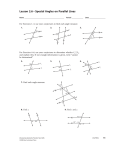
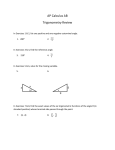
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Reactivity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
C C Contents Table of Contents i List of Figures ix List of Tables xiii List of Examples A1 Introductory Concepts in Chemistry A1.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.2 The Vocabulary of Chemistry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.3 Element Names and Symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.4 Regions of the Periodic Table, Cations and Anions . . . . . . . . . . A1.5 Naming Inorganic Compounds (Nomenclature) . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.6 Fundamental Units of Measurement for Chemistry . . . . . . . . . . A1.7 Accuracy and Precision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.8 Significant Figures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.9 Multiple Measurements: Averages and Standard Deviations . . . . A1.10 Logarithms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.11 Solving Problems Using Dimensional Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . A1.12 Molecules, Molecular Formulae, Molecular Mass and Formula Mass A1.13 The Mole, Avogadro’s Number and Molar Mass . . . . . . . . . . . xv . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1 1 6 7 7 16 17 17 22 23 24 26 28 Table of Contents i A1.14 Empirical Formula and Mass % . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 A1.15 Answers to Exercises A1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 A2 Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry A2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A2.2 Writing Chemical Equations . . . . . . . . . A2.3 Procedure for Balancing Chemical Equations A2.4 Stoichiometry and Mass . . . . . . . . . . . . A2.5 Determining the Limiting Reagent . . . . . . A2.6 Actual, Theoretical and Percent Yield . . . . A2.7 Elemental Analysis and Empirical Formula . A2.8 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A2.9 Answers to Exercises A2 . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39 39 39 41 47 50 53 56 61 64 Atomic Structure 1.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.3 Subatomic Particles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.4 Mass Number, Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass . 1.5 Electromagnetic Radiation: a Useful Probe of Atomic 1.6 Atomic Line Spectra and the Bohr Model . . . . . . . 1.7 Quantum Mechanics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.8 Shapes of Atomic Orbitals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.9 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.10 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.11 Answers to Exercises 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67 67 67 68 69 72 74 79 84 87 88 93 The Periodic Table 2.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule 2.4 Relative Energies of Atomic Orbitals . . . 2.5 Electron Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97 97 97 98 100 103 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Table of Contents ii 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 3 4 Valence and Core Electrons . . . The Periodic Table and Electron Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . Additional Exercises . . . . . . . Answers to Exercises 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109 111 113 113 116 Periodic Properties of the Elements 3.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.3 Effective Nuclear Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.4 Atomic Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.5 The Size of Ions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 Ionization Energy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.7 Electron Affinity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.8 Electronegativity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.9 Solid State Properties: Metals, Metalloids and Non-Metals 3.10 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.11 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.12 Answers to Exercises 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 . 119 . 119 . 120 . 121 . 122 . 123 . 127 . 128 . 129 . 130 . 130 . 134 Chemical Bonding and MO Theory 4.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.3 Electrostatic Interactions and Ionic Bonding 4.4 Covalent Bonding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 Delocalized Electron Model . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 Molecular Orbital Diagram for Dihydrogen . 4.7 Second Row Diatomic Molecules . . . . . . . 4.8 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.9 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.10 Answers to Exercises 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137 137 137 138 139 142 143 145 151 151 155 Table of Contents iii 5 6 7 The Lewis Bonding Model 5.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.3 Lewis Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.4 Sequential Procedure for Drawing Lewis Structures . . . . . . 5.5 Alternative Procedure for Drawing Lewis Structures . . . . . . 5.6 Lewis Structures for Structural Isomers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.7 Resonance, Energy Equivalent Structures and “Curly Arrows” 5.8 Limitations of the Lewis Bonding Model . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.9 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.10 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.11 Answers to Exercises 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159 159 159 160 165 169 172 174 179 179 180 183 Molecular Structure and the VSEPR Model 6.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.3 Principles of the VSEPR Model . . . . . . . 6.4 Procedure for Predicting Molecular Shape . 6.5 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.6 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.7 Answers to Exercises 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187 187 187 188 192 196 198 201 Valence Bond Theory (Hybridization) 7.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.3 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.4 Hybridization in Compounds Containing the Heavy Elements 7.5 Compounds Involving Lone Pairs in Hybrid Orbitals . . . . . 7.6 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.7 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.8 Answers to Exercises 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207 207 207 208 215 217 218 219 222 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Table of Contents iv 8 9 Bond 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 8.8 8.9 Polarity and Molecular Polarity Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Electronegativity and Bond Polarity . . . . . . . . . . . Molecular Polarity and Dipole Moment . . . . . . . . . Polarity of Polyatomic Ions and Ionic Compounds . . . Non-covalent Intermolecular and Inter-ion Interactions Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Answers to Exercises 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Quantitative Description of Aqueous Solutions 9.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.3 General Characteristics of Aqueous Solutions . 9.4 Solution Concentration . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.5 Mass % . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.6 Mole Fraction (X) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.7 Molarity (M) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.8 Dilution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.9 Reactions Involving Aqueous Solutions . . . . 9.10 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.11 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.12 Answers to Exercises 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Qualitative View of Acid-Base Equilibria in 10.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.3 Strong Acids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.4 Strong Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.5 Weak Acids and Weak Bases . . . . . . . . 10.6 The Equilibrium Constant . . . . . . . . . 10.7 Autodissociation of Water . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Aqueous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225 225 225 226 228 230 231 236 236 238 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241 . 241 . 241 . 242 . 244 . 244 . 246 . 247 . 249 . 252 . 254 . 254 . 258 Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261 261 261 262 263 264 267 269 Table of Contents v 10.8 10.9 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 pKa and pKb . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Polyprotic Acids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Structural Influences on the Magnitude of pKa Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Answers to Exercises 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . or pKb . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270 277 279 283 284 290 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295 295 295 296 299 301 307 315 317 318 321 12 Applications of Acid-Base Equilibria: Buffer Solutions 12.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.3 Buffer Solutions from a Weak Acid and Its Conjugate Base . . . . . 12.4 Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.5 Buffering Action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.6 Buffer Solutions from Weak Acids (Bases) and Strong Bases (Acids) 12.7 Preparation of Buffer Solutions of a Desired pH . . . . . . . . . . . 12.8 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.9 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.10 Answers to Exercises 12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325 325 325 326 329 331 335 339 345 345 348 11 Quantitative Acid-Base Chemistry in Aqueous Solution 11.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.3 pH and pOH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.4 Acid-Base Reactions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.5 Titrations Involving Strong Acids and Strong Bases . . . . 11.6 Determining the pH for Solutions of Weak Acids and Weak 11.7 Solutions of Acidic or Basic Salts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.8 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.9 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.10 Answers to Exercises 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Table of Contents vi 13 Coordination Chemistry 13.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.3 Lewis Acids and Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.4 Complex Ions and Transition Metal Coordination Compounds . . 13.5 Ligands and Oxidation Numbers of the Central Metal . . . . . . . 13.6 Electron Counting in Transition Metal Complexes . . . . . . . . . 13.7 Coordination Geometries of Complex Ions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.8 Bonding and Electronic Structure of Transition Metal Complexes 13.9 Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes . . . . . . . . 13.10 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.11 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.12 Answers to Exercises 13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Gases 14.1 Contents in Brief . . . . . . . . . . . 14.2 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.3 The Mercury Barometer and Pressure 14.4 The Ideal Gas Law . . . . . . . . . . 14.5 Density of Gases . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.6 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures . . 14.7 Real Gases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.8 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14.9 Additional Exercises . . . . . . . . . . 14.10 Answers to Exercises 14 . . . . . . . . Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351 351 351 352 357 358 364 366 367 369 371 373 376 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379 . 379 . 379 . 380 . 382 . 388 . 390 . 396 . 398 . 398 . 403 407 Table of Contents vii