* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active directory
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
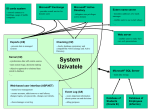
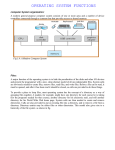
A centralized system Active Directory is Microsoft's trademarked directory service, an integral part of the Windows architecture. Like other directory services, such as Active Directory is a centralized and standardized system that automates network management of user data, security and distributed resources and enables interoperation with other directories. Active Directory is designed especially for distributed networking environments. Active Directory was new to Windows 2000 Server and further enhanced for Windows Server 2003, making it an even more important part of the operating system. Windows Server 2003 Active Directory provides a single reference, called a directory service, to all the objects in a network, including users, groups, computers, printers, policies and permissions. For a user or an administrator, Active Directory provides a single hierarchical view from which to access and manage all of the network's resources. There are many reasons to implement Active Directory. First and foremost, Microsoft Active Directory is generally considered to be a significant improvement over Windows NT Server 4.0 domains or even standalone server networks. Active Directory has a centralized administration mechanism over the entire network. It also provides for redundancy and fault tolerance when two or more domain controllers are deployed within a domain. Active Directory automatically manages the communications between domain controllers to ensure the network remains viable. Users can access all resources on the network for which they are authorized through a single sign-on. All resources in the network are protected by a robust security mechanism that verifies the identity of users and the authorizations of resources on each access. Even with Active Directory's improved security and control over the network, most of its features are invisible to end users; therefore, migrating users to an Active Directory network will require little re-training. Active Directory offers a means of easily promoting and demoting domain controllers and member servers. Systems can be managed and secured via Group Policies. It is a flexible hierarchical organizational model that allows for easy management and detailed specific delegation of administrative responsibilities. Perhaps most importantly, however, is that Active Directory is capable of managing millions of objects within a single domain. Active Directory networks are organized using four types of divisions or container structures. These four divisions are forests, domains, organizational units and sites. Forests: The collection of every object, its attributes and attribute syntax in the Active Directory. Domain: A collection of computers that share a common set of policies, a name and a database of their members. Organizational units: Containers in which domains can be grouped. They create a hierarchy for the domain and create the structure of the Active Directory's company in geographical or organizational terms. Sites: Physical groupings independent of the domain and OU structure. Sites distinguish between locations connected by low- and high-speed connections and are defined by one or more IP subnets. Microsoft includes LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) as part of Active Directory. LDAP is a software protocol for enabling anyone to locate organizations, individuals and other resources such as files and devices in a network, whether on the public Internet or on a corporate intranet. In a network, a directory tells you where in the network something is located. On TCP/IP networks (including the Internet), the domain name system (DNS) is the directory system used to relate the domain name to a specific network address (a unique location on the network). However, you may not know the domain name. LDAP allows you to search for individuals without knowing where they're located (although additional information will help with the search). An LDAP directory is organized in a simple "tree" hierarchy consisting of the following levels: The root directory (the starting place or the source of the tree), which branches out to Countries, each of which branches out to Organizations, which branch out to Organizational units (divisions, departments and so forth), which branch out to (include an entry for) Individuals (which include people, files and shared resources, such as printers) It will provide fully integrated security in the form of user logon's and authentication. 2. It makes easy in administration in the form of group policies and permissions. 3. It makes easy to identify the resources. 4. It will provide scalability and flexibility 5. It is tightly integrated with DNS services for all its operations, which will provide better in identifications and migrations. 6. It services will provide Automatic replication of information between the domain controllers. 7. It supports integration of the other directory services also. 8. It supports multiple authentication protocols.