* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam Basic Beliefs From Wikipedia Edited by Dr. Gayhart The Five
LGBT in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Women as imams wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the Netherlands wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam Basic Beliefs From Wikipedia Edited by Dr. Gayhart
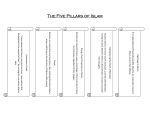
The Five Pillars of Islam are five basic acts in Islam, considered mandatory by believers and are the
foundation of Muslim life. They are summarized in the famous hadith of Gabriel.
They make up Muslim life, prayer, concern for the needy, self purification and the pilgrimage. They
are:
1.Shahadah: declaring there is no god except God, and Muhammad is God's Messenger
2.Salat: ritual prayer five times a day
3.Zakat: giving 2.5% of one’s savings to the poor and needy
4.Sawm: fasting and self-control during the holy month of Ramadan
5.Hajj: pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a lifetime[5][6] if one is able
Shahada is a declaration of faith and trust that professes that there is only one God (Allah)
and that Muhammad is God's messenger.[10] "There is no god but God (and) Muhammad is the
messenger of God." It is essential to utter it to become a Muslim and to convert to Islam.
Salat (ṣalāh) is the Islamic prayer. Salat consists of five daily prayers according to the Sunna;
the names are according to the prayer times: Fajr (dawn), Dhuhr (noon), ʿAṣr (afternoon), Maghrib
(evening), and ʿIshāʾ (night). The Fajr prayer is performed before sunrise, Dhuhr is performed in the
midday after the sun has surpassed its highest point, Asr is the evening prayer before sunset,
Maghrib is the evening prayer after sunset and Isha is the night prayer. All of these prayers are
recited while facing in the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca and forms an important aspect of the
Muslim Ummah. Muslims must wash before prayer; this washing is called wudu ("purification"). The
prayer is accompanied by a series of set positions including; bowing with hands on knees, standing,
prostrating and sitting in a special position (not on the heels, nor on the buttocks). A Muslim may
perform their prayer anywhere, such as in offices, universities, and fields. However, the mosque is the
more preferable place for prayers because the mosque allows for fellowship
Zakāt or alms-giving is the practice of charitable giving based on accumulated wealth. The
word zakāt can be defined as purification and growth because it allows an individual to achieve
balance and encourages new growth. The principle of knowing that all things belong to God is
essential to purification and growth. Zakāt is obligatory for all Muslims who are able to do so. It is the
personal responsibility of each Muslim to ease the economic hardship of others and to strive towards
eliminating inequality.[12] Zakāt consists of spending a portion of one's wealth for the benefit of the
poor or needy, like debtors or travelers. A Muslim may also donate more as an act of voluntary charity
(sadaqah), rather than to achieve additional divine reward.[13]
There are five principles that should be followed when giving the zakāt:
The giver must declare to God his intention to give the zakāt.
The zakāt must be paid on the day that it is due.
After the offering, the payer must not exaggerate on spending his money more than usual
means.
Payment must be in kind. This means if one is wealthy then he or she needs to pay a portion
of their income. If a person does not have much money, then they should compensate for it in
different ways, such as good deeds and good behavior toward others.
The zakāt must be distributed in the community from which it was taken
Sawm: fasting Ritual fasting is an obligatory act during the month of Ramadan.[19] Muslims
must abstain from food and drink from dawn to dusk during this month, and are to be especially
mindful of other sins.[19] Fasting is necessary for every Muslim that has reached puberty (unless
he/she suffers from a medical condition which prevents him/her from doing so).[20]
The fast is meant to allow Muslims to seek nearness and to look for forgiveness from God, to
express their gratitude to and dependence on him, atone for their past sins, and to remind them of
the needy.[21] During Ramadan, Muslims are also expected to put more effort into following the
teachings of Islam by refraining from violence, anger, envy, greed, lust, profane language, gossip
and to try to get along with fellow Muslims better. In addition, all obscene and irreligious sights and
sounds are to be avoided.[22]
Fasting during Ramadan is obligatory, but is forbidden for several groups for whom it would be
very dangerous and excessively problematic. These include pre-pubescent children, those with a
medical condition such as diabetes, elderly people, and pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Observing fasts is not permitted for menstruating women. Other individuals for whom it is
considered acceptable not to fast are those who are ill or traveling. Missing fasts usually must be
made up for soon afterward, although the exact requirements vary according to circumstance
Hajj: Pilgrimage to Mecca The Hajj is a pilgrimage that occurs during the Islamic month of
Dhu al-Hijjah to the holy city of Mecca. Every able-bodied Muslim is obliged to make the
pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their life.[27] When the pilgrim is around 10 km (6.2 mi) from
Mecca, he/she must dress in Ihram clothing, which consists of two white sheets. Both men and
women are required to make the pilgrimage to Mecca. After a Muslim makes the trip to Mecca,
he/she is known as a hajj/hajja (one who made the pilgrimage to Mecca).[28] The main rituals of
the Hajj include walking seven times around the Kaaba termed Tawaf, touching the Black Stone
termed Istilam, traveling seven times between Mount Safa and Mount Marwah termed Sa'yee, and
symbolically stoning the Devil in Mina termed Ramee.[28]
The pilgrim, or the haji, is honored in the Muslim community. Islamic teachers say that the Hajj should
be an expression of devotion to God, not a means to gain social standing. The believer should be
self-aware and examine their intentions in performing the pilgrimage. This should lead to constant
striving for self-improvement.[29] A pilgrimage made at any time other than the Hajj season is called
an Umrah, and while not mandatory is strongly recommended. Also, they make a pilgrimage to the
holy city of Jerusalem in their alms-giving feast.
From Questions about Islam http://www.questionsaboutislam.com/faith-beliefs-practices/mainpractices-rituals-of-islam.php
So after this long introduction, what are the practices and rituals of Islam? The following is a
summary of some of the most important practices.
Prayers: The Muslim prayer is a combination of physical actions, verbal sayings, and an internal
feeling in the heart. Muslims are required to be in a state of calmness, serenity and humbleness
while performing their prayers. Once the prayer is started, a series of sayings and actions are
performed. The sayings include reciting parts of the holy Qur'an, the holy book of Islam, as well as
other sayings glorifying God and thanking Him for all of His blessings upon us. It also gives
Muslims the opportunity to ask God for anything they desire. This could include asking for help in
getting a job, passing an exam, having a child, asking God for forgiveness of sins or anything else.
Muslims are required to pray at least five times every day, and are encouraged to pray extra
prayers if they can. The required prayers have specific times that they are to be performed at.
These are dawn, noon, mid afternoon, sunset and at night.
Fasting: Fasting means to refrain from having all kinds of food, drink and sexual intercourse from
dawn to sunset. Muslims are required to fast during the month of Ramadan every year. Ramadan
is a month based on the lunar cycle, as opposed to the solar calendar used today by most people.
Therefore, the start and end of the month of Ramadan change each year according to the lunar
cycles. Ramadan can be either 29 or 30 days. Muslims are also encouraged to fast on other
optional days. It is viewed as a way to cleanse the soul of all worldly desires and devout oneself
completely to the obedience of God. It is also an opportunity for wealthy Muslims to experience life
without food and drink for a day, which is meant to remind them of the poor and encourage them
to have sympathy and to be generous in donating to help the poor and the needy.
Pilgrimage: Also known as the Hajj, the pilgrimage is a physical and spiritual journey that every
financially and physically able Muslim is expected to make at least once in their lifetime. Muslims
travel to the holy city of Makkah, located in what is known today as Saudi Arabia, to perform the
required rites of the pilgrimage. There, they are expected to spend their days in complete devotion
to worship and to asking God for forgiveness and for anything else they wish to ask for. They also
perform specific rituals, such as walking around the Kaaba, the black cube-shaped building
located in Makkah.
Charity: A very important aspect of Islam is giving charity to the poor. Muslims are required to
give certain percentages of any type of wealth that they have accumulated. For example, Muslims
must give 2.5% of the money they have saved each year. It is important to note that this is not
based on income, it is based on savings. A small portion of the money that is sitting in the bank
accounts of wealthy people and not helping anyone is used every year to help the poor. This
ensures some re-distribution of wealth among Muslims. Also, Muslims are strongly encouraged to
make charitable giving a habit. Most Muslims donate to charity on a weekly basis when they
attend Friday prayer services at the Masjid, the Islamic place of worship.
Purification: Before performing certain rituals, most importantly before prayers, Muslims are
expected to perform a form of purification, known as ablution or "wudu" in Arabic. This involves
washing the hands, face, arms and feet with water. Since Muslims are required to pray at least
five times every day at various times throughout the day from dawn until the night, this ensures
that Muslims maintain a high level of hygiene.
Animal Sacrifice: The term "Animal Sacrifice" may sound weird, unusual or shocking to some
people when they first hear or read it. But the reality is that the majority of people in the world do
eat the meat of many different kinds of animals. Muslims believe that it is God whom has given us
the right to kill these animals and eat them. Therefore, Muslims are required to mention God at the
time the animal is killed. This reminds us that these animals were created by God and that God
gave us the permission to benefit from them. This is why it is called a "sacrifice", and this is why it
is considered a religious practice. Muslims are encouraged to perform animal sacrifice at special
occasions in the Islamic calendar. In these special occasions, it is expected that part of the meat
of the animal would be donated to the poor.