* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AND Gate - touqeer hussain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
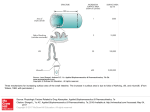
Chapter#16 Introductory Electronics 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.1.1 • Explain the process of thermionic emission emitted from a filament Thermionic emission is the phenomenon of emission of electrons from the surface of a metal, when it is heated to a high temperature. OR 5/8/2017 When a metal is heated some of the electrons may gain enough energy to escape from the surface of metal. This effect is called thermionic emission. 5/8/2017 Thermionic emission can also be produced by electrically heating metals like tungsten, tantalum, throated tungsten and metals coated with oxides of barium, strontium etc. are commonly used. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.2.1 • Describe the simple construction and use of an electron gun as a source of electron beam 5/8/2017 • Electron gun consists of a glass tube at very low pressure. Tungsten filament heated by 6 V. • A beam of electron produces a supply. A high +ve potential is applied to cylindrical anode to accelerate the electron to a high speed and they shoot straight through the hole of the anode as a fine beam of electrons. This beam of electron is cathode ray because they are emitted from cathode. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.3.1 • Describe the effect of electric field on an electron beam 5/8/2017 An electric field can be produced between two parallel plates placed horizontally some distance apart by applying potential difference across them. When electron beam passes between two plates, the electrons are deflected toward the positive plate. 5/8/2017 • It is found greater the electric field strength, greater would be degree of deflection of the electron beam. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.4.1 • Describe the effect of magnetic field on an electron beam 5/8/2017 • The electron beam passes through the magnetic field between poles of a magnet at right angle. The electron beam is deflected by the magnetic field. 5/8/2017 • The Fleming's left hand rule is applied to determine the direction of deflection by considering that electron beam is equivalent to positive are conventional current in opposite direction. We find that deflection in downward 5/8/2017 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.5.1 • Describe the basic principle of CRO and make a list of uses 5/8/2017 • Cathode ray oscilloscope is a versatile and exciting application of the effect of electric field on charged particles. The cathode rays as the name suggests are rays coming from the negative electrode (cathode). 5/8/2017 • Cathode ray oscilloscope is used to measure the voltage and time and show how voltage varies with time. It do this by drying graph on screen. • The vertical scale represent voltage and horizontal scale time. 5/8/2017 • The cathode ray oscilloscope uses narrow beam of electrons to trace out wave form and other signals on fluorescent screen. The beam of electrons produces bright spot on fluorescent screen. By deflecting the beam of electrons the spot can be moved. 5/8/2017 • There are two sets of deflecting plates. The y-plates move the beam vertically by connecting A.C supply across the y-input terminals. The X-plates move the beam horizontally. Normally the movement is produced by a circuit called time base inside the oscilloscope. 5/8/2017 5/8/2017 5/8/2017 • USES OF CATHODE RAY OSCILLOCOPE • Measuring peak voltage: 5/8/2017 • To measure voltage gain control is set at 5 v/cm. this means that spot moves 1cm vertically for every 5 volts across the Y-input terminal. The amplitude represent the peak voltage on wave form. As the amplitude is 2cm. • Peak voltage = 2cm x 5v/cm = 10v. 5/8/2017 • Measuring time and frequency: To measure the time, the time base control is set at 10ms/cm. This means that spot take 10ms (millisecond) to move one 1cm horizontally. As the horizontal peak to distance is 4.0cm. 5/8/2017 • Peak to peak time = 4cm x 10ms/cm = 40ms. = 0.04 sec. • This means spot take 0.04sec to trace one complete cycle this time is called period. F = 1/T = 1/0.04 = 25Hz. Frequency is 25 Hz. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.6.1 • Differentiate between analogue and digital electronics • All of electronics can be divided into two broad categories analog and digital. 5/8/2017 a. Analogue electronics: 5/8/2017 • In analogue method the information is converted into electrical voltage or currents that vary continuously. For example microphone converts sound waves into continuous electrical signals which are then amplified and then fed into sound-speaker. 5/8/2017 • Examples of analogue system: T.V and radio volume, conventional watches with needles are the examples of analogue system: • Analogue meters display their reading by the deflection of pointer over continuous scale. They gives the value of current, voltage and resistance by the deflection of needles. 5/8/2017 • Digital electronics: 5/8/2017 • In digital electronics the information is converted into electrical voltage that have only one of two values either high (5V) or low (0V). • They include switching type circuits. A switch is a digital device which allow a lamp to be either on or off. 5/8/2017 • Example of digital system: • Digital multimeters , digital watches, digital computers are popular examples of digital system because they display their readings as digits. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.6.2 • Describe that digital signals can carry more information 5/8/2017 • In digital system information can be stored easily and also can be processed easily. • Digital system can be designed easily with the help of integrated circuits (IC’s) and hundreds of IC’s are available. Maintenance of digital system is easy and they are cheaper, Digital system require less power and it s results are accurate. 5/8/2017 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.17.1 • State the basic operations of digital electronics 5/8/2017 • There are three basic operations of digital electronics which are AND operation, OR operation and NOT operation are required to determine the value of output if the values of input variables of a circuit are known are called basic operations of digital electronics. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.18.1 • Identify and draw the symbols for the logic gates • (NOT,OR ,AND,NOR and NAND) 1.NOT GATE: 5/8/2017 2.OR GATE: 5/8/2017 3. AND GATE: 5/8/2017 4. NOR GATE: 5/8/2017 5.NAND GATE: 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.8.2 • State the action of the logic gates in truth table from with two inputs • Logic gates:- Electronic switches which controls video recorders, security lamps, alarm system are called logic gates. 5/8/2017 • In practical logic gates works electronically using tiny transmitters as switches. They are manufactured as integrated circuits (IC’s) with each chip holding several gates. The chip also needs D.C power supply. Typically this is a 5 V supply, with one terminal marked 5V and 0Volts. 5/8/2017 • Logic gates are the combinations of electronic switches. These switches are operated by applying voltages to the input of the logic gates. The input can be high (5V) or low (0V). The output of a logic gate is also a voltage that can be high or low. 5/8/2017 • Logic gates are usually made in the form of integrated circuits (IC’s) each IC has many logic gates made on tiny piece of silicon packed in plastic. • Logic gates are used in switching circuits, computers and other electronic systems. 5/8/2017 • They open and give a high out put voltages i.e (5V) depending on combination of voltages at their inputs. Which is usually more than one? • There are three logic gates AND Gate, OR Gate and NOT Gate. Their symbols and truth tables are shown in figure. 5/8/2017 • AND Gate:Its output is high, if inputs A and B are high X = A.B It read as X equal A AND B. 5/8/2017 • OR Gate:- Its output is high if its at least one of its input is high. X = A+B 5/8/2017 • NOT Gate:Its output is high, if input is low and vice versa. 5/8/2017 • NAND Gate: • It is equivalent to AND Gate with its output is inverted by NOT Gate. • Its output is high if input A and B are not both high. X = A.B It is read as X equals A AND B NOT. 5/8/2017 • NOR Gate: • It is equivalent to OR Gate but output is inverted by NOT Gate. • It’s output is high if neither input A NOR input B is high. 5/8/2017 • SLO#16.8.3 • Describe the simple uses of logic gates • A gate can add, subtract, count, make simple decisions and even store information’s. • Gate is the basic building block of digital system. A gate is like a switch. It is either ON or OFF. • ON represents logic 1 and OFF logic 0. • Gates are also called digital circuits, logic circuits and switching circuits. 5/8/2017 5/8/2017