* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood vessels - MRs. Saikali
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
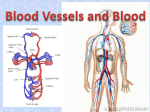
Blood vessels 11.3 Arteries • The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels • Arteries take blood away from the heart • The main artery is the aorta • Aorta branches into other major arteries, which take blood to different limbs and organs Arteries • Carotid artery takes blood to the brain • Brachial arteries take blood to the arms • Thoracic artery take blood to the thorax and then into the hepatic, renal and gastric arteries for the liver, kidneys and stomach respectively • Iliac artery takes blood to the lower limbs Layers of the arteries • The arteries have three layers of tissues: – An outer layer of connective tissues (stretches to support blood flow) – A middle layer of smooth muscles (regulate blood flow by altering vascular resistance by constriction and dilation) – A smooth inner single layer of epithelial cells called the endothelium Pulse • When blood is forced through the artery by the contraction of the heart, the artery expands • The expansion can be felt as the pulse • The artery has to be large, close to the skin and in front of a bone • Do mini investigation page 488 Arterioles • The major arteries diverge into minor arteries, and then into smaller vessels called arterioles • Arterioles reach more deeply into the muscles and organs of the body • Arterioles have smooth muscle in their wall, thus they can be controlled by the nervous system Arterioles • Signals from the nerves can regulate the diameter of the arterioles and control the blood flow to certain parts of the body – Vasodilation: an increase in the diameter of arterioles that increases the blood flow to tissues – Vasoconstriction: a decrease in the diameter of the arterioles that decreases the blood flow to tissues Arterioles • Vasoconstriction is an important feature of the circulatory system. Without it your body will need 200 L of blood to fill all the blood vessels • The ability to control blood flow ensure that the 5 L of blood we have is distributed where it is needed Capillaries • Arterioles diverge into capillary beds • Capillary beds contain 10 to 100 capillaries that branch among the cells and tissues of the body • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q530H1 WxtOw Capillaries • Capillaries are narrow diameter tubes • Can fit blood cells in a single-file lines • Supply oxygen and nutrients to every cell throughout the body tissues • Carbon dioxide and other waste produced during aerobic cellular respiration diffuse into the tissue fluid and then into the capillaries Fluid exchange • High fluid concentration on the arterial side cause water to diffuse from the blood to the tissue fluid • On the venous side, high concentration of water in the tissue fluid causes water to move from the tissue fluid to the blood • This maintains a balance between the fluids in the circulatory system and the tissues Controlling blood flow Page 489 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yeX0uDpPB j4 Venules and veins • The capillaries connect the arteries to the veins • On one side we have the arteries and arterioles carrying oxygenated blood and nutrients to the tissues • On the other side the capillaries merge into small vessels called venules that merge to form large vessels called veins Venules and veins • Venules and veins carry deoxygenated blood containing carbon dioxide and other waste products from the tissues to the heart • The middle layer of smooth muscle is not as thick as the arteries • The walls in the veins are not as elastic as the arteries • Blood pressure in veins are lower than in arteries Venules and veins • Veins have valves to prevent the backflow of blood • Because veins have to work against gravity to get blood back to the heart, • contraction of skeletal muscle assists with the flow of blood back to the heart • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HNuPWd fjDoc Blood pressure • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qWti317 qb_w