthesis ii. i. Prove theorems about triangles.5 (CCSS: G-CO.10) State precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. (CCSS: GCO.1) i. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) Level of Thinking Resource Correlation (Connecting to Algebra, Systems of equations pg 152) Academic Vocabulary 3.2 Angles formed by parallel lines and transversals pg 155 (3.2 Tech lab Explore Parallel lines and transversals. Pg 154 Requires geometry software) . © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org 10 Page ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective . Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically c. Prove geometric theorems (CCSS: G-CO) We will apply the angles formed by a transversal to prove two lines are parallel. i. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) We will apply the properties of a transversal to construct parallel lines Level of Thinking Apply Evaluate Synthesis Resource Correlation Academic Vocabulary 3.3 Proving lines parallel pg 162 (3.3 Geometry Lab, Construct Parallel Lines pg 170) d. Make geometric constructions. (CCSS: G-CO) i. Make formal geometric constructions7 with a variety of tools and methods.8 (CCSS: GCO.12) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org 11 Page ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective Objects in the plane can be transformed, and those transformations can be described and analyzed mathematically c. Prove geometric theorems (CCSS: G-CO) We will prove and apply theorems about perpendicular lines. i. Prove theorems about lines and angles.4 (CCSS: GCO.9) d. Make geometric constructions. (CCSS: G-CO) ii. 3. Objects in the plane can be described and analyzed algebraically TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Level of Thinking Apply Evaluate Synthesis Resource Correlation 3.4 Perpendicular Lines pg 172 (3.4 Geometry Lab Construct Perpendicular Lines pg 179) We will apply properties of perpendicular lines to construct perpendicular bisectors and perpendicular lines. Academic Vocabulary Perpendicular bisector Distance from a point to a line Make formal geometric constructions7 with a variety of tools and methods.8 (CCSS: GCO.12) a. Express Geometric Properties with Equations. (CCSS: G-GPE) ii. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. (CCSS: GGPE) We will find the slope of a line and apply slope evaluate if lines are parallel or perpendicular. Apply Evaluate 3.5 Slope of lines pg 182 Rise Run slope 2. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems.12(CCSS: GGPE.5) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org 12 Page ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry TIMELINE: 1st Quarter GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 3. Objects in the plane can be described and analyzed algebraically a. Express Geometric Properties with Equations. (CCSS: G-GPE) We will graph lines and write their equations in slope-intercept and pointslope form. We will evaluate lines to classify them as parallel, intersecting or coinciding) ii. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. (CCSS: GGPE) Level of Thinking Apply Analysis Synthesis Resource Correlation 3.6 Lines in the Coordinate Plane pg 190 Academic Vocabulary Point Slope Form Slope-Intercept Form (3.6 Technology Lab pg 188 Explore parallel and perpendicular lines ) 2. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems.12(CCSS: GGPE.5) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org 13 Page ROCKY FORD CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT: Geometry GRADE: High School Grade Level Expectation Evidence Outcome Student-Friendly Learning Objective 1. Visual displays and summary statistics condense the information in data sets into usable knowledge b. Summarize, represent, and interpret data on two categorical and quantitative variables. (CCSS: S-ID) We will review scatterplots and apply linear equation skills learned in 3.6 to graphing and writing equations for lines associated with data sets. ii. Represent data on two quantitative variables on a scatter plot, and describe how the variables are related. (CCSS: S-ID.6) Level of Thinking TIMELINE: 1st Quarter Resource Correlation Scatter Plots and Lines of Best Fit – Connecting Geometry to Data Analysis pg 198 Academic Vocabulary Scatterplot Lines of Best Fit 2.Informally assess the fit of a function by plotting and analyzing residuals. (CCSS: S-ID.6b) 3. Fit a linear function for a scatter plot that suggests a linear association. (CCSS: S-ID.6c) © Learning Keys, 800.927.0478, www.learningkeys.org 14 Page