* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
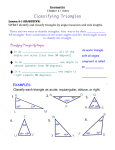
8-5 8-5 Triangles Triangles Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Course Course 11 8-5 Triangles Warm Up 1. What are two angles whose sum is 90°? complementary angles 2. What are two angles whose sum is 180°? supplementary angles 3. A part of a line between two points is called a _________. segment 4. Two lines that intersect at 90° are ______________. perpendicular Course 1 8-5 Triangles Problem of the Day Find the total number of shaded triangles in each figure. 3 Course 1 6 10 8-5 Triangles Learn to classify triangles and solve problems involving angle and side measures of triangles. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Vocabulary acute triangle obtuse triangle right triangle scalene triangle isosceles triangle equilateral triangle Course 1 8-5 Triangles A triangle is a closed figure with three line segments and three angles. Triangles can be classified by the measures of their angles. An acute triangle has only acute angles. An obtuse triangle has one obtuse angle. A right triangle has one right angle. Acute triangle Course 1 Obtuse triangle Right triangle 8-5 Triangles To decide whether a triangle is acute, obtuse, or right, you need to know the measures of its angles. The sum of the measures of the angles in any triangle is 180°. You can see this if you tear the corners from a triangle and arrange them around a point on a line. By knowing the sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle, you can find unknown angle measures. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Additional Example 1: Application Sara designed this triangular trophy. The measure of E is 38°, and the measure of F is 52°. Classify the triangle. To classify the triangle, find the measure of D on the trophy. m D = 180° – (38° + 52°) E D F D = 180° – 90° Subtract the sum of the known angle measures m D = 90° from 180° So the measure of D is 90°. Because DEF has one right angle, the trophy is a right triangle. m Course 1 8-5 Triangles Check It Out: Example 1 Sara designed this triangular trophy. The measure of E is 22°, and the measure of F is 22°. Classify the triangle. To classify the triangle, find the measure of D on the trophy. m E D F D = 180° – (22° + 22°) m D = 180° – 44° Subtract the sum of the known angle measures m D = 136° from 180° So the measure of D is 136°. Because DEF has one obtuse angle, the trophy is an obtuse triangle. Course 1 8-5 Triangles You can use what you know about vertical, adjacent, complementary, and supplementary angles to find the measures of missing angles. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Remember! Vertical angles are congruent. The sum of the measures of complementary angles is 90°. The sum of the measures of supplementary angles is 180°. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Additional Example 2A: Using Properties of Angles to Label Triangles Use the diagram to find the measure of each indicated angle. Q QTR P QTR and STR are supplementary angles, so the sum of mQTR and mSTR is 180°. mQTR = 180° – 68° = 112° Course 1 T 68° R 55° S 8-5 Triangles Additional Example 2B: Using Properties of Angles to Label Triangles QRT QRT and SRT are complementary angles, so the sum of mQRT and mSRT is 90°. m SRT = 180° – (68° + 55°) = 180° – 123° = 57° m QRT = 90° – 57° = 33° Course 1 Q P T 68° R 55° S 8-5 Triangles Check It Out: Example 2A Use the diagram to find the measure of each indicated angle. MNO M MNO and PNO are N supplementary angles, so the sum of m MNO and mPNO is 180°. m MNO = 180° – 44° = 136° Course 1 L 44° O 60° P 8-5 Triangles Check It Out: Example 2B MON MON and PON are complementary angles, so the sum of m MON and m PON is 90°. m m MON = 90° – 76° L N PON = 180° – (44° + 60°) = 180° – 104° = 76° = 14° Course 1 M 44° O 60° P 8-5 Triangles Triangles can be classified by the lengths of their sides. A scalene triangle has no congruent sides. An isosceles triangle has at least two congruent sides. An equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Additional Example 3: Classifying Triangles by Lengths of Sides Classify the triangle. The sum of the lengths of the sides is 19.5 in. M c + (6.5 + 6.5) = 19.5 c + 13 = 19.5 6.5 in. 6.5 in. c + 13 – 13 = 19.5 – 13 c = 6.5 L c N Side c is 6.5 inches long. Because LMN has three congruent sides, it is an equilateral triangle. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Check It Out: Example 3 Classify the triangle. The sum of the lengths of the sides is 15.6 in. B d + (7.2 + 7.2) = 16.6 d + 14.4 = 16.6 7.2 in. 7.2 in. d + 14.4 – 14.4 = 16.6 – 14.4 d = 2.2 A d C Side d is 2.2 inches long. Because ABC has two congruent sides, it is an isosceles triangle. Course 1 8-5 Triangles Insert Lesson Title Here Lesson Quiz If the angles can form a triangle, classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right. not a 1. 37°, 53°, 90° right 2. 65°, 110°, 25° triangle 3. 61°, 78°, 41° acute 4. 115°, 25°, 40° obtuse The lengths of three sides of a triangle are given. Classify the triangle. 5. 12, 16, 25 scalene Course 1 6. 10, 10, 15 isosceles