* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War 2 - Issaquah Connect
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
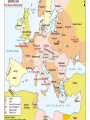
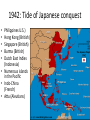
World War 2--1937-1945 • Why did WW2 happen? • What was WW2? • Why did the allies win? • Who “won” WW2? “Tonight the sun goes down on more suffering than ever before in the world.” The bloodiest war ever: 50-85 million dead, mostly civilians from bombing, starvation, genocide, and mass murder Fighting across the world on land, sea, air, and under water…in deserts, jungles, arctic freeze, cities What caused WW2? • Complicated, but many think that WW2 in Europe was really a continuation of WW1. OPPOSING SIDES • • • • • • • AXIS POWERS vs Germany + Austria Japan Italy Hungary Romania Finland • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • ALLIED POWERS Soviet Union Britain + Empire (India) U.S. France China Belgium Holland Norway Poland Yugoslavia Greece Australia Canada New Zealand South Africa WW2 was not really one war, but was several conflicts lumped together • • • • • • • 1937: Japan invades China 1939: Germany invades Poland 1939: Soviet Union attacks Finland 1940: Italy attacks Greece 1941: Germany invades Soviet Union 1941: Japan attacks U.S. (Pearl Harbor) Many countries switched sides during the course of the war • Numerous civil wars (Italy, Yugoslavia, China) Germany invades Poland Sept. 1, 1939 • Surprise attack “Blitzkrieg” use of armor and swift attacks • German warplanes invaded Polish air space, bomb Warsaw, capital • France and Britain declare war and mobilize • http://www.spartacus.s choolnet.co.uk/2WWap peasement.htm Germany and Soviet Union Divide Poland http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= s8dW3zSd4EA&feature=related Germany conquers Europe • April-June 1940, German “blitzkrieg” through: – Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Holland, and France – British retreat from Dunkirk • Pro-Nazi French puppet gov’t set up in city of Vichy (Vichy France) France falls in six weeks Germans outnumbered-even early in WW2 • When Germany attacked France in May 1940, British and French had more, troops, more artillery, more tanks • Germans concentrated their armor, more powerful, more mobile • Germans also had more planes 1940: Nazi Luftwaffe (airforce) attacks Britain Battle of Britain, summer of 1940. British Royal Air Force victorious, averts German invasion of Britain April 1941 Germany overruns the Balkans • Italy and Greece fighting; not going well for the Italians… • Hitler steps in to save the Italians, Germany occupies Yugoslavia and Greece. • Few casualties but German invasion of USSR is delayed… January 1942 “Final Solution to the Jewish Question” SS Head Heinrich HimmlReinhard Heydrich June 1941, Germany attacks USSR, setting off the largest war in history • The Eastern Front over 2,000 miles long • 6 million Soviet troops vs. 3 million Germans, Hungarians, Romanians, Finns • By December 1941, 6 months into the war, Soviets had lost 4 million soldiers, 8,000 aircraft, 17,000 tanks • By the end of the War, 27 million Soviet soldiers and civilians died • 10 million Germans killed, wounded or captured Russo-German War 1941-45 5-6 million Soviet POWs-more than 3 million died 2 million Germans captured, more than a 1 million disappeared. Only 5,000 of 90,000 Germans captured at Stalingrad in 1943 ever returned …it was incredibly brutal …atrocities were widespread War in Asia: Japanese Expansion Greater East Asia Co-prosperity Sphere 1937 Japan invades China • 1931 - Invades Manchuria • December 1937 “Rape of Nanjing” 250-300,000 Chinese dead, at least 20,000 raped. 50% of the population • People were bayoneted, buried and burned alive, beheaded. The Pacific War • • • • In 1940, United States and Great Britain reacted to Japanese expansion with an oil boycott (Japan got 80% of its oil from West). In December 1941, Japan attacked the Allied powers at Pearl Harbor and several other points throughout the Pacific, destroying much of the US navy. The turning point in the Pacific War was the battle of Midway in June 1942. From then on, the Allied forces slowly won back the territories occupied by Japan including Saipan. In 1944, intensive air raids started over Japan. In spring 1945, US forces invaded Okinawa in one of the war's bloodiest battles. Pearl Harbor, Dec. 7, 1941 “A date which will live in infamy” -FDR • American losses: • 8 of 8 battleships destroyed or damaged • More than 2,400 military dead • Nearly 350 aircraft destroyed or damaged 1942: Tide of Japanese conquest • • • • • Philippines U.S.) Hong Kong (British) Singapore (British) Burma (British) Dutch East Indies (Indonesia) • Numerous islands in the Pacific • Indo-China (French) • Attu (Aleutians) Bataan Death March 1942 76,000 Americans and Filipinos captured in the Philippines Marched 80 miles to POW camps, thousands are killed June 1942: Tide turns Battle of Midway • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SHfm7GX 3tHY&feature=related Americans “island hop” toward Japan • Battles were bloody • Japanese fought to the death (suicide over surrender) Japanese POWs • “Never live to experience shame as a prisoner. By dying you will avoid leaving a stain on your honor.” • -Senjinkun, Japanese “Code of Battlefield Conduct” • Very few surrendered at first, more as war wore on and it was clear Japan would lose. Meanwhile…back in Europe, the Allies counterattack 1942: • o o o Strategic bombing of Germany and Europe begins and intensifies British forces take El Alamein in North Africa Russians counter-attack at Stalingrad Full American support to Britain, France, Russia Stalingrad: the turning point in the war-August 1942-February 1943 German submarine strategy to cut off allied supplies, fails • 80 % of all German submariners die 1943: The Allies invade Italy • July, allies take Sicily and attack mainland • September, Italy surrenders • Germany invades, civil war in Italy. Fascists under Mussolini against communists, socialists and other partisans • Bloody fighting last nearly 2 years. Mussolini executed April 1945 D-Day June 6, 1944 • British, Americans, Canadians land in Normandy • Largest armada ever assembled, 12,000 allied planes vs. 170 German planes • Germans put up fierce resistance, but landing is successful • Within 3 months, Americans are at the borders of Germany, then are stopped End of the war 1944-1945 • “The most professionally skilful army of modern times,” but Germany faced overwhelming odds • German units, ½ strength, often composed of wounded soldiers, old men and boys • 2 million Allied troops in the West alone • Germans had almost no air force and so little fuel that oxen were used to tow airplanes to the runways Soviets & Americans meet at the Elbe River, dividing Germany in two • April 25th, 1945 Fall of Germany 1945, Russians: push Germans from Poland Auschwitz liberated in January Berlin taken in April in a battle that kills another 300,000 people Nazi leaders surrender on May 7, “V-E Day” next day By the end of 1944, Japan is basically finished • U.S. submarines cut off Japan’s oil supply • U.S. bombing devastates Japanese mainland • Japan resorts to desperate tactics Battle of Iwo Jima: Feb-Mar 1945 • 2 months of Allied bombardment on island only 4.5 miles x 2.5 miles. • Allies land 2,400 casualties in the first day • Nearly 7,000 Americans killed and 19,000 wounded • Only 216 of the 19,000 Japanese defenders surrendered; the rest died. • http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=fp_LXObnCj8&featu re=fvsr Japanese kamikaze (“Divine Wind”) Kamikaze film clips • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bEWOX8Vgd4&feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lyLiS2sFyU&feature=related • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VNeu_Dg JG6Y World War 2 ends May 1945-Germany Surrenders Sept 1945- Japan surrenders Japanese War Crimes • Starvation • POW treatment • mass executions (Nanjing) • rape and forced prostitution (Korean “comfort women”) Why did the Allies win? • Industrial and economic power. The U.S. alone produced 2/3 of the Allied military equipment used in WWII, including 41 billion rounds of ammunition. • Overwhelmed outnumbered Germans and Japanese. The U.S alone mobilized 16 million for the military. The Red Army was also huge. China was the most populous nation in the world. • Strategic bombing diverted German and Japanese resources and disrupted production. Cost was high--more than U.S. 50,000+ planes lost overseas, including nearly 40,000 in west • The Soviet Union “took one for the team” 27 million dead, compared to U.S. 410,000. Populations of the two were similar in size • Access to natural resources. Japan and Germany lacked oil and in the end their militaries couldn’t function without it. • The U.S. developed the atomic bomb and the Germans and Japanese did not. Legacies of World War II • Increased nationalism among colonies -> decolonization • Unleashing of new technology-> nuclear arms race • International Human Rights (UDHR, Nuremberg and Tokyo Trials) • Creation of buffer zone for the Soviet Union (eastern Europe) • Cold war -> avoidance of a global (nuclear) war through proxy wars Books and Movies about WW 2 • • • • • • • • MOVIES “Schindler’s List” “The Best Years of Our Lives” “Stalingrad” (German) “Saving Private Ryan” “Das Boot” (German) “The Great Escape” “Letters from Iwo Jima” “Midnight Clear” • • • • • • • BOOKS Midnight Clear Correlli’s Mandolin Love and War in the Apennines (NF) Schindler’s List (NF) Night (NF) Hiroshima (NF) An Artist of the Floating World GOP TOWN HALLS • http://www.cnn.com/2 017/02/22/politics/con gress-missing-townhalls-trnd/index.html • http://www.truthdig.co m/avbooth/item/econo mist_richard_wolff_expl ains_the_differences_2 0170222